Understanding and Teaching Evolution, University of California
... mechanisms. Random mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, however natural selection, the process by which some variants survive and others do not, is not random. For example, some aquatic animals are more likely to survive and reproduce if they can move quickly through water. Speed he ...
... mechanisms. Random mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, however natural selection, the process by which some variants survive and others do not, is not random. For example, some aquatic animals are more likely to survive and reproduce if they can move quickly through water. Speed he ...
REVIEW DAY
... some antelopes are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? • a. acquired characteristics • b. reproductive isolation • c. survival of the fittest • d. descent with modification ...
... some antelopes are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? • a. acquired characteristics • b. reproductive isolation • c. survival of the fittest • d. descent with modification ...
Evolution Notes II
... • Galapagos Islands: (Finches and Tortoises) • Wrote: “The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection”. ...
... • Galapagos Islands: (Finches and Tortoises) • Wrote: “The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection”. ...
File - Ms. M`s Biology Class
... Geographic isolation—a population is separated by a physical barrier ▪ May be separated by a mountain, canyon, river, etc. or because of flooding or other changes in habitat ▪ Organisms no longer mate and are forced to develop different adaptations to survive ...
... Geographic isolation—a population is separated by a physical barrier ▪ May be separated by a mountain, canyon, river, etc. or because of flooding or other changes in habitat ▪ Organisms no longer mate and are forced to develop different adaptations to survive ...
Evolution Reading Updated 2008
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
Evolution Test Review
... 7. Members of (different or the same) species share the same group of alleles called a (gene pool or gene frequency). 8. The whale’s flipper and the arms of a human are examples of (vestigial organs or homologous structures) because they have the same bones but use them for different functions. 9. T ...
... 7. Members of (different or the same) species share the same group of alleles called a (gene pool or gene frequency). 8. The whale’s flipper and the arms of a human are examples of (vestigial organs or homologous structures) because they have the same bones but use them for different functions. 9. T ...
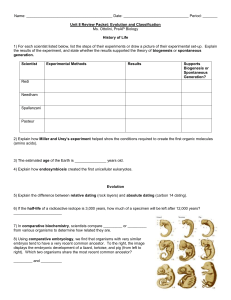
Evolution and Classification Review Packet
... organisms and classify organisms. Use worksheets given in class to help you review these skills. 23) The science of classifying organisms into groups according to their characteristics and evolutionary history is called __________________. 24) The man who developed the binomial system of classificat ...
... organisms and classify organisms. Use worksheets given in class to help you review these skills. 23) The science of classifying organisms into groups according to their characteristics and evolutionary history is called __________________. 24) The man who developed the binomial system of classificat ...
evolution notes Elinow
... Natural Selection: within a varied population, individuals whose characteristics adapt them best to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce; these individuals will leave behind more offspring ...
... Natural Selection: within a varied population, individuals whose characteristics adapt them best to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce; these individuals will leave behind more offspring ...
Natural Selection
... early in the Earth’s history provided an environment capable of generating complex organic molecules and simple cell-like structures. (a) Describe one scientific model for the origin of organic molecules on Earth. (b) Explain how RNA has the essential features of the earliest genetic material. (c) P ...
... early in the Earth’s history provided an environment capable of generating complex organic molecules and simple cell-like structures. (a) Describe one scientific model for the origin of organic molecules on Earth. (b) Explain how RNA has the essential features of the earliest genetic material. (c) P ...
Darwin, Malthus, and Limiting Factors
... variations, and humans select those variations they find useful. • Darwin had no idea how heredity worked, or about heritable variation, but he did know that variation occurred within natural populations just as in domesticated plants and animals. • Darwin’s breakthrough came when he realized that t ...
... variations, and humans select those variations they find useful. • Darwin had no idea how heredity worked, or about heritable variation, but he did know that variation occurred within natural populations just as in domesticated plants and animals. • Darwin’s breakthrough came when he realized that t ...
Darwin and the Theory of Natural Selection
... – Didn’t make connections between fossils and living species – Catastrophism: geological landscape is a result of cataclysmic events. These made life forms go extinct; Organisms went extinct and were repopulated by new organisms of modern appearance ...
... – Didn’t make connections between fossils and living species – Catastrophism: geological landscape is a result of cataclysmic events. These made life forms go extinct; Organisms went extinct and were repopulated by new organisms of modern appearance ...
Mechanism of Evolution
... Darwin and Wallace suggested a process. This process is known as natural selection. It works by over production of offspring and the presence of natural variation. Too many offspring Populations tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. The production of offspring involves the ...
... Darwin and Wallace suggested a process. This process is known as natural selection. It works by over production of offspring and the presence of natural variation. Too many offspring Populations tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. The production of offspring involves the ...
Darwin
... • Who was Gregor Mendel? • What contributions did Mendel make to the science of biology? • Give 5 facts about Charles Darwin. ...
... • Who was Gregor Mendel? • What contributions did Mendel make to the science of biology? • Give 5 facts about Charles Darwin. ...
Evolution - AP Biology (Chapter 17-21).
... gives rise to a different species or higher taxonomic group 3. taxonomic levels: C. Lamarck (1809) – Inheritance of acquired characteristics (Giraffe – not correct) D. Charles Darwin (1859) – Origin of Species by means of Natural Selection – developed the theory of evolution proposing that species ...
... gives rise to a different species or higher taxonomic group 3. taxonomic levels: C. Lamarck (1809) – Inheritance of acquired characteristics (Giraffe – not correct) D. Charles Darwin (1859) – Origin of Species by means of Natural Selection – developed the theory of evolution proposing that species ...
Evolution
... Adaptive Radiation many similar but distinctive species evolve relatively rapidly from a single species or from a small number of species. ...
... Adaptive Radiation many similar but distinctive species evolve relatively rapidly from a single species or from a small number of species. ...
Name ______ Pd ___ Biology Evolution Review – SMITH 2016 KEY
... 29. If the same unique blood protein is present in different species, what does this suggest? Common ancestry, an evolutionary relationship 30. What is natural selection? Darwin’s theory of how evolution could occur, explains how traits of a population can change over time 31. What is endosymbiosis ...
... 29. If the same unique blood protein is present in different species, what does this suggest? Common ancestry, an evolutionary relationship 30. What is natural selection? Darwin’s theory of how evolution could occur, explains how traits of a population can change over time 31. What is endosymbiosis ...
Three evolvability requirements for open-ended
... At the first level, the problem of evolvability centres on the genotype-phenotype mapping. Harvey’s ‘Species Adaptation Genetic Algorithm’ (SAGA) theory (Harvey 1992) addresses this issue. In this paradigm a population evolves for many thousands of generations, with gradual changes in genotype infor ...
... At the first level, the problem of evolvability centres on the genotype-phenotype mapping. Harvey’s ‘Species Adaptation Genetic Algorithm’ (SAGA) theory (Harvey 1992) addresses this issue. In this paradigm a population evolves for many thousands of generations, with gradual changes in genotype infor ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... C. Disruptive Selection = _________ extreme forms are more successful than the average ...
... C. Disruptive Selection = _________ extreme forms are more successful than the average ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... b) Mendel was working on his pea experiments for heredity (1856-1863) c) Darwin never read Mendel’s work d) Not until the 1900’s did the two ideas come together to show how natural selection and heredity worked together ...
... b) Mendel was working on his pea experiments for heredity (1856-1863) c) Darwin never read Mendel’s work d) Not until the 1900’s did the two ideas come together to show how natural selection and heredity worked together ...
Evolution - Killeen ISD
... (more than can survive with given food) • Individuals in population have variations • Certain variations are more useful (these will survive better) • Over time, “good” genes prevail in the population, while “bad” ones fade out ...
... (more than can survive with given food) • Individuals in population have variations • Certain variations are more useful (these will survive better) • Over time, “good” genes prevail in the population, while “bad” ones fade out ...