Genetic Constraints and the Evolution of Display Trait Sexual
... Sexual dimorphism is a pervasive pattern in nature. The sexes often differ in size, shape, and the degree to which sexual display traits are developed, with the last comprising a substantial component of biological diversity (Darwin 1871; Andersson 1994). Ultimately, the degree to which sexual dimor ...
... Sexual dimorphism is a pervasive pattern in nature. The sexes often differ in size, shape, and the degree to which sexual display traits are developed, with the last comprising a substantial component of biological diversity (Darwin 1871; Andersson 1994). Ultimately, the degree to which sexual dimor ...
Chapter 2 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Raw materials are not used up when organisms die They are recycled back into the ecosystem for use by other organisms Rainfall and temperature are the two most important factors limiting species distribution These physical conditions with their sets of similar plants and animals are called biomes Co ...
... Raw materials are not used up when organisms die They are recycled back into the ecosystem for use by other organisms Rainfall and temperature are the two most important factors limiting species distribution These physical conditions with their sets of similar plants and animals are called biomes Co ...
Evolution Regents Practice Ms. Fazio TEACHER ANSWER KEY
... situation in which genetic variation and selection pressures are few. In this case natural selection and speciation will likely be slow or nonexistent. (2) Reproduction of a species having a very low mutation rate in a changing environment is not the situation that would most likely result in the hi ...
... situation in which genetic variation and selection pressures are few. In this case natural selection and speciation will likely be slow or nonexistent. (2) Reproduction of a species having a very low mutation rate in a changing environment is not the situation that would most likely result in the hi ...
Review Evolution of Sex: Why Do Organisms Shuffle
... Sexual processes alter associations among alleles. To understand the evolution of sex, we need to know both the short-term and long-term consequences of changing these genetic associations. Ultimately, we need to identify which evolutionary forces — for example, selection, genetic drift, migration — ...
... Sexual processes alter associations among alleles. To understand the evolution of sex, we need to know both the short-term and long-term consequences of changing these genetic associations. Ultimately, we need to identify which evolutionary forces — for example, selection, genetic drift, migration — ...
Natural selection stops the evolution of male attractiveness
... among contemporary natural populations, however, and there is little evidence from artificial selection experiments that sexual fitness can evolve. Here, we demonstrate that a multivariate male trait preferred by Drosophila serrata females can respond to selection and results in the maintenance of mal ...
... among contemporary natural populations, however, and there is little evidence from artificial selection experiments that sexual fitness can evolve. Here, we demonstrate that a multivariate male trait preferred by Drosophila serrata females can respond to selection and results in the maintenance of mal ...
Genome-wide patterns of divergence during speciation: the lake
... form, typically growing slower, maturing at a much earlier age and size, and living in the limnetic zone of lakes, and a larger ‘normal’ form, which grows faster, reaches a larger size, matures at a later age and lives within the benthic zone of lakes. Their phenotypic divergence is recent (less tha ...
... form, typically growing slower, maturing at a much earlier age and size, and living in the limnetic zone of lakes, and a larger ‘normal’ form, which grows faster, reaches a larger size, matures at a later age and lives within the benthic zone of lakes. Their phenotypic divergence is recent (less tha ...
Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently confounding
... advantage over the previously common resident phenotype, regardless of frequency of the novel phenotype in the population immediately following the mass-migration event. The evolutionary dynamics occurring in this framework do not occur because of rare advantage and, in most cases, will not result i ...
... advantage over the previously common resident phenotype, regardless of frequency of the novel phenotype in the population immediately following the mass-migration event. The evolutionary dynamics occurring in this framework do not occur because of rare advantage and, in most cases, will not result i ...
Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently
... advantage over the previously common resident phenotype, regardless of frequency of the novel phenotype in the population immediately following the mass-migration event. The evolutionary dynamics occurring in this framework do not occur because of rare advantage and, in most cases, will not result i ...
... advantage over the previously common resident phenotype, regardless of frequency of the novel phenotype in the population immediately following the mass-migration event. The evolutionary dynamics occurring in this framework do not occur because of rare advantage and, in most cases, will not result i ...
Modern application of evolutionary theory to psychology: Key
... behaviorally; no two individuals are exactly the same (even monozygotic twins vary). Because of these variations, some individuals may be better able to survive and reproduce in their current environment than other individuals. If the variations are heritable (i.e., if they have a genetic component) ...
... behaviorally; no two individuals are exactly the same (even monozygotic twins vary). Because of these variations, some individuals may be better able to survive and reproduce in their current environment than other individuals. If the variations are heritable (i.e., if they have a genetic component) ...
The actuality of Lamarck: towards the
... A bewildering array of “replicators,” besides the DNA genes, and a variety of alternative hereditary pathways have been found. In addition to more classical cases of cytoplasmatic inheritance and maternal imprinting, there are plasmids, transposons, retroviruses, prions and other regulatory proteins ...
... A bewildering array of “replicators,” besides the DNA genes, and a variety of alternative hereditary pathways have been found. In addition to more classical cases of cytoplasmatic inheritance and maternal imprinting, there are plasmids, transposons, retroviruses, prions and other regulatory proteins ...
Name Period - TJ
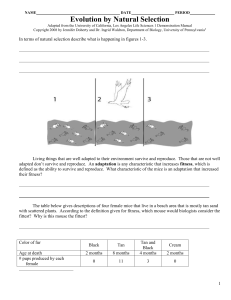
... In summary, Charles Darwin described the idea of natural selection as a fundamental mechanism of change. Natural selection is a process in which the various heritable traits within a population are acted upon by environmental stresses. Those organisms possessing heritable traits that make them bette ...
... In summary, Charles Darwin described the idea of natural selection as a fundamental mechanism of change. Natural selection is a process in which the various heritable traits within a population are acted upon by environmental stresses. Those organisms possessing heritable traits that make them bette ...
A Review of the Evolutionary Psychology Debates
... What is currently called “evolutionary psychology”—that is, the recent attempts at melding current evolutionary and psychological theories—has been most strongly advocated in a long essay by the anthropologist John Tooby and the psychologist Leda Cosmides, entitled “The Psychological Foundations of ...
... What is currently called “evolutionary psychology”—that is, the recent attempts at melding current evolutionary and psychological theories—has been most strongly advocated in a long essay by the anthropologist John Tooby and the psychologist Leda Cosmides, entitled “The Psychological Foundations of ...
biology sequencing
... An explanation of observable phenomena based on available empirical data and guided by a system of logic that includes scientific laws; provides a system of assumptions, accepted principles, and rules of procedure devised to analyze, predict, or otherwise explain the nature or behavior of a specific ...
... An explanation of observable phenomena based on available empirical data and guided by a system of logic that includes scientific laws; provides a system of assumptions, accepted principles, and rules of procedure devised to analyze, predict, or otherwise explain the nature or behavior of a specific ...
Multi-level Selection and the Major Transitions in - Philsci
... realise is that it in effect invokes group selection. From the selective point of view, replicating molecules combining themselves into compartments is strictly analogous to individual organisms combining themselves into colonies or groups. But Dawkins is an implacable opponent of group selection, i ...
... realise is that it in effect invokes group selection. From the selective point of view, replicating molecules combining themselves into compartments is strictly analogous to individual organisms combining themselves into colonies or groups. But Dawkins is an implacable opponent of group selection, i ...
Lecture 3: Origin of Life (Part-I)
... Introduction: In the previous lecture, we discussed the chemical theory to explain the origin of life. Life is originated as primitive cell with ability to replicate, absorb nutrition and repair the damage. These single cells are the starting material to form multicellular system and eventually the ...
... Introduction: In the previous lecture, we discussed the chemical theory to explain the origin of life. Life is originated as primitive cell with ability to replicate, absorb nutrition and repair the damage. These single cells are the starting material to form multicellular system and eventually the ...
The Evolution of Darwinism: Selection, Adaptation, and Progress in
... But note: These scientific theories are the products of brains, which are themselves the products of natural processes. Darwin’s theory provided the framework for the first credible naturalistic explanation for human existence, including the origin, function, and nature of those capacities that enable ...
... But note: These scientific theories are the products of brains, which are themselves the products of natural processes. Darwin’s theory provided the framework for the first credible naturalistic explanation for human existence, including the origin, function, and nature of those capacities that enable ...
THE PREDICTION OF ADAPTIVE EVOLUTION: EMPIRICAL
... that recently described by Walling et al. (2010). Briefly, we simultaneously analyzed paternity of all lambs born between 1985 and 2009, using the molecular data as previously described (e.g., Overall et al. 2005), but with recent cohorts having been genotyped at a core set of 18 microsatellite loci ...
... that recently described by Walling et al. (2010). Briefly, we simultaneously analyzed paternity of all lambs born between 1985 and 2009, using the molecular data as previously described (e.g., Overall et al. 2005), but with recent cohorts having been genotyped at a core set of 18 microsatellite loci ...
The Beak of the Finch
... put it, natural selection takes place within a generation, but evolution takes place across generations. In the drought of 1977, they had seen and documented natural selection in action. The decimation of the finches by selection had been as ruthless as the aristocratic breeder of bulldogs in Darwin ...
... put it, natural selection takes place within a generation, but evolution takes place across generations. In the drought of 1977, they had seen and documented natural selection in action. The decimation of the finches by selection had been as ruthless as the aristocratic breeder of bulldogs in Darwin ...
6 - BHU
... natural selection provides a frame work for explaining how allele frequencies are maintained in the populations; it also explains how species become adapted to the environments in which they live. One can observe several species in their native environments, and in some cases, it seems obvious how c ...
... natural selection provides a frame work for explaining how allele frequencies are maintained in the populations; it also explains how species become adapted to the environments in which they live. One can observe several species in their native environments, and in some cases, it seems obvious how c ...
1 The Origin of the Origin - Beck-Shop
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
1 The Origin of the Origin - Beck-Shop
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
Excerpt - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
... Darwin wrote up his account of the trip around the world on the Beagle, and what started as a formal report for the Admiralty turned into one of the most popular of travel books at a time when society just loved stories of exploration in distant and strange lands (Darwin 1839). Darwin was also newly ...
ATHBY Course Outline - Hedland Senior High School
... in speciation and evolution. Evidence for these changes comes from fossils and comparative anatomy and biochemical studies. A number of trends appear in the evolution of hominids and these may be traced using phylogenetic trees. The selection pressures on humans have changed due to the control human ...
... in speciation and evolution. Evidence for these changes comes from fossils and comparative anatomy and biochemical studies. A number of trends appear in the evolution of hominids and these may be traced using phylogenetic trees. The selection pressures on humans have changed due to the control human ...
Competitive speciation
... provisional solution to the two secondary problems (which turn out to be very closely related). The result is a novel mechanism of speciation incorporating disruptive selection and explaining a means by which it may appear in natural circumstances. I propose calling this new process competitive spec ...
... provisional solution to the two secondary problems (which turn out to be very closely related). The result is a novel mechanism of speciation incorporating disruptive selection and explaining a means by which it may appear in natural circumstances. I propose calling this new process competitive spec ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.