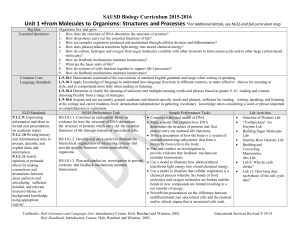
B1 Revision Mind Maps
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
... Bacteria mutate by chance Bacteria with mutation not killed by antibiotic These cells can survive to reproduce And pass the gene for resistance to their offspring – population of resistant bacteria increases What is a sterile culture. Culture of only one type of microorganism. Give 2 reasons it is i ...
Speciation: New Migratory Direction Provides Route
... between the two peaks determines how easily the population can move from one peak to the other. If the valley is shallow, the population can easily move by gradual change to the new peak; if the valley is deep, only a major mutation can move an individual to the new peak, but breeding between that i ...
... between the two peaks determines how easily the population can move from one peak to the other. If the valley is shallow, the population can easily move by gradual change to the new peak; if the valley is deep, only a major mutation can move an individual to the new peak, but breeding between that i ...
HS-SCI-APB-Unit 4 -- Chapter 24- Origin of
... The umystery of mysteries" that captivated Darwin is speciation, the process by which one species splits into two or more species. Speciation fascinated Darwin (and many biologists since) because it is responsible for the tremendous diversity of life, repeatedly yielding new species that differ from ...
... The umystery of mysteries" that captivated Darwin is speciation, the process by which one species splits into two or more species. Speciation fascinated Darwin (and many biologists since) because it is responsible for the tremendous diversity of life, repeatedly yielding new species that differ from ...
Unit 1 •From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
... Different species are related. There are many similarities among plants, animals and microorganisms. 1. How can there be so many similarities among organisms yet so many different plants, animals, and microorganisms? 2. How does biodiversity affect humans? 3. What scientific information supports com ...
... Different species are related. There are many similarities among plants, animals and microorganisms. 1. How can there be so many similarities among organisms yet so many different plants, animals, and microorganisms? 2. How does biodiversity affect humans? 3. What scientific information supports com ...
Unit 1 •From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
... Different species are related. There are many similarities among plants, animals and microorganisms. 1. How can there be so many similarities among organisms yet so many different plants, animals, and microorganisms? 2. How does biodiversity affect humans? 3. What scientific information supports com ...
... Different species are related. There are many similarities among plants, animals and microorganisms. 1. How can there be so many similarities among organisms yet so many different plants, animals, and microorganisms? 2. How does biodiversity affect humans? 3. What scientific information supports com ...
- Wiley Online Library
... © 2013 The Authors. Evolutionary Applications published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
... © 2013 The Authors. Evolutionary Applications published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
Topic XIV – Immune System - Science - Miami
... system, vaccines, and antibiotics. (ALD) Relate the significance of genetic factors, environmental factors, and pathogenic agents to both individual and public health. (ALD) Compare and contrast types of infectious agents that may infect the human body, including viruses, bacteria, fungi and par ...
... system, vaccines, and antibiotics. (ALD) Relate the significance of genetic factors, environmental factors, and pathogenic agents to both individual and public health. (ALD) Compare and contrast types of infectious agents that may infect the human body, including viruses, bacteria, fungi and par ...
Download
... Office hours: By appointment only Course Description: This is a graduate seminar course that will explore several aspects of human health through the perspective of how natural selection and evolution influence risk for infectious, chronic and psychological diseases and disorders, and how a better u ...
... Office hours: By appointment only Course Description: This is a graduate seminar course that will explore several aspects of human health through the perspective of how natural selection and evolution influence risk for infectious, chronic and psychological diseases and disorders, and how a better u ...
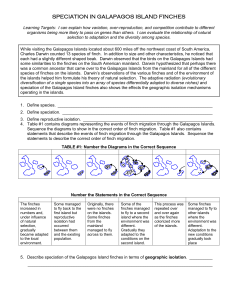
ACTIVITY: GALAPAGOS FINCHES
... Learning Targets: I can explain how variation, over-reproduction, and competition contribute to different organisms being more likely to pass on genes than others. I can evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and the diversity among species. While visiting the Galapagos Islands ...
... Learning Targets: I can explain how variation, over-reproduction, and competition contribute to different organisms being more likely to pass on genes than others. I can evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and the diversity among species. While visiting the Galapagos Islands ...
Culture as a system of adaptation and survival
... 4. Memes may also increase in frequency if they lead one to achieve influential position in social hierarchy (discussed below) These differences can produce very different outcomes from genetic evolution; specifically, they allow us to predict that: 1) Cultural evol. will generally be much more rapi ...
... 4. Memes may also increase in frequency if they lead one to achieve influential position in social hierarchy (discussed below) These differences can produce very different outcomes from genetic evolution; specifically, they allow us to predict that: 1) Cultural evol. will generally be much more rapi ...
AQA B1 Revision Checklist
... combustion of wood and fossil fuels. Explain the role of microorganisms and detritus feeders in decay. B1.7 Genetic variation and its control B1.7.1 Why organisms are different Classify characteristics as being due to genetic or environmental causes. Decide the best way to present information ...
... combustion of wood and fossil fuels. Explain the role of microorganisms and detritus feeders in decay. B1.7 Genetic variation and its control B1.7.1 Why organisms are different Classify characteristics as being due to genetic or environmental causes. Decide the best way to present information ...
1 - DrMillsLMU
... greater average body size. In contrast, when the weather was wetter finches with small beaks became more abundant. There is considerable variation in each trait and, depending on the context and situation, each trait may be seen as beneficial or harmful. This may be applied to behavioral disposition ...
... greater average body size. In contrast, when the weather was wetter finches with small beaks became more abundant. There is considerable variation in each trait and, depending on the context and situation, each trait may be seen as beneficial or harmful. This may be applied to behavioral disposition ...
Descent with Modification
... give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals ...
... give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals ...
Chapter 22 PowerPoint - Darwinian View of Life
... give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals ...
... give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals ...
File
... reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals • "The higher chances of survival, the more offspring they have" ...
... reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals • "The higher chances of survival, the more offspring they have" ...
File
... producing more offspring than the environment can support • Observation #4: Owing to lack of food or other resources, many of these offspring do not ...
... producing more offspring than the environment can support • Observation #4: Owing to lack of food or other resources, many of these offspring do not ...
Quinn, “The Gentle Darwinians, What Darwin`s
... uncanny backroom politician, can make him sound like a bit of a phony, or at least, like a shrewder operator than we want our saints to be.” Gopnik comes no closer to playing devil’s advocate. His Darwin is not just groundbreaking naturalist, but poet and egalitarian who “set out to widen the scope ...
... uncanny backroom politician, can make him sound like a bit of a phony, or at least, like a shrewder operator than we want our saints to be.” Gopnik comes no closer to playing devil’s advocate. His Darwin is not just groundbreaking naturalist, but poet and egalitarian who “set out to widen the scope ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution The Puzzle of Life`s
... Skinks are a type of lizard. In some species, legs have become so small they no longer function in walking. Why would an organism possess organs with little or no function? One explanation: The gene code is present to make the organ, but function has been lost through change over time. If the organ ...
... Skinks are a type of lizard. In some species, legs have become so small they no longer function in walking. Why would an organism possess organs with little or no function? One explanation: The gene code is present to make the organ, but function has been lost through change over time. If the organ ...
in evolution - University of California, Berkeley
... (d) Since all possible adaptive mutations are fixed, and since neutral mutations are unknown, virtually all new mutations are deleterious, unless the environment has changed very recently. Even a recent change in the environment does not make new mutations necessary, because of (a). ...
... (d) Since all possible adaptive mutations are fixed, and since neutral mutations are unknown, virtually all new mutations are deleterious, unless the environment has changed very recently. Even a recent change in the environment does not make new mutations necessary, because of (a). ...
Ch 1 Themes of Biology - Holly H. Nash
... Evolution, the Core Theme of Biology Evolution is the one idea that makes logical sense of everything we know about living organisms The scientific explanation for both the unity and diversity of organisms is the concept that living organisms are modified descendants of common ancestors Many ...
... Evolution, the Core Theme of Biology Evolution is the one idea that makes logical sense of everything we know about living organisms The scientific explanation for both the unity and diversity of organisms is the concept that living organisms are modified descendants of common ancestors Many ...
Fig. 22-6 - Geneva Area City Schools
... • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on the origin of species and natural selection but did not introduce his theory publicly, anticipating an uproar • In June 1858, Darwin received a manuscript from Alfred Russell Wallace, who had developed a theory of natural selection similar to Darwin’s • Darwin qu ...
... • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on the origin of species and natural selection but did not introduce his theory publicly, anticipating an uproar • In June 1858, Darwin received a manuscript from Alfred Russell Wallace, who had developed a theory of natural selection similar to Darwin’s • Darwin qu ...
Species selection and driven mechanisms jointly generate a large
... Evolution by natural selection is easy. Only heritable variation in fitness is needed for entities to evolve by natural selection (Lewontin 1970). In principle, many hierarchical levels can satisfy these criteria, from selfish genetic elements up through populations of organisms to the species level ...
... Evolution by natural selection is easy. Only heritable variation in fitness is needed for entities to evolve by natural selection (Lewontin 1970). In principle, many hierarchical levels can satisfy these criteria, from selfish genetic elements up through populations of organisms to the species level ...
Speciation by Natural and Sexual Selection: Models and Experiments.
... compete against a large fraction of the population, while extreme phenotypes have fewer competitors and therefore higher fitness. Models of speciation typically treat spatial variation in fitness and frequency-dependent selection within a locality as different mechanisms for producing disruptive sel ...
... compete against a large fraction of the population, while extreme phenotypes have fewer competitors and therefore higher fitness. Models of speciation typically treat spatial variation in fitness and frequency-dependent selection within a locality as different mechanisms for producing disruptive sel ...
Document
... Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 • Darwin made two main points – Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors – Natural selection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification” ...
... Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 • Darwin made two main points – Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors – Natural selection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification” ...
Document
... Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 • Darwin made two main points – Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors – Natural selection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification” ...
... Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 • Darwin made two main points – Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors – Natural selection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification” ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.