Multifactorial Traits
... contradict a belief in God? • Many scientists of all religious faiths believe in both. • Some people feel evolution contradicts the literal interpretation of the Bible. ...
... contradict a belief in God? • Many scientists of all religious faiths believe in both. • Some people feel evolution contradicts the literal interpretation of the Bible. ...
Speciation - Mrs. Cardoza Biology
... Speciation is the formation of a new species. Species is defined as organisms that are physically similar and can produce fertile offspring. Changes in gene frequencies that lead to the development of a new species are more likely to occur in small populations than in large ones. Small groups may be ...
... Speciation is the formation of a new species. Species is defined as organisms that are physically similar and can produce fertile offspring. Changes in gene frequencies that lead to the development of a new species are more likely to occur in small populations than in large ones. Small groups may be ...
Lecture notes evolution ch 22 and 23 a.p.
... CHAPTER 22: Descent With Modification -In 1859, Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection and the study of Biology would never be the same. Two key points were made by Darwin: 1. Evolution: Life on Earth has been transformed from its earliest forms to the vast d ...
... CHAPTER 22: Descent With Modification -In 1859, Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection and the study of Biology would never be the same. Two key points were made by Darwin: 1. Evolution: Life on Earth has been transformed from its earliest forms to the vast d ...
CHARLES DARWIN AND EVOLUTION I. Geologists have
... a. Evolution-defined by Darwin as “decent with modification.” Essentially what he was saying was that species change with time. According to Darwin, this would account for the great diversity of life on Earth. b. Evolution occurs through a process Darwin referred to as Natural Selection. c. Key Poin ...
... a. Evolution-defined by Darwin as “decent with modification.” Essentially what he was saying was that species change with time. According to Darwin, this would account for the great diversity of life on Earth. b. Evolution occurs through a process Darwin referred to as Natural Selection. c. Key Poin ...
Document
... Variation and gene pools • Gene pool – consists of all genes • Genetic variation – 2 main sources • Mutation –Change in sequence of DNA • Crossing over –Occurs during production of gametes ...
... Variation and gene pools • Gene pool – consists of all genes • Genetic variation – 2 main sources • Mutation –Change in sequence of DNA • Crossing over –Occurs during production of gametes ...
Population Genetics
... • Founder’s effect – a few individuals colonize a remote spot – causes drift ...
... • Founder’s effect – a few individuals colonize a remote spot – causes drift ...
Name Date Class
... A Species with similar evolutionary histories are not classified together. B Species with different evolutionary histories are classified more closely together. C Species with similar evolutionary histories are classified more closely together. D Species with similar evolutionary histories are class ...
... A Species with similar evolutionary histories are not classified together. B Species with different evolutionary histories are classified more closely together. C Species with similar evolutionary histories are classified more closely together. D Species with similar evolutionary histories are class ...
Unit Engage Review ppt
... • Earth is really, really old • Scientists have built a historical timeline by following the process of science. – Careful observation of fossils – Logical Inference ...
... • Earth is really, really old • Scientists have built a historical timeline by following the process of science. – Careful observation of fossils – Logical Inference ...
final exam review guide
... -Origin of life on earth according to Oparin’s Theory, Miller’s experiment -What were the first organisms on earth? When did humans evolve? -Evidence for change on Earth and evolution: fossils, anatomical and embryological, homology, vestigial structures etc., biochemical similarities -Theories of E ...
... -Origin of life on earth according to Oparin’s Theory, Miller’s experiment -What were the first organisms on earth? When did humans evolve? -Evidence for change on Earth and evolution: fossils, anatomical and embryological, homology, vestigial structures etc., biochemical similarities -Theories of E ...
Ecology Unit Outline - nnhsbiology
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
chapter 15 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... can lead to change. Helpful variations may gradually accumulate in a species while the unfavorable ones disappear. Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness in its environment ...
... can lead to change. Helpful variations may gradually accumulate in a species while the unfavorable ones disappear. Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness in its environment ...
darwin - Columbia College
... Within each species there is always variation. Competition. For any species, at almost all times, more organisms are born than can survive and reproduce to their full potential. Variation with respect to fitness. For any species, some of the variation is relevant to the ability to survive and reprod ...
... Within each species there is always variation. Competition. For any species, at almost all times, more organisms are born than can survive and reproduce to their full potential. Variation with respect to fitness. For any species, some of the variation is relevant to the ability to survive and reprod ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... hearing. 6 legs with well developed upper leg muscles Well developed canine teeth ...
... hearing. 6 legs with well developed upper leg muscles Well developed canine teeth ...
Name Date Period ______ Take Home Test : Evolution
... 32. When lions prey on a herd of antelope, some antelope are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? a. acquired characteristics b. reproductive isolation c. survival of the fittest d. descent with modification 33. On the ...
... 32. When lions prey on a herd of antelope, some antelope are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? a. acquired characteristics b. reproductive isolation c. survival of the fittest d. descent with modification 33. On the ...
SBI3U – Evolution Unit Test Name
... 15. Principles of uniformitarianism include which of the following? a. All animals share the same DNA. b. Earth is continually being changed by new forces over time. c. Natural laws are dynamic and change over time. d. Geological change is slow and gradual. ...
... 15. Principles of uniformitarianism include which of the following? a. All animals share the same DNA. b. Earth is continually being changed by new forces over time. c. Natural laws are dynamic and change over time. d. Geological change is slow and gradual. ...
diversity and evolution - Winona State University
... Evolution by natural selection established truths ...
... Evolution by natural selection established truths ...
Chapter 15 Outline
... -Use and disuse -Inheritance of acquired traits -How was LaMark incorrect ...
... -Use and disuse -Inheritance of acquired traits -How was LaMark incorrect ...
Natural Selection
... coyotes have a common ancestor that lived millions of years ago. •Convergent evolution: similar conditions may result in coincidentally similar organisms. Example: porpoises are mammals that originally lived on land and had hair, feet with claws, external ears, and mammal-like tails. They moved to t ...
... coyotes have a common ancestor that lived millions of years ago. •Convergent evolution: similar conditions may result in coincidentally similar organisms. Example: porpoises are mammals that originally lived on land and had hair, feet with claws, external ears, and mammal-like tails. They moved to t ...
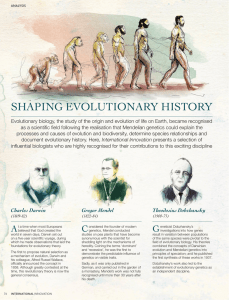
shaping evolutionary history
... a monastery, Mendel’s work was not fully recognised until more than 30 years after his death. ...
... a monastery, Mendel’s work was not fully recognised until more than 30 years after his death. ...
AP Biology - Evolution Review Key Terms
... Name a feature humans share with a common ancestor. Why is this true? How do we know all organisms evolved from a common ancestor? Bird wings and bat wings are an example of what idea? Bird wings and dragonfly wings are an example of what idea? If species 1 and 2 have similar appearances but differe ...
... Name a feature humans share with a common ancestor. Why is this true? How do we know all organisms evolved from a common ancestor? Bird wings and bat wings are an example of what idea? Bird wings and dragonfly wings are an example of what idea? If species 1 and 2 have similar appearances but differe ...
Evolution
... a. Uniformitarianism states that past geological events can be best explained by observing the ongoing events of the present and generalizing backward through time. b. It further asserts that current geological structures are the result of long-term natural forces. 3. Transformism had posited the pr ...
... a. Uniformitarianism states that past geological events can be best explained by observing the ongoing events of the present and generalizing backward through time. b. It further asserts that current geological structures are the result of long-term natural forces. 3. Transformism had posited the pr ...
Chapter 5 Lecture IBESS NatSel
... • Penguins live where it’s cold and where there’s lots of water. There’s more food for them in the water, so they evolved to “fly” underwater. • Puffins live where it’s slightly warmer. There’s lots of food sources outside of the water, so they continued to fly normally. ...
... • Penguins live where it’s cold and where there’s lots of water. There’s more food for them in the water, so they evolved to “fly” underwater. • Puffins live where it’s slightly warmer. There’s lots of food sources outside of the water, so they continued to fly normally. ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.