Spring 2012
... ____ produces gametes in animals and spores in other organisms. The stage of meiosis during which homologous chromosomes separate is: The most significant difference between mitosis and meiosis is: Genetic variation results from: Gregor Mendel deduced the laws of: Dr. Smith’s parents have normal hea ...
... ____ produces gametes in animals and spores in other organisms. The stage of meiosis during which homologous chromosomes separate is: The most significant difference between mitosis and meiosis is: Genetic variation results from: Gregor Mendel deduced the laws of: Dr. Smith’s parents have normal hea ...
Going places: forced and natural molecular evolution
... mutants of ~-lactamase each resulted in a ~20-fold improvement in catalytic c o n s t a n t (kcat) , while the kc.~ of the double mutant was 859-fold higher than that of the wild type. The statistics of random mutations mean that if only screening, rather than selection, is possible, one is forced t ...
... mutants of ~-lactamase each resulted in a ~20-fold improvement in catalytic c o n s t a n t (kcat) , while the kc.~ of the double mutant was 859-fold higher than that of the wild type. The statistics of random mutations mean that if only screening, rather than selection, is possible, one is forced t ...
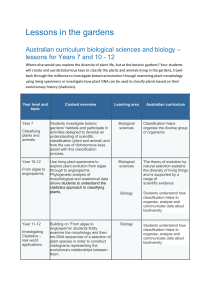
Curriculum information for Biological sciences and Biology
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
Lesson Overview
... 2. Species vary locally – different yet related species occupy different habitats in one area. 3. Species vary over time – fossils of extinct species are similar to current species. ...
... 2. Species vary locally – different yet related species occupy different habitats in one area. 3. Species vary over time – fossils of extinct species are similar to current species. ...
Evolution (organic)
... The concept of natural selection Darwin thought of natural selection as the result of “struggle for life”: since the resources are in general rare in an environment, and since the rate of increase of a population exceeds in general the availability of resources (an idea that he famously took from M ...
... The concept of natural selection Darwin thought of natural selection as the result of “struggle for life”: since the resources are in general rare in an environment, and since the rate of increase of a population exceeds in general the availability of resources (an idea that he famously took from M ...
15-3 Darwin Presents His Case
... • Because more organisms are produced than can survive, they compete for limited resources. • Each unique organism has different advantages and disadvantages in the struggle for existence. Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. These organisms pass thei ...
... • Because more organisms are produced than can survive, they compete for limited resources. • Each unique organism has different advantages and disadvantages in the struggle for existence. Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. These organisms pass thei ...
Different tests, different conclusions: evolutionary
... macromutation is considered one with a small chance of being favoured by selection, or of a definition based on frequency of occurrence. They suggest the type of mutation is more important than the magnitude: mutations that ‘stretch’ an existing structure are more likely to contribute to evolutionar ...
... macromutation is considered one with a small chance of being favoured by selection, or of a definition based on frequency of occurrence. They suggest the type of mutation is more important than the magnitude: mutations that ‘stretch’ an existing structure are more likely to contribute to evolutionar ...
Biology - domain E
... (a) All living organisms (species or types) that we see, today were created as such. (b) The diversity was always the same since creation and will be the same in future also. (c) Earth is about 4000 years old. Natural Selection as a Mechanism of Evolution • Darwin made a sea voyage round the world i ...
... (a) All living organisms (species or types) that we see, today were created as such. (b) The diversity was always the same since creation and will be the same in future also. (c) Earth is about 4000 years old. Natural Selection as a Mechanism of Evolution • Darwin made a sea voyage round the world i ...
key - Sacramento State
... Describe the three empirical observations that Darwin made upon which he based his argument and the logical deduction that follows from these observations. His first observation was that individuals of a species vary in their traits and that this variation was heritable. Second, he observed that ...
... Describe the three empirical observations that Darwin made upon which he based his argument and the logical deduction that follows from these observations. His first observation was that individuals of a species vary in their traits and that this variation was heritable. Second, he observed that ...
Chapter 6 Student Packet
... a. Darwin understood immediately why Galápagos organisms had many different adaptations. b. Darwin thought that Galápagos organisms gradually changed over many generations. c. Darwin believed that evolution had occurred on the Galápagos Islands. d. Selective breeding helped Darwin understand how evo ...
... a. Darwin understood immediately why Galápagos organisms had many different adaptations. b. Darwin thought that Galápagos organisms gradually changed over many generations. c. Darwin believed that evolution had occurred on the Galápagos Islands. d. Selective breeding helped Darwin understand how evo ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... – species evolve in response to changes in each other ...
... – species evolve in response to changes in each other ...
No Slide Title - Cloudfront.net
... • Ideas About Breeding In Darwin’s time, farmers and breeders had produced many kinds of farm animals and plants. These plants and animals had traits that were desired by the farmers and breeders. • A trait is a form of a genetically determined ...
... • Ideas About Breeding In Darwin’s time, farmers and breeders had produced many kinds of farm animals and plants. These plants and animals had traits that were desired by the farmers and breeders. • A trait is a form of a genetically determined ...
ppt - Furman University
... appreciate the struggle for existence which everywhere goes on from long-continued observation of the habits of animals and plants, it at once struck me that under these circumstances favourable variations would tend to be preserved, and unfavourable ones to be destroyed. The result of this would be ...
... appreciate the struggle for existence which everywhere goes on from long-continued observation of the habits of animals and plants, it at once struck me that under these circumstances favourable variations would tend to be preserved, and unfavourable ones to be destroyed. The result of this would be ...
Opposition to Evolution
... The record of earth history, as preserved in the earth's crust, especially in the rocks and fossil deposits, is primarily a record of catastrophic intensities of natural processes, operating largely within uniform natural laws, rather than one of gradualism and relatively uniform process rates. Ther ...
... The record of earth history, as preserved in the earth's crust, especially in the rocks and fossil deposits, is primarily a record of catastrophic intensities of natural processes, operating largely within uniform natural laws, rather than one of gradualism and relatively uniform process rates. Ther ...
Chapter 7
... think that species could evolve over time. It became clear to Darwin that Earth was much older than anyone had imagined. ...
... think that species could evolve over time. It became clear to Darwin that Earth was much older than anyone had imagined. ...
allele frequency is how common is that allele in the population how
... a population is a localized group of interbreeding individuals gene pool is collection of alleles in the population ...
... a population is a localized group of interbreeding individuals gene pool is collection of alleles in the population ...
Biol1404-Exam3_fall04.doc
... C) addition of exons to the mRNA. D) deletion of exons from the mRNA. E) combination of two different chromosomes together 28. The incorrect theory that "organisms (such as giraffes) can modify their bodies through use or disuse of parts, and that these modifications can be passed on to their offspr ...
... C) addition of exons to the mRNA. D) deletion of exons from the mRNA. E) combination of two different chromosomes together 28. The incorrect theory that "organisms (such as giraffes) can modify their bodies through use or disuse of parts, and that these modifications can be passed on to their offspr ...
Environmental AP
... 59. Energy moving from potential energy to kinetic energy is an example of 60. Heat is an example of 61. The rate of doing work is called 62. Leibig’s principle states 63. Shelford determined 64. Another name for maximums and minimums 65. The concept of limiting factors was created by 66. This facto ...
... 59. Energy moving from potential energy to kinetic energy is an example of 60. Heat is an example of 61. The rate of doing work is called 62. Leibig’s principle states 63. Shelford determined 64. Another name for maximums and minimums 65. The concept of limiting factors was created by 66. This facto ...
Die (Ir-)Rationalität religiöser Überzeugungen
... Species multiply: the diversification of life involves populations of one species diverging until they become separate species Gradualism: evolutionary change occurs through incremental small steps; new species are not created suddenly. Natural selection: some variants change individual’s survival & ...
... Species multiply: the diversification of life involves populations of one species diverging until they become separate species Gradualism: evolutionary change occurs through incremental small steps; new species are not created suddenly. Natural selection: some variants change individual’s survival & ...
File
... An Ancient, Changing Earth In Darwin’s day, most Europeans believed that Earth and all its life forms were only a few thousand years old and had not changed very much in that time. Several scientists who lived around the same time as Darwin began to challenge these ideas. These scientists had an imp ...
... An Ancient, Changing Earth In Darwin’s day, most Europeans believed that Earth and all its life forms were only a few thousand years old and had not changed very much in that time. Several scientists who lived around the same time as Darwin began to challenge these ideas. These scientists had an imp ...
biology
... b. man is the result of a purposeless and ________ process (without him in mind) c. man is a part of ______ and has emerged as the result of a ___________ process d. __________ is the basic source of knowledge e. __________ and ________ ____________ are the mechanisms of evolution f. “evolution is a ...
... b. man is the result of a purposeless and ________ process (without him in mind) c. man is a part of ______ and has emerged as the result of a ___________ process d. __________ is the basic source of knowledge e. __________ and ________ ____________ are the mechanisms of evolution f. “evolution is a ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... • The primitive atmosphere promoted chemical reactions, which led to the synthesis of ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (radiation, electric energy, X-rays, etc. all give off energy!) • Miller later demonstrated that this could happen in a lab: ...
... • The primitive atmosphere promoted chemical reactions, which led to the synthesis of ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (radiation, electric energy, X-rays, etc. all give off energy!) • Miller later demonstrated that this could happen in a lab: ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.