Military History Anniversaries 01 thru 31 AUG
... Aug 04 1969 – Vietnam: At the apartment of French intermediary Jean Sainteny in Paris, American representative Henry Kissinger and North Vietnamese representative Xuan Thuy begin secret peace negotiations. The negotiations will eventually fail. Aug 05 1861 – Civil War: Congress adopts the nation’s f ...
... Aug 04 1969 – Vietnam: At the apartment of French intermediary Jean Sainteny in Paris, American representative Henry Kissinger and North Vietnamese representative Xuan Thuy begin secret peace negotiations. The negotiations will eventually fail. Aug 05 1861 – Civil War: Congress adopts the nation’s f ...
Military History Anniversaries 0201 thru 0228
... by an American squadron of B-17s assisting in the Soviet's Vistula-Oder Offensive. Feb 15 1898 – U.S. battleship Maine mysteriously blows up in Havana Harbor, Cuba killing more 274 crew members and bringing the United States closer to war with Spain. Feb 15 1942 - World War II: Fall of Singapore. Fo ...
... by an American squadron of B-17s assisting in the Soviet's Vistula-Oder Offensive. Feb 15 1898 – U.S. battleship Maine mysteriously blows up in Havana Harbor, Cuba killing more 274 crew members and bringing the United States closer to war with Spain. Feb 15 1942 - World War II: Fall of Singapore. Fo ...
Turning Back the German Army (cont.)
... The Americans were able to win the Battle of the Atlantic because the convoy system protected cargo ships and radar, sonar, and depth charges located and damaged German submarines. ...
... The Americans were able to win the Battle of the Atlantic because the convoy system protected cargo ships and radar, sonar, and depth charges located and damaged German submarines. ...
chapter twenty-five world war ii, 1941–1945
... CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter covers the American involvement in World War II and its effects on the United States. America began trying to ensure isolation by enacting a series of neutrality laws but as the war broke out in Europe and Asia, the U.S. gradually altered the neutrality laws. Even befor ...
... CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter covers the American involvement in World War II and its effects on the United States. America began trying to ensure isolation by enacting a series of neutrality laws but as the war broke out in Europe and Asia, the U.S. gradually altered the neutrality laws. Even befor ...
Chapter 24 - Patrick Minges
... and landing crafts. By the end of the day, they had gained a toehold in France. By July 1, more than one million Allied troops had landed. Germany now faced a hopeless two-front war, as the Soviets advanced from the east. In December 1944, Hitler ordered a counterattack, known as the Battle of the B ...
... and landing crafts. By the end of the day, they had gained a toehold in France. By July 1, more than one million Allied troops had landed. Germany now faced a hopeless two-front war, as the Soviets advanced from the east. In December 1944, Hitler ordered a counterattack, known as the Battle of the B ...
1 Pearl Harbor Define: The attack on Pearl Harbor in
... Cause/Effect: German physicists had found that by splitting the Uranium atom, they could utilize the new found energy as a weapon in war. In response to Germany’s new knowledge, the United States passed a research program called the Manhattan Project. The project received its name in late 1941 when ...
... Cause/Effect: German physicists had found that by splitting the Uranium atom, they could utilize the new found energy as a weapon in war. In response to Germany’s new knowledge, the United States passed a research program called the Manhattan Project. The project received its name in late 1941 when ...
World War-II Documentaries
... Produced by John Ford. This Oscar-winning documentary on the Pacific War begins with Japa- nese preparations before the bombing of Pearl Harbor and ends with the U.S. dropping the atom- ic bombs on Nagasaki and Hiroshima. Aside from the interesting footage on the Japanese home front before Pearl Ha ...
... Produced by John Ford. This Oscar-winning documentary on the Pacific War begins with Japa- nese preparations before the bombing of Pearl Harbor and ends with the U.S. dropping the atom- ic bombs on Nagasaki and Hiroshima. Aside from the interesting footage on the Japanese home front before Pearl Ha ...
USH CH 17 Test Review
... -destroyers with sonar; planes with radar -construction of Liberty ships speeds up ...
... -destroyers with sonar; planes with radar -construction of Liberty ships speeds up ...
US Hst II -- Handout 7-1a
... -- Stalin kept demanding that Britain and US open a _______ front to take some pressure off of Russia as he wanted to force Hitler into a ____-front war. -- The Western Allies decided that they were not yet ready to invade Europe so they put Operation _____________ (a _________ invasion) on hold. -- ...
... -- Stalin kept demanding that Britain and US open a _______ front to take some pressure off of Russia as he wanted to force Hitler into a ____-front war. -- The Western Allies decided that they were not yet ready to invade Europe so they put Operation _____________ (a _________ invasion) on hold. -- ...
Chapter 17
... to businesses to give them full employment rights. FDR also created the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) in order to continually develop and improve technologies for the war effort. The OSRD also pushed for medical improvements to keep the soldiers from getting diseases on the ...
... to businesses to give them full employment rights. FDR also created the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) in order to continually develop and improve technologies for the war effort. The OSRD also pushed for medical improvements to keep the soldiers from getting diseases on the ...
The United States in World War II
... Germany controls 9/10 of city by September Another harsh winter hits Massive counter offensive by Soviets Surround Germans Hitler tells German generals to stay and fight ...
... Germany controls 9/10 of city by September Another harsh winter hits Massive counter offensive by Soviets Surround Germans Hitler tells German generals to stay and fight ...
Pushing Back the Axis
... last six months of 1942. These numbers were small, however, compared to the massive new campaign. Between January 1943 and May 1945, the Royal Air Force and the United States Eighth Army Air Force dropped approximately 53,000 tons (48,230 t) of explosives on Germany every month. The bombing campaign ...
... last six months of 1942. These numbers were small, however, compared to the massive new campaign. Between January 1943 and May 1945, the Royal Air Force and the United States Eighth Army Air Force dropped approximately 53,000 tons (48,230 t) of explosives on Germany every month. The bombing campaign ...
3-538 - George C. Marshall Foundation
... with large vessels during daylight hours. It was a persuasive show of Allied air superiority. (Kenney, General Kenney Reports, p. 204; Maurice Matloff, Strategic Planning for Coalition Warfare, 1943–1944, a volume in the United States Army in World War II [Washington: GPO, 1959], p. 92.) Meanwhile G ...
... with large vessels during daylight hours. It was a persuasive show of Allied air superiority. (Kenney, General Kenney Reports, p. 204; Maurice Matloff, Strategic Planning for Coalition Warfare, 1943–1944, a volume in the United States Army in World War II [Washington: GPO, 1959], p. 92.) Meanwhile G ...
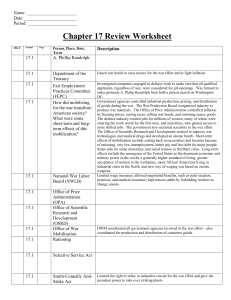
Chapter 17 Review Worksheet
... surrendered to the Allies in 1945, MacArthur became the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, rebuilding Japan during the Allied occupation. Although the Yalta agreements were attacked as a “sellout,” it seemed important at the time to keep the Soviet Union from making a separate peace with German ...
... surrendered to the Allies in 1945, MacArthur became the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, rebuilding Japan during the Allied occupation. Although the Yalta agreements were attacked as a “sellout,” it seemed important at the time to keep the Soviet Union from making a separate peace with German ...
2.Major Operations of the US in Europe - Academic
... “Marshall is the greatest man of World War II. He managed to get along with Roosevelt, the Congress, Churchill, the Navy and the Joint Chiefs of Staff and he made a grand record in China. When I asked him to [be] my special envoy to China, he merely said, ‘Yes, Mr. President I'll go.’ No argument on ...
... “Marshall is the greatest man of World War II. He managed to get along with Roosevelt, the Congress, Churchill, the Navy and the Joint Chiefs of Staff and he made a grand record in China. When I asked him to [be] my special envoy to China, he merely said, ‘Yes, Mr. President I'll go.’ No argument on ...
America in World War II - North Penn School District
... • Significance: Turning point of WWII in the Pacific ...
... • Significance: Turning point of WWII in the Pacific ...
WWII Events
... Normandy, France to liberate the Western part of Europe from German control. • This was the war’s largest sea invasion known as D-Day. • Surprised the Germans; the Allies won. • On August 25, 1944 Allied forces freed Paris ...
... Normandy, France to liberate the Western part of Europe from German control. • This was the war’s largest sea invasion known as D-Day. • Surprised the Germans; the Allies won. • On August 25, 1944 Allied forces freed Paris ...
Chapter 17 Worksheet
... ____ 17. This general led the American troops that liberated Paris from German occupation. ____ 18. The initial success of this German offensive battle was due mainly to the Allies' being caught off guard. Choose the letter of the best answer. ____ 19. In December of 1941, who commanded the Allied f ...
... ____ 17. This general led the American troops that liberated Paris from German occupation. ____ 18. The initial success of this German offensive battle was due mainly to the Allies' being caught off guard. Choose the letter of the best answer. ____ 19. In December of 1941, who commanded the Allied f ...
20.2 THE EARLY BATTLES
... Africa began Commanded by General Dwight D. Eisenhower.. 1. The American forces in Morocco were led byGeneral George Patton and captured the city of Casablanca. 2. Battle of Kasserine Pass a. Americans faced the German army for the first time. b. Outmaneuvered and out-fought, Americans suffered huge ...
... Africa began Commanded by General Dwight D. Eisenhower.. 1. The American forces in Morocco were led byGeneral George Patton and captured the city of Casablanca. 2. Battle of Kasserine Pass a. Americans faced the German army for the first time. b. Outmaneuvered and out-fought, Americans suffered huge ...
Americans in World War II
... forces in Africa. After several hard fought battles in Algeria and Tunisia Axis powers in Africa surrendered in May of 1943. • Invading Italy –General George Patton led Allied troop invasion of Italy. • Allies captured Rome in June of 1944 making it the first Axis capital to fall. Mussolini shot in ...
... forces in Africa. After several hard fought battles in Algeria and Tunisia Axis powers in Africa surrendered in May of 1943. • Invading Italy –General George Patton led Allied troop invasion of Italy. • Allies captured Rome in June of 1944 making it the first Axis capital to fall. Mussolini shot in ...
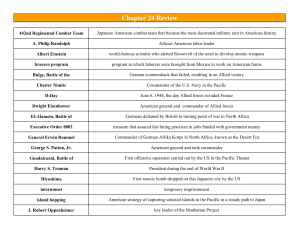
Chapter 24 Review
... American strategy of capturing selected islands in the Pacific in a steady path to Japan ...
... American strategy of capturing selected islands in the Pacific in a steady path to Japan ...
Document
... 1. Battle of Midway – (June of 1942) A battle in the Pacific between the U.S. and Japan (considered a turning point). The U.S. defeated Japan. After the battle, Japan's shipbuilding and pilot training programs were unable to keep pace in replacing their losses, while the U.S. steadily increased outp ...
... 1. Battle of Midway – (June of 1942) A battle in the Pacific between the U.S. and Japan (considered a turning point). The U.S. defeated Japan. After the battle, Japan's shipbuilding and pilot training programs were unable to keep pace in replacing their losses, while the U.S. steadily increased outp ...
Click here (part 2)
... Soviet soldiers and civilians were killed or captured, but Soviet resistance and the brutal Russian winter of 1942/43 defeated the Germans, who surrendered (91,000 troops) on January, 1943. • Stalingrad was the farthest eastern point of the German army’s advance into the USSR…a major turning point i ...
... Soviet soldiers and civilians were killed or captured, but Soviet resistance and the brutal Russian winter of 1942/43 defeated the Germans, who surrendered (91,000 troops) on January, 1943. • Stalingrad was the farthest eastern point of the German army’s advance into the USSR…a major turning point i ...
The War Goes Global
... the Americans from North West Africa, the Germans were squeezed between these two armies • While the German and Italian forces put up fierce resistance, they surrender in May of 1943 • 275,000 German soldiers surrendered ...
... the Americans from North West Africa, the Germans were squeezed between these two armies • While the German and Italian forces put up fierce resistance, they surrender in May of 1943 • 275,000 German soldiers surrendered ...
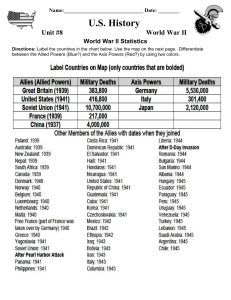
Military history of the United States during World War II

The military history of the United States' involvement in World War II covers the war against Japan, Germany and Italy starting with the 7 December 1941 attack on Pearl Harbor. During the first two years of the global conflict, the United States had maintained formal neutrality as made officially in the 1937 Quarantine Speech delivered by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt on 5 October 1937 in Chicago, while supplying Britain, the Soviet Union, and China with war material through the Lend-Lease Act which was signed into law on 11 March 1941, as well as deploying the U.S. military to replace the British invasion forces in Iceland (for early U.S. combat activity in the Pacific Theater, see the Flying Tigers). US economic sanction on Japan as part of the effort to deter Japanese military aggression in Asia-Pacific outraged the Empire of Japan as the major cause of Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. During the war, over 16 million Americans served in the United States Armed Forces, with 290,000 killed in action and 670,000 wounded. There were also 130,201 American POWs, of whom 116,129 returned home after the war. Key civilian advisors to President Franklin D. Roosevelt included Secretary of War Henry Stimson, who mobilized the nation's industries and induction centers to supply the Army, commanded by General George C. Marshall and the Army Air Forces under General Hap Arnold. The Navy, led by Admiral Ernest King, proved more autonomous. Overall priorities were set by Roosevelt and the Joint Chiefs, chaired by William D. Leahy. Highest priority went to the defeat of Germany in Europe, but first the war against Japan in the Pacific was more urgent after the sinking of the main battleship fleet at Pearl Harbor.Admiral King put Admiral Chester W. Nimitz, based in Hawaii, in charge of the Central Pacific War against Japan. The result was a series of some of the most famous naval battles in history. The Imperial Japanese Navy had the advantage, taking the Philippines as well as British and Dutch possessions, and threatening Australia but in June 1942, its main carriers were sunk during the Battle of Midway, and the Americans seized the initiative. The Pacific War became one of island hopping, so as to move air bases closer and closer to Japan. The Army, based in Australia under General Douglas MacArthur, steadily advanced across New Guinea to the Philippines, with plans to invade the Japanese home islands in late 1945. With its merchant fleet sunk by American submarines, Japan ran short of aviation gasoline and fuel oil, as the U.S. Navy in June 1944 captured islands within bombing range of the Japanese home islands. Strategic bombing directed by General Curtis Lemay destroyed all the major Japanese cities, as the U.S. captured Okinawa after heavy losses in spring 1945. With conventional and atomic bombs falling and an invasion imminent, Japan surrendered.The war against Germany involved aid to Britain, her allies, and the Soviet Union, with the U.S. supplying munitions until it could ready an invasion force. U.S. forces were first tested to a limited degree in the North African Campaign and then employed more significantly with British Forces in Italy in 1942-43, where U.S. forces, representing about a third of Allied forces deployed, bogged down after Italy surrendered and the Germans took over. Finally the main invasion of France took place in June 1944, under Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower. Meanwhile, the Army Air Forces and RAF systematically targeted German transportation links and synthetic oil plants, as it knocked out what was left of the Luftwaffe post Battle of Britain in 1944. With the Soviets unstoppable in the east, and the Allies unstoppable in the west, Germany was squeezed to death. Berlin fell to the Soviets in May 1945, and with Hitler dead, the Germans surrendered.The military effort was strongly supported by civilians on the home front, who provided the military personnel, the munitions, the money, and the morale to fight the war to victory. World War II cost the U.S an estimated $341 Billion in 1945 dollars - equivalent to 74% of America's GDP and expenditures during the war. In 2015 dollars, the war cost over $4.5 Trillion.