PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... to what number of significant figures? [1] 65 Using the data, determine the concentration of the HCl(aq). [1] ...
... to what number of significant figures? [1] 65 Using the data, determine the concentration of the HCl(aq). [1] ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... 3. Two isotopes of uranium are U-237 and U-238. Both would be expected to have the same (A) mass (D) number of neutrons (B) number of protons (E) half-life (C) decay mode 4. Whose gold foil experiment concluded that the positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region? (A) Thompson (D) C ...
... 3. Two isotopes of uranium are U-237 and U-238. Both would be expected to have the same (A) mass (D) number of neutrons (B) number of protons (E) half-life (C) decay mode 4. Whose gold foil experiment concluded that the positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region? (A) Thompson (D) C ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE
... NOW, multiply each of these by the same number to get a whole number ration (instead of 1/3 : 1). If you multiply by 3 you get a ratio of 1:3, so the formula will be HfCl3). 21. IN the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) it remains con ...
... NOW, multiply each of these by the same number to get a whole number ration (instead of 1/3 : 1). If you multiply by 3 you get a ratio of 1:3, so the formula will be HfCl3). 21. IN the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) it remains con ...
ic199p5a
... chloride structure, because the radius ratio determines which structure should be the most stable and the CsCl structure is most likely when the ions are closest to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that ...
... chloride structure, because the radius ratio determines which structure should be the most stable and the CsCl structure is most likely when the ions are closest to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... The masses of individual atoms are expressed as atomic mass units (amu) or µ. The atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This means a proton or a neutron has mass equal to approximately one atomic mass unit. In many cases the amount of each isotope in the sample, or its re ...
... The masses of individual atoms are expressed as atomic mass units (amu) or µ. The atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This means a proton or a neutron has mass equal to approximately one atomic mass unit. In many cases the amount of each isotope in the sample, or its re ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O. It is a hydrated compound because water molecules are included within its crystal structure. There are 12 moles of H2O for every 1 mole of KAl(SO4)2. The compound contains two different positive ions. The gram-formula mass of KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O is 474 grams per mole. 66 Identify one ...
... KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O. It is a hydrated compound because water molecules are included within its crystal structure. There are 12 moles of H2O for every 1 mole of KAl(SO4)2. The compound contains two different positive ions. The gram-formula mass of KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O is 474 grams per mole. 66 Identify one ...
Flexbook - Ions and Ion Formation
... of family 3A. The large jump occurs between the 3rd and 4th ionization energies, so we know that only the first three electrons can be easily removed from this atom. The logic for the formation of anions is very similar to that for cations. A fluorine atom, for example, has a high electron affinity ...
... of family 3A. The large jump occurs between the 3rd and 4th ionization energies, so we know that only the first three electrons can be easily removed from this atom. The logic for the formation of anions is very similar to that for cations. A fluorine atom, for example, has a high electron affinity ...
Click Here To File
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
bonding, structure, properties and energy changes
... Endothermic reactions If heat energy is absorbed during a reaction, the temperature of the surroundings decreases and the reaction is described as being endothermic. When methylated spirits (‘meths’) is spilt on the skin it quickly evaporates. This is an endothermic process – the meths absorbs heat ...
... Endothermic reactions If heat energy is absorbed during a reaction, the temperature of the surroundings decreases and the reaction is described as being endothermic. When methylated spirits (‘meths’) is spilt on the skin it quickly evaporates. This is an endothermic process – the meths absorbs heat ...
3UE-Exam Review-June2010 - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... 19. When is ionic bonding likely to occur between two atoms? a) when both atoms have low ionization energy and low electron affinity b) when both atoms have high ionization energy and low electron affinity c) when both atoms have high ionization energy and high electron affinity d) when one atom has ...
... 19. When is ionic bonding likely to occur between two atoms? a) when both atoms have low ionization energy and low electron affinity b) when both atoms have high ionization energy and low electron affinity c) when both atoms have high ionization energy and high electron affinity d) when one atom has ...
Naming Binary Inorganic Compounds
... It is easiest to remember those formulae that end in “ate” and derive the others from it. The compound that contains __________________ will have an “ite” suffix. One fewer oxygen than the “ite” compound will have a _________ prefix. The compound that contains one more oxygen than the “ate” compound ...
... It is easiest to remember those formulae that end in “ate” and derive the others from it. The compound that contains __________________ will have an “ite” suffix. One fewer oxygen than the “ite” compound will have a _________ prefix. The compound that contains one more oxygen than the “ate” compound ...
chemistry — released form
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
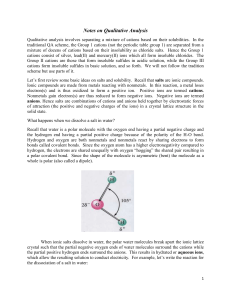
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... acid) now reacts with the NH3 (the Lewis base) to form the complex ion Cu(NH3)42+ which is soluble. As the NH3 reacts with the Cu2+, the concentration of Cu2+ decreases and the above equilibrium will shift right to produce more Cu2+. This means that the solid Cu(OH)2 must dissociate; in other words ...
... acid) now reacts with the NH3 (the Lewis base) to form the complex ion Cu(NH3)42+ which is soluble. As the NH3 reacts with the Cu2+, the concentration of Cu2+ decreases and the above equilibrium will shift right to produce more Cu2+. This means that the solid Cu(OH)2 must dissociate; in other words ...
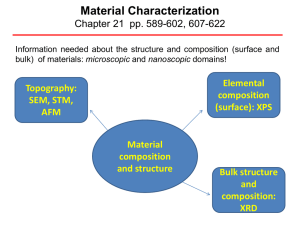
Material Characterization
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
Balancing ANY chemical Equation
... balance the easiest elements first. The easiest elements to balance are the ones that appear in the fewest substances in the equation. Therefore, to determine balancing order, count ...
... balance the easiest elements first. The easiest elements to balance are the ones that appear in the fewest substances in the equation. Therefore, to determine balancing order, count ...
Atomic Structure PPQs 2
... State ONE similarity and ONE difference between these two isotopes in terms of the numbers of their fundamental particles. Similarity .......................................................................................................... Difference ................................................ ...
... State ONE similarity and ONE difference between these two isotopes in terms of the numbers of their fundamental particles. Similarity .......................................................................................................... Difference ................................................ ...
practice exercise - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Solution Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+ and the anion is SO42–. (If you thou ...
... Solution Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+ and the anion is SO42–. (If you thou ...
practice exercise
... Solution (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element, which means this element is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion has three more protons than electrons, it has a net charge of 3+. Thus, the s ...
... Solution (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element, which means this element is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion has three more protons than electrons, it has a net charge of 3+. Thus, the s ...
Fall 2008 Blank Exam 1 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), last name, first name, middle initial, and student identification number. Leave the class section numb ...
... and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), last name, first name, middle initial, and student identification number. Leave the class section numb ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... ♦ Chemical identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons. ♦ The nucleus also contains neutral particles, neutrons, which are essential for the stability of the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of the atom but have no charge. Atomic Mass Units ...
... ♦ Chemical identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons. ♦ The nucleus also contains neutral particles, neutrons, which are essential for the stability of the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of the atom but have no charge. Atomic Mass Units ...
LN_atoms_etc
... Chemical identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons. The nucleus also contains neutral particles, neutrons, which are essential for the stability of the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of the atom but have no charge. Atomic Mass Units ...
... Chemical identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons. The nucleus also contains neutral particles, neutrons, which are essential for the stability of the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of the atom but have no charge. Atomic Mass Units ...
4.IonicCompounds - Gleneaglesunit1and2chemistry2012
... combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
... combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
Ch. 9
... Silicon dioxide, SiO2, is a molecular compound. It is also a mineral called quartz (left). Quartz is found in nearly every type of rock. Most sand grains (center) are bits of quartz. Glass is made from sand. ...
... Silicon dioxide, SiO2, is a molecular compound. It is also a mineral called quartz (left). Quartz is found in nearly every type of rock. Most sand grains (center) are bits of quartz. Glass is made from sand. ...
Mass Spectrometry and Organic
... •Potential question; Is the largest m/z the molecular ion or is it a prominent fragment from an even heavier molecule? ...
... •Potential question; Is the largest m/z the molecular ion or is it a prominent fragment from an even heavier molecule? ...
Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectroscopy
... of Alcohols • Alcohols usually lose a water molecule. • M+ may not be visible. ...
... of Alcohols • Alcohols usually lose a water molecule. • M+ may not be visible. ...