Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... are the moving charges. When charges are not flowing, the net charge in the wire is zero. When charges are flowing the net charge in the wire is zero because for every one charge that enters one side, another charge leaves the other side and the total number of protons and neutrons doesn’t change. D ...
... are the moving charges. When charges are not flowing, the net charge in the wire is zero. When charges are flowing the net charge in the wire is zero because for every one charge that enters one side, another charge leaves the other side and the total number of protons and neutrons doesn’t change. D ...
Electric Current
... What is a voltage difference? • The voltage difference (V) is the difference in the voltage or the electric potential energy. Think of it like an electric pressure. • With a battery, electrons are on one end, the negative end. They want to travel to the positive end of the battery. • Voltage is mea ...
... What is a voltage difference? • The voltage difference (V) is the difference in the voltage or the electric potential energy. Think of it like an electric pressure. • With a battery, electrons are on one end, the negative end. They want to travel to the positive end of the battery. • Voltage is mea ...
Name____________________________ Reading
... 5. What 2 metals would you use from table 17.1 to make the highest voltage battery cell? ...
... 5. What 2 metals would you use from table 17.1 to make the highest voltage battery cell? ...
CirCuits
... They give off light and heat Brightness increases as current increases Since energy is lost as light and heat more voltage is required to have the same current As current increases, resistance increases because the light bulb heats up ...
... They give off light and heat Brightness increases as current increases Since energy is lost as light and heat more voltage is required to have the same current As current increases, resistance increases because the light bulb heats up ...
Voltage Current (electric) Resistance (electric) direct current
... Electricity . an electric current of constant direction, having a magnitude that does not vary or varies only slightly. Abbreviation: dc ...
... Electricity . an electric current of constant direction, having a magnitude that does not vary or varies only slightly. Abbreviation: dc ...
Electricity
... Note: It is actually the electrons that are flowing from negative to positive, but for sake of tradition and convention we say the positive charge flows from positive to negative. (Protons don’t move!) ...
... Note: It is actually the electrons that are flowing from negative to positive, but for sake of tradition and convention we say the positive charge flows from positive to negative. (Protons don’t move!) ...
Voltage/DC current
... - It is measured in Volts. - The higher the voltage, the greater the energy for the electrons to leave. Analogy: Electric flow is similar to water flow. A waterfall, for example, provides a lot of energy when water flows down. We would say that it has a high voltage. - Be careful! If you use too muc ...
... - It is measured in Volts. - The higher the voltage, the greater the energy for the electrons to leave. Analogy: Electric flow is similar to water flow. A waterfall, for example, provides a lot of energy when water flows down. We would say that it has a high voltage. - Be careful! If you use too muc ...
The Power Diode
... (resistor R), the current flowing in the load resistor is therefore proportional to the voltage (Ohm´s Law), and the voltage across the load resistor is the same as the supply voltage, Vs (minus Vf), that is the "DC" voltage across the load is sinusoidal for the first half cycle only. Then Vout = V ...
... (resistor R), the current flowing in the load resistor is therefore proportional to the voltage (Ohm´s Law), and the voltage across the load resistor is the same as the supply voltage, Vs (minus Vf), that is the "DC" voltage across the load is sinusoidal for the first half cycle only. Then Vout = V ...
Basic Electronics
... • One watt of power is equal to the work done in one second by one volt moving one coulomb of charge. Since one coulomb a second is an ampere. • P=ExI • P = I2 x R • P = E2 / R ...
... • One watt of power is equal to the work done in one second by one volt moving one coulomb of charge. Since one coulomb a second is an ampere. • P=ExI • P = I2 x R • P = E2 / R ...
01 Rectifiers
... power to Straight line DC power. To do this we use a device called a Rectifier. Basically a rectifier can be as simple as 1 diode. As you know a diode will only pass current in one direction and that is when the Cathode is biased in a more negative condition compared to its Anode. ...
... power to Straight line DC power. To do this we use a device called a Rectifier. Basically a rectifier can be as simple as 1 diode. As you know a diode will only pass current in one direction and that is when the Cathode is biased in a more negative condition compared to its Anode. ...
Lec_18-Thyristors
... One of the most important type of power semiconductor device. Compared to transistors, thyristors have lower on-state conduction losses and higher power handling capability. However, they have worse switching performances than transistors. ...
... One of the most important type of power semiconductor device. Compared to transistors, thyristors have lower on-state conduction losses and higher power handling capability. However, they have worse switching performances than transistors. ...
Thyristors Introduction & Characteristics
... One of the most important type of power semiconductor device. Compared to transistors, thyristors have lower on-state conduction losses and higher power handling capability. However, they have worse switching performances than transistors. ...
... One of the most important type of power semiconductor device. Compared to transistors, thyristors have lower on-state conduction losses and higher power handling capability. However, they have worse switching performances than transistors. ...
Unit Plan: Ohm`s Law – Current, voltage and resistance
... not. I can then explain that the ratio of the voltage to the current is resistance. Some materials have constant resistances in a given range and others do not. This can lead into a discussion of Ohm’s Law and the difference between Ohmic and non-Ohmic materials. I would then discuss the change in r ...
... not. I can then explain that the ratio of the voltage to the current is resistance. Some materials have constant resistances in a given range and others do not. This can lead into a discussion of Ohm’s Law and the difference between Ohmic and non-Ohmic materials. I would then discuss the change in r ...
AC Current and Voltage
... current. • An a.c. current is so-called as it continuously changes size and direction. • A voltage that produces such a current is called an a.c. voltage. • When working with a.c. currents and voltages we often need to use a kind of average value. ...
... current. • An a.c. current is so-called as it continuously changes size and direction. • A voltage that produces such a current is called an a.c. voltage. • When working with a.c. currents and voltages we often need to use a kind of average value. ...
Engineering Review – Electric Circuits I
... This can be applied to a node to determine the current in a leg of the other legs are know, by summing the currents in and out of the node. ...
... This can be applied to a node to determine the current in a leg of the other legs are know, by summing the currents in and out of the node. ...
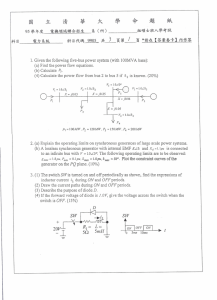
1. Given the following five-bus power system (with lOOMVA base): (b)
... The generator voltage VG is 13.2kV(1ine-teline), the transmission line impedance Zline = 10 jlOO R, and the load impedance Zlocrd= 300 R. Use the per-unit analysis technique, find the acutal values of the generator current, the transmission line current, the load current, and the load voltage. ...
... The generator voltage VG is 13.2kV(1ine-teline), the transmission line impedance Zline = 10 jlOO R, and the load impedance Zlocrd= 300 R. Use the per-unit analysis technique, find the acutal values of the generator current, the transmission line current, the load current, and the load voltage. ...
P–n diode

This article provides a more detailed explanation of p–n diode behavior than that found in the articles p–n junction or diode.A p–n diode is a type of semiconductor diode based upon the p–n junction. The diode conducts current in only one direction, and it is made by joining a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer. Semiconductor diodes have multiple uses including rectification of alternating current to direct current, detection of radio signals, emitting light and detecting light.