File
... A binary code represents text or computer processor instructions using the digits 0 and 1. A binary code assigns a bit string to each symbol or instruction. For example, a binary string of eight binary digits (bits) can represent any of 256 possible values and can therefore correspond to a variety ...
... A binary code represents text or computer processor instructions using the digits 0 and 1. A binary code assigns a bit string to each symbol or instruction. For example, a binary string of eight binary digits (bits) can represent any of 256 possible values and can therefore correspond to a variety ...
Alternating Current * Learning Outcomes
... While in direct current (d.c.), current always flows in the same direction (positive to negative), alternating current (a.c.) continuously changes directions. The current does not change direction abruptly – it is a gradual process of acceleration, fitting models of waves and SHM. Thus when we ...
... While in direct current (d.c.), current always flows in the same direction (positive to negative), alternating current (a.c.) continuously changes directions. The current does not change direction abruptly – it is a gradual process of acceleration, fitting models of waves and SHM. Thus when we ...
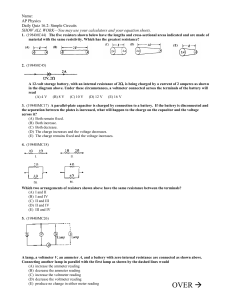
Quiz 16.2–AP–Simple Circuits w- multi battery loop
... A 12-volt storage battery, with an internal resistance of 2, is being charged by a current of 2 amperes as shown in the diagram above. Under these circumstances, a voltmeter connected across the terminals of the battery will read (A) 4 V (B) 8 V (C) 10 V (D) 12 V (E) 16 V 3. (1984BMC17) A parallel- ...
... A 12-volt storage battery, with an internal resistance of 2, is being charged by a current of 2 amperes as shown in the diagram above. Under these circumstances, a voltmeter connected across the terminals of the battery will read (A) 4 V (B) 8 V (C) 10 V (D) 12 V (E) 16 V 3. (1984BMC17) A parallel- ...
Final Exam_Summer 2013
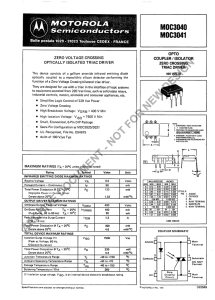
... =20 Ω, and IZK(Min) =0.2 mA. The line resistance used is 500 Ω. Calculate the following, with supporting circuit analysis. A circuit model for the diode is shown in Fig.2. (a) Draw the equivalent circuit for the whole system. (b) Calculate the line regulation and the amount of fluctuation of the out ...
... =20 Ω, and IZK(Min) =0.2 mA. The line resistance used is 500 Ω. Calculate the following, with supporting circuit analysis. A circuit model for the diode is shown in Fig.2. (a) Draw the equivalent circuit for the whole system. (b) Calculate the line regulation and the amount of fluctuation of the out ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... We also know that i3 = ½ of i2 = 1 mA. Using Ohm’s law, solve for the resistance values. R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given ...
... We also know that i3 = ½ of i2 = 1 mA. Using Ohm’s law, solve for the resistance values. R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given ...
EE302 Lesson 1: Introduction
... negative charges. These separated charges have potential energy. The voltage (or potential difference) between two points is defined as one volt if it requires one joule of energy to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another. W V Q ...
... negative charges. These separated charges have potential energy. The voltage (or potential difference) between two points is defined as one volt if it requires one joule of energy to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another. W V Q ...
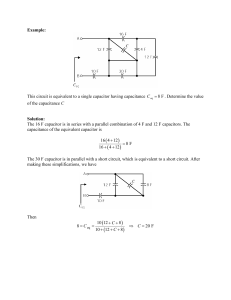
Example: This circuit is equivalent to a single capacitor having
... This circuit contains 7 capacitors each having capacitance C. The voltage source voltage is given by v ( t ) = 4 cos ( 3 t ) V Find the current i(t) when C = 1 F. ...
... This circuit contains 7 capacitors each having capacitance C. The voltage source voltage is given by v ( t ) = 4 cos ( 3 t ) V Find the current i(t) when C = 1 F. ...
INTERNETWORKING I
... the weakening of a data signal as it moves through the media. Signals lose energy as they move through the media due to resistance to the media itself. What is the definition of reflection in electrical signals? it is the result of impedance mismatch in electrical signals. When voltage hits a discon ...
... the weakening of a data signal as it moves through the media. Signals lose energy as they move through the media due to resistance to the media itself. What is the definition of reflection in electrical signals? it is the result of impedance mismatch in electrical signals. When voltage hits a discon ...
Here we`ll find the initial value of capacitor voltage - Rose
... Note that ic(0) is actually the opposite of the inductor current. So ic(0) = -20 mA. Substitute that and the capacitance into the equation for dvc(0) / dt. This says that the voltage’s initial rate of change is -10,000 V/s. This large number indicates a rapid rate of change. It’s not necessarily a “ ...
... Note that ic(0) is actually the opposite of the inductor current. So ic(0) = -20 mA. Substitute that and the capacitance into the equation for dvc(0) / dt. This says that the voltage’s initial rate of change is -10,000 V/s. This large number indicates a rapid rate of change. It’s not necessarily a “ ...
INTRODUCTION TO OHM`S LAW
... Changing the resistance in a circuit will also cause a change in current flow. if the voltage applied to a circuit is held constant, and the resistance in the circuit is increased. With more opposition to current flow in the circuit, the circuit current will decrease. On the other hand, if the resis ...
... Changing the resistance in a circuit will also cause a change in current flow. if the voltage applied to a circuit is held constant, and the resistance in the circuit is increased. With more opposition to current flow in the circuit, the circuit current will decrease. On the other hand, if the resis ...
Ferroresonance in Voltage Transformer (VT)
... During the oscillation, the current can drive the magnetizing force to saturate the VT. When the VT is saturated, the reactance to ground will diminish and the current to ground through the primary of the VT will go high. At the end of the sinusoid the VT will drop out of saturation, but with a low ...
... During the oscillation, the current can drive the magnetizing force to saturate the VT. When the VT is saturated, the reactance to ground will diminish and the current to ground through the primary of the VT will go high. At the end of the sinusoid the VT will drop out of saturation, but with a low ...
Systems Repair Worksheet
... 13. Diodes are popular in ________________ systems where they are used to rectify AC to DC. 14. ____________ diodes allow reverse polarity flow with out damage after their “threshold or zener voltage” is reached. They are used often in charging system voltage regulators. (14.2 zener voltage) 15. ___ ...
... 13. Diodes are popular in ________________ systems where they are used to rectify AC to DC. 14. ____________ diodes allow reverse polarity flow with out damage after their “threshold or zener voltage” is reached. They are used often in charging system voltage regulators. (14.2 zener voltage) 15. ___ ...
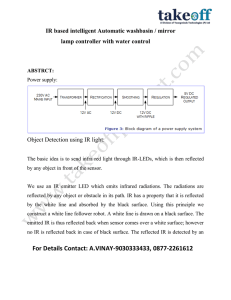
IR based intelligent Automatic washbasin / mirror lamp controller
... electron holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence and the color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy gap of the semiconductor. An LED is often small in area (less than 1 mm2), and integ ...
... electron holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence and the color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy gap of the semiconductor. An LED is often small in area (less than 1 mm2), and integ ...
Solid State Relais
... positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires although it is common practice to leave the neutral wire the way it is and switch the phase or hot wire. See diagram for 'LOAD'. As long as thereis no dc voltage present (left side of circuit diagram), the phototransistor within the TIL111 blocks an ...
... positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires although it is common practice to leave the neutral wire the way it is and switch the phase or hot wire. See diagram for 'LOAD'. As long as thereis no dc voltage present (left side of circuit diagram), the phototransistor within the TIL111 blocks an ...
Hall Effect Devices as Current Sensors
... Light (photons) and heat (phonons) increase minority current carriers in reverse biased semiconductors and thus increase conduction. Light and heat after all are just electromagnetic radiation at different frequencies. Hall Effect Devices are semiconductors that respond to magnetic fields at DC to 1 ...
... Light (photons) and heat (phonons) increase minority current carriers in reverse biased semiconductors and thus increase conduction. Light and heat after all are just electromagnetic radiation at different frequencies. Hall Effect Devices are semiconductors that respond to magnetic fields at DC to 1 ...
P–n diode

This article provides a more detailed explanation of p–n diode behavior than that found in the articles p–n junction or diode.A p–n diode is a type of semiconductor diode based upon the p–n junction. The diode conducts current in only one direction, and it is made by joining a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer. Semiconductor diodes have multiple uses including rectification of alternating current to direct current, detection of radio signals, emitting light and detecting light.