The Velocity of Light - Gravitational Relativity
... (1) Old Universe Deism in which God created the universe but natural law produced our present universe and life without the intervention of God (2) Old Universe evolutionary theism whereby God created the universe and then gave the universe and life order over long periods of time through the proces ...
... (1) Old Universe Deism in which God created the universe but natural law produced our present universe and life without the intervention of God (2) Old Universe evolutionary theism whereby God created the universe and then gave the universe and life order over long periods of time through the proces ...
Slide 1
... Not a big difference, but it is measurable. The actual experiment has been done with jets flying around the earth, and the predicted time dilation has been observed.1 As expected, the earth observer measures a bigger number for the time. The moving clock on the spacecraft measured a smaller number. ...
... Not a big difference, but it is measurable. The actual experiment has been done with jets flying around the earth, and the predicted time dilation has been observed.1 As expected, the earth observer measures a bigger number for the time. The moving clock on the spacecraft measured a smaller number. ...
relativity phys311
... Our (possibly inherited) lack of appreciation that the world of the very fast and the world of the very small may well be very different from the world we are used to makes modern physics difficult to comprehend, but Heisenberg showed the way, see above, we have to stick to the mathematical schemes ...
... Our (possibly inherited) lack of appreciation that the world of the very fast and the world of the very small may well be very different from the world we are used to makes modern physics difficult to comprehend, but Heisenberg showed the way, see above, we have to stick to the mathematical schemes ...
Fall 2003 Digression: on the constancy of c.
... Our thought experiment with the conductor and test charge suggests that a conductor which is electrically neutral in one reference frame might not be electrically neutral in another. How can we reconcile this with charge invariance? Our modern physics textbook author claims there is no problem, beca ...
... Our thought experiment with the conductor and test charge suggests that a conductor which is electrically neutral in one reference frame might not be electrically neutral in another. How can we reconcile this with charge invariance? Our modern physics textbook author claims there is no problem, beca ...
The Theory of Anti-Relativity, Chapter 1
... is only a proportionality factor, not a velocity. Finally, it has been disclosed by insiders within the space program, N.A.S.A., of a “certain complication”. It was found that when far outside the Earth’s field of influence the stars and sun are NOT VISIBLE! However, the Earth and the Moon are plain ...
... is only a proportionality factor, not a velocity. Finally, it has been disclosed by insiders within the space program, N.A.S.A., of a “certain complication”. It was found that when far outside the Earth’s field of influence the stars and sun are NOT VISIBLE! However, the Earth and the Moon are plain ...
Contents and Introduction
... 12.1.1 The dual field and invariants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.1.2 Motion of particles in a static uniform field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.1.3 Precession of the spin of a charged particle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.2 Electromagnetic energy ...
... 12.1.1 The dual field and invariants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.1.2 Motion of particles in a static uniform field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.1.3 Precession of the spin of a charged particle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 12.2 Electromagnetic energy ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter H1
... The observer moving along with the protons will measure an electric force F eE , where E is the electric field caused by one of the protons at the position of the other. The observer in the lab will measure an electric force Fe eE and a magnetic force Fm evB since the lab observer sees a mov ...
... The observer moving along with the protons will measure an electric force F eE , where E is the electric field caused by one of the protons at the position of the other. The observer in the lab will measure an electric force Fe eE and a magnetic force Fm evB since the lab observer sees a mov ...
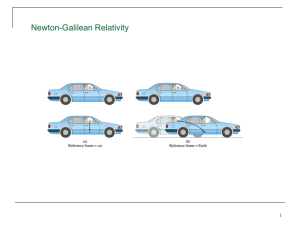
The Principle of Relativity Outline
... Particles of the same mass but different material, shapes, and sizes in the same location all fall towards Earth with the same acceleration! (Galileo) Allow us to define inertial reference frame – otherwise aluminum would behave differently than wood. Important property of nature. ...
... Particles of the same mass but different material, shapes, and sizes in the same location all fall towards Earth with the same acceleration! (Galileo) Allow us to define inertial reference frame – otherwise aluminum would behave differently than wood. Important property of nature. ...
RS2-107: Mass and Gravity - Reciprocal System of theory
... Step measure is the conventional method of measuring finite quantities, just like pacing off steps to measure distance. This is associated with the first unit of motion, speed, with the range2 of 0→1. Coordinate time can also be “step measured,” but unfortunately our mechanics and technology only al ...
... Step measure is the conventional method of measuring finite quantities, just like pacing off steps to measure distance. This is associated with the first unit of motion, speed, with the range2 of 0→1. Coordinate time can also be “step measured,” but unfortunately our mechanics and technology only al ...
Relativistic Effects - The Physics of Bruce Harvey
... Mass is responsible for slowing the universe down. Without it, all the electric forces between electrons and protons would cause everything to rush together with infinite acceleration and the universe would end in a big bang as soon as it was created. This means that every single process in nature i ...
... Mass is responsible for slowing the universe down. Without it, all the electric forces between electrons and protons would cause everything to rush together with infinite acceleration and the universe would end in a big bang as soon as it was created. This means that every single process in nature i ...
Learning material
... This is a very subtle statement that captures virtually all of relativity. It says three things: first that there are such coordinates x and t in which the proper time takes this form. Such coordinates are called Minkowski coordinates and this expression for proper time is referred ...
... This is a very subtle statement that captures virtually all of relativity. It says three things: first that there are such coordinates x and t in which the proper time takes this form. Such coordinates are called Minkowski coordinates and this expression for proper time is referred ...
Special Relativity
... • At relativistic speeds, (v some appreciable fraction of c), time dilation is significant. ...
... • At relativistic speeds, (v some appreciable fraction of c), time dilation is significant. ...
Short answers Short Problems
... 5. When Uranium-235 is hit by a neutron, it becomes Uranium-236 for a very short period. U-236 has a very short half-life and decays into Barium and Krypton (Ba-141 and Kr-92) while releasing 3 neutrons, which means that we could have up to 3 more U-235 atoms hit resulting in 9 more projectile neutr ...
... 5. When Uranium-235 is hit by a neutron, it becomes Uranium-236 for a very short period. U-236 has a very short half-life and decays into Barium and Krypton (Ba-141 and Kr-92) while releasing 3 neutrons, which means that we could have up to 3 more U-235 atoms hit resulting in 9 more projectile neutr ...
TIME ASYMMETRY IN ELECTRODYNAMICS AND COSMOLOGY
... of time are strongly related. A new feature into this argument was introduced by Hogarth4 many years later. He pointed out that the above argument ignores the cosmological time arrow. In an expanding universe the past and future light cones do not behave symmetrically where absorption is concerned. ...
... of time are strongly related. A new feature into this argument was introduced by Hogarth4 many years later. He pointed out that the above argument ignores the cosmological time arrow. In an expanding universe the past and future light cones do not behave symmetrically where absorption is concerned. ...
Standard Weights and Measures
... As mentioned in the text, the oldest clocks in the world are sundials. Many designs for sundials exist. They have evolved from simple designs of flat horizontal or vertical plates to more elaborate forms, which compensate for the motion of the sun in the sky during the course of the year. For exampl ...
... As mentioned in the text, the oldest clocks in the world are sundials. Many designs for sundials exist. They have evolved from simple designs of flat horizontal or vertical plates to more elaborate forms, which compensate for the motion of the sun in the sky during the course of the year. For exampl ...
Example Midterm Solutions
... The proper frame for the lifetime of the Mamahuhu particle is in the Mamahuhu’s frame. This is because we would measure the “birth” and decay (into something else) of the particle as events that happen at the same spot in that frame. In the Mamahuhu’s frame, the lifetime is 1.8×10−4 s . In a lab fra ...
... The proper frame for the lifetime of the Mamahuhu particle is in the Mamahuhu’s frame. This is because we would measure the “birth” and decay (into something else) of the particle as events that happen at the same spot in that frame. In the Mamahuhu’s frame, the lifetime is 1.8×10−4 s . In a lab fra ...
The Age of Einstein
... believe that a strong case will be made for the phrase “the Age of Einstein”; no other person in the 20th-century advanced our understanding of the physical universe in such a dramatic way. He introduced many original concepts, each one of a profound nature. His discovery of the universal equivalenc ...
... believe that a strong case will be made for the phrase “the Age of Einstein”; no other person in the 20th-century advanced our understanding of the physical universe in such a dramatic way. He introduced many original concepts, each one of a profound nature. His discovery of the universal equivalenc ...
Precise Measurement of Time
... life, it was subject to marked periodicities: the change from day to night and the change in seasons. These periodicities had a profound effect on the evolution of biological organisms; most animals have a circadian rhythm which leads them to need sleep at approximately 24-hour interval even if they ...
... life, it was subject to marked periodicities: the change from day to night and the change in seasons. These periodicities had a profound effect on the evolution of biological organisms; most animals have a circadian rhythm which leads them to need sleep at approximately 24-hour interval even if they ...
special relativity via electro-magnetic clocks
... We have derived the special relativistic effects of length contraction, time dilation, and mass increase quite simply from Heaviside's equation of classical electromagnetism. Since the standard derivation of Heaviside's equation involves retarded potentials, our analysis implies that the relativisti ...
... We have derived the special relativistic effects of length contraction, time dilation, and mass increase quite simply from Heaviside's equation of classical electromagnetism. Since the standard derivation of Heaviside's equation involves retarded potentials, our analysis implies that the relativisti ...
c - Telkom University
... Frank’s clock is at the same position in system K when the sparkler is lit in (a) and when it goes out in (b). Mary, in the moving system K’, is beside the sparkler at (a). Melinda then moves into the position where and when the sparkler extinguishes at (b). Thus, Melinda, at the new position, measu ...
... Frank’s clock is at the same position in system K when the sparkler is lit in (a) and when it goes out in (b). Mary, in the moving system K’, is beside the sparkler at (a). Melinda then moves into the position where and when the sparkler extinguishes at (b). Thus, Melinda, at the new position, measu ...
Special Relativity
... Imagine that in the frame S we have a clock beating in one second intervals. The clock is stationary in S (i.e. the time interval in S is T=t1-t2, for x2=x1=x). For an observer in S' (in motion with respect to S) the time interval of the clock in S is given by the Lorentz Transformation. t'1=(t1-(v. ...
... Imagine that in the frame S we have a clock beating in one second intervals. The clock is stationary in S (i.e. the time interval in S is T=t1-t2, for x2=x1=x). For an observer in S' (in motion with respect to S) the time interval of the clock in S is given by the Lorentz Transformation. t'1=(t1-(v. ...
CHAPTER 2: Special Theory of Relativity
... Frank’s clock is at the same position in system K when the sparkler is lit in (a) and when it goes out in (b). Mary, in the moving system K’, is beside the sparkler at (a). Melinda then moves into the position where and when the sparkler extinguishes at (b). Thus, Melinda, at the new position, measu ...
... Frank’s clock is at the same position in system K when the sparkler is lit in (a) and when it goes out in (b). Mary, in the moving system K’, is beside the sparkler at (a). Melinda then moves into the position where and when the sparkler extinguishes at (b). Thus, Melinda, at the new position, measu ...
The Einstein – Lorentz Dispute Revisited
... transformations and their consequent "contractions" resolved the "aether" problems. The Lorentz transforms and the Lorentz contractions are familiar to all physicists and are fundamental to the Theory of Relativity. In the early 1900's Einstein took the further step of denying that any "aether" or m ...
... transformations and their consequent "contractions" resolved the "aether" problems. The Lorentz transforms and the Lorentz contractions are familiar to all physicists and are fundamental to the Theory of Relativity. In the early 1900's Einstein took the further step of denying that any "aether" or m ...
The principle of constancy of the speed of Light in free-space
... Recently theory of „time varying speed of light‟ has been proposed independently by Moffat [1] and Albrecht and Magueijo [2] as an alternative of Inflationary Cosmological model. Several other authors also advocate for such hypothesis from different grounds [3-4 and references therein] . Such a radi ...
... Recently theory of „time varying speed of light‟ has been proposed independently by Moffat [1] and Albrecht and Magueijo [2] as an alternative of Inflationary Cosmological model. Several other authors also advocate for such hypothesis from different grounds [3-4 and references therein] . Such a radi ...
Time

Time is a measure in which events can be ordered from the past through the present into the future, and also the measure of durations of events and the intervals between them. Time is often referred to as the fourth dimension, along with the three spatial dimensions.Time has long been a major subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars.Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems.Some simple definitions of time include ""time is what clocks measure"", which is a problematically vague and self-referential definition that utilizes the device used to measure the subject as the definition of the subject, and ""time is what keeps everything from happening at once"", which is without substantive meaning in the absence of the definition of simultaneity in the context of the limitations of human sensation, observation of events, and the perception of such events.Two contrasting viewpoints on time divide many prominent philosophers.One view is that time is part of the fundamental structure of the universe—a dimension independent of events, in which events occur in sequence.Sir Isaac Newton subscribed to this realist view, and hence it is sometimes referred to as Newtonian time.The opposing view is that time does not refer to any kind of ""container"" that events and objects ""move through"", nor to any entity that ""flows"", but that it is instead part of a fundamental intellectual structure (together with space and number) within which humans sequence and compare events. This second view, in the tradition of Gottfried Leibnizand Immanuel Kant,holds that time is neither an event nor a thing, and thus is not itself measurable nor can it be travelled.Time is one of the seven fundamental physical quantities in both the International System of Units and International System of Quantities. Time is used to define other quantities—such as velocity—so defining time in terms of such quantities would result in circularity of definition.An operational definition of time, wherein one says that observing a certain number of repetitions of one or another standard cyclical event (such as the passage of a free-swinging pendulum) constitutes one standard unit such as the second, is highly useful in the conduct of both advanced experiments and everyday affairs of life. The operational definition leaves aside the question whether there is something called time, apart from the counting activity just mentioned, that flows and that can be measured. Investigations of a single continuum called spacetime bring questions about space into questions about time, questions that have their roots in the works of early students of natural philosophy.Furthermore, it may be that there is a subjective component to time, but whether or not time itself is ""felt"", as a sensation, or is a judgment, is a matter of debate.Temporal measurement has occupied scientists and technologists, and was a prime motivation in navigation and astronomy. Periodic events and periodic motion have long served as standards for units of time. Examples include the apparent motion of the sun across the sky, the phases of the moon, the swing of a pendulum, and the beat of a heart. Currently, the international unit of time, the second, is defined by measuring the electronic transition frequency of caesium atoms (see below). Time is also of significant social importance, having economic value (""time is money"") as well as personal value, due to an awareness of the limited time in each day and in human life spans.