Ground Nonmonotonic Modal Logics - Dipartimento di Informatica e
... Recently, there have been a number of attempts to reconcile fix-point and semantic characterizations of modal nonmonotonic logics. In particular, Schwarz [30] proposed a semantics for McDermott and Doyle’s logics. However, the notion of minimal knowledge underlying the above cited works is stronger ...
... Recently, there have been a number of attempts to reconcile fix-point and semantic characterizations of modal nonmonotonic logics. In particular, Schwarz [30] proposed a semantics for McDermott and Doyle’s logics. However, the notion of minimal knowledge underlying the above cited works is stronger ...
memorandum - Hindu American Foundation
... Page 152, “The Vedas”: current text, “The oldest of the Vedas, the Rigveda, was probably written before 1000 BC.” Replace with, “The oldest of the Vedas, the Rigveda, was redacted in the form it is known to this day by 1500 BC.” ...
... Page 152, “The Vedas”: current text, “The oldest of the Vedas, the Rigveda, was probably written before 1000 BC.” Replace with, “The oldest of the Vedas, the Rigveda, was redacted in the form it is known to this day by 1500 BC.” ...
A Qualitative Theory of Dynamic Interactive Belief Revision
... We develop here a notion of doxastic actions 1 , general enough to cover most examples of multi-agent communication actions encountered in the literature, but also flexible enough to deal with (both static and dynamic) belief revision, and in particular to implement various “belief-revision policies ...
... We develop here a notion of doxastic actions 1 , general enough to cover most examples of multi-agent communication actions encountered in the literature, but also flexible enough to deal with (both static and dynamic) belief revision, and in particular to implement various “belief-revision policies ...
Reasoning about Complex Actions with Incomplete Knowledge: A
... language for reasoning about actions presented in [6]. Such language mainly focuses on ramification problem but does not provide a formalization of incomplete initial states with an explicit representation of undefined fluents. Such an explicit representation is needed if we want to model an agent wh ...
... language for reasoning about actions presented in [6]. Such language mainly focuses on ramification problem but does not provide a formalization of incomplete initial states with an explicit representation of undefined fluents. Such an explicit representation is needed if we want to model an agent wh ...
Foundations for Knowledge
... quantifying-in (“knowing what”), which cannot be expressed in Reiter’s approach. There are at least two reasons for this: for one, tests for Reiter are situation-suppressed formulas and hence cannot refer to future situations; for another, in order to make inferences about what the agent does not kn ...
... quantifying-in (“knowing what”), which cannot be expressed in Reiter’s approach. There are at least two reasons for this: for one, tests for Reiter are situation-suppressed formulas and hence cannot refer to future situations; for another, in order to make inferences about what the agent does not kn ...
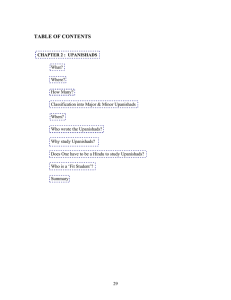
TABLE OF CONTENTS - rnarayanaswami.net
... The answer to both these questions is a loud and clear ‘no’. Firstly, Upanishads are part of Vedas which describe the Sanatana Dharma (the Eternal and Everlasting Fair-minded, Proper and Right way of living). Sanatana Dharma was practiced by inhabitants of the Indus Valley which was later on called ...
... The answer to both these questions is a loud and clear ‘no’. Firstly, Upanishads are part of Vedas which describe the Sanatana Dharma (the Eternal and Everlasting Fair-minded, Proper and Right way of living). Sanatana Dharma was practiced by inhabitants of the Indus Valley which was later on called ...
The Lotus Sutra: A Contemporary Translation of a Buddhist Classic
... think that part of what discouraged me initially was the poor choice of terms in the translation I had read. Nearly a decade later I decided to move to Japan to study the Lotus Sutra and improve my skills in Japanese and Chinese languages. I was encouraged both by Nikkyo Niwano, the founder and then ...
... think that part of what discouraged me initially was the poor choice of terms in the translation I had read. Nearly a decade later I decided to move to Japan to study the Lotus Sutra and improve my skills in Japanese and Chinese languages. I was encouraged both by Nikkyo Niwano, the founder and then ...
relevant reasoning as the logical basis of
... extensional notion of material implication (denoted by → in this paper) which is defined as A→B =df ¬(A∧¬B) or A→B =df ¬A∨B. However, the material implication is just a truth-function of its antecedent and consequent but not requires that there must exist a necessarily relevant and/or conditional re ...
... extensional notion of material implication (denoted by → in this paper) which is defined as A→B =df ¬(A∧¬B) or A→B =df ¬A∨B. However, the material implication is just a truth-function of its antecedent and consequent but not requires that there must exist a necessarily relevant and/or conditional re ...
Introduction to first order logic for knowledge representation
... the following characteristics: The alphabet of a logical languages typically contains basic symbols that are used to indicate the basic (atomic) components of the (part of the) world the logic is supposed to describe. The alphabet is composed of two subsets: the logical symbols and the non logical s ...
... the following characteristics: The alphabet of a logical languages typically contains basic symbols that are used to indicate the basic (atomic) components of the (part of the) world the logic is supposed to describe. The alphabet is composed of two subsets: the logical symbols and the non logical s ...
Towards an Epistemic Logic of Grounded Belief
... an ideal agent cannot posses knowledge of falsity. For any situation it seems strange to say that one may know a falsehood in that situation. The principle that in any situation if one knows some proposition φ, then φ is true goes back to at least Plato (1999a) and possibly Parmenides. However, some ...
... an ideal agent cannot posses knowledge of falsity. For any situation it seems strange to say that one may know a falsehood in that situation. The principle that in any situation if one knows some proposition φ, then φ is true goes back to at least Plato (1999a) and possibly Parmenides. However, some ...
Vedanta
... Traditional Vedānta considers scriptural evidence, or shabda pramāna, as the most authentic means of knowledge, while perception, or pratyaksa, and logical inference, or anumana, are considered to be subordinate (but valid).[40][41] Vedanta rejects ritual in favor of renunciation, which makes Vedant ...
... Traditional Vedānta considers scriptural evidence, or shabda pramāna, as the most authentic means of knowledge, while perception, or pratyaksa, and logical inference, or anumana, are considered to be subordinate (but valid).[40][41] Vedanta rejects ritual in favor of renunciation, which makes Vedant ...
7 LOGICAL AGENTS
... The central component of a knowledge-based agent is its knowledge base, or KB. A knowledge base is a set of sentences. (Here “sentence” is used as a technical term. It is related but not identical to the sentences of English and other natural languages.) Each sentence is expressed in a language call ...
... The central component of a knowledge-based agent is its knowledge base, or KB. A knowledge base is a set of sentences. (Here “sentence” is used as a technical term. It is related but not identical to the sentences of English and other natural languages.) Each sentence is expressed in a language call ...
pdf
... he also allows for different subjective domains at each world. He goes further by using what is called neighborhood semantics, also called Montague-Scott structures (Fagin et al., 1995). As is well known, neighborhood semantics provide a more general approach for modeling knowledge than the standar ...
... he also allows for different subjective domains at each world. He goes further by using what is called neighborhood semantics, also called Montague-Scott structures (Fagin et al., 1995). As is well known, neighborhood semantics provide a more general approach for modeling knowledge than the standar ...
On Linear Inference
... what do we mean? To discuss this, some terminology: we say “even(t)” is a proposition and “even(t) true” is a judgment. Following Martin-Löf, a judgment is an object of knowledge. We obtain knowledge by making inferences from judgments we already know. We can then read the rule above as If we know ...
... what do we mean? To discuss this, some terminology: we say “even(t)” is a proposition and “even(t) true” is a judgment. Following Martin-Löf, a judgment is an object of knowledge. We obtain knowledge by making inferences from judgments we already know. We can then read the rule above as If we know ...
Intro - Hymns and Chants
... a later date.[52][53] The Vedas each have an Index or Anukramani, the principal work of this kind being the general Index or Sarvānukramaṇī.[54][55] Prodigous energy was expended by ancient Indian culture in ensuring that these texts were transmitted from generation to generation with inordinate fide ...
... a later date.[52][53] The Vedas each have an Index or Anukramani, the principal work of this kind being the general Index or Sarvānukramaṇī.[54][55] Prodigous energy was expended by ancient Indian culture in ensuring that these texts were transmitted from generation to generation with inordinate fide ...
Default Reasoning in a Terminological Logic
... The field of TLs has lately been an active area of research, with the attention of researchers especially focusing on the investigation of their logical and computational properties. Nevertheless, few researchers have addressed the problem of extending these logics with the ability to perform defaul ...
... The field of TLs has lately been an active area of research, with the attention of researchers especially focusing on the investigation of their logical and computational properties. Nevertheless, few researchers have addressed the problem of extending these logics with the ability to perform defaul ...
A Nonstandard Approach to the. Logical Omniscience Problem
... What about logical omniscience? Notice that notions like "validity" and "logical consequence" (which played a prominent part in our informal description of logical omniscience) are not absolute notions; their formal definitions depend on how truth is defined and on the class of worlds being consider ...
... What about logical omniscience? Notice that notions like "validity" and "logical consequence" (which played a prominent part in our informal description of logical omniscience) are not absolute notions; their formal definitions depend on how truth is defined and on the class of worlds being consider ...
The pursuit of happiness: An Advaita Vedanta perspective (PDF
... According to Sivananda (1999), Sutras gave the essence of the arguments on a topic condensing maximum of thoughts into these aphorisms in as few words as possible. “Great intellectual people only, can compose Sutras. They are clues or aids to memory. They cannot be understood without a lucid comment ...
... According to Sivananda (1999), Sutras gave the essence of the arguments on a topic condensing maximum of thoughts into these aphorisms in as few words as possible. “Great intellectual people only, can compose Sutras. They are clues or aids to memory. They cannot be understood without a lucid comment ...
a,b,c
... don’t know all that was going on: they only have a partial view of the situation. Example: poker (in contrast to chess). A player may be uncertain about the real situation of the game at a given time: e.g. they simply cannot distinguish between a situation in which another player has a winning hand ...
... don’t know all that was going on: they only have a partial view of the situation. Example: poker (in contrast to chess). A player may be uncertain about the real situation of the game at a given time: e.g. they simply cannot distinguish between a situation in which another player has a winning hand ...
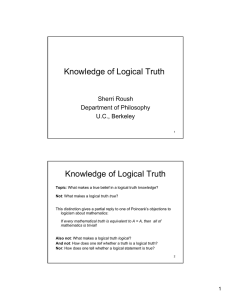
Knowledge of Logical Truth Knowledge of Logical Truth
... Suppose we have a monotonic logic in which this account of knowledge of logical truth is available. Why should we think this is the best account of knowledge of that kind of logical truth? The logical truths do have this property, so in being responsive to this property you are being responsive to s ...
... Suppose we have a monotonic logic in which this account of knowledge of logical truth is available. Why should we think this is the best account of knowledge of that kind of logical truth? The logical truths do have this property, so in being responsive to this property you are being responsive to s ...
Lecture - 04 (Logic Knowledge Base)
... called premises and another proposition called the conclusion. • Proof is intended to show deductively that an argument is sound (or valid). – An argument is sound iff it cannot be the case that its premises are true and its conclusion is false. ...
... called premises and another proposition called the conclusion. • Proof is intended to show deductively that an argument is sound (or valid). – An argument is sound iff it cannot be the case that its premises are true and its conclusion is false. ...
Three Solutions to the Knower Paradox
... Having presented the first point common to the three solutions, let us now pass to introduce the second one. Such point relates to the notion of knowledge. Indeed each of the three solutions to the Knower Paradox treats knowledge as if it were intimately connected with the notion of proof. They thus ...
... Having presented the first point common to the three solutions, let us now pass to introduce the second one. Such point relates to the notion of knowledge. Indeed each of the three solutions to the Knower Paradox treats knowledge as if it were intimately connected with the notion of proof. They thus ...
Grades K-5 Essential Elements without Illinois Learning Standards
... EE.SL.2.1.a Engage in multiple-turn exchanges with peers with support from an adult. EE.SL.2.1.b Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. EE.SL.2.1.c Ask for clarification and further explanation as needed about the topics and texts under discussion. ...
... EE.SL.2.1.a Engage in multiple-turn exchanges with peers with support from an adult. EE.SL.2.1.b Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. EE.SL.2.1.c Ask for clarification and further explanation as needed about the topics and texts under discussion. ...