Query Optimization
... • An interesting sort order is a particular sort order of tuples that could be useful for a later operation. – Generating the result of r1 r2 r3 sorted on the attributes common with r4 or r5 may be useful, but generating it sorted on the attributes common only r1 and r2 is not useful. – Using merge- ...
... • An interesting sort order is a particular sort order of tuples that could be useful for a later operation. – Generating the result of r1 r2 r3 sorted on the attributes common with r4 or r5 may be useful, but generating it sorted on the attributes common only r1 and r2 is not useful. – Using merge- ...
The Definitive Guide to SQLite
... Together the two can help with a wide variety of tasks, such as aggregating log file data, monitoring disk quotas, or performing bandwidth accounting in stateful firewalls. Furthermore, since SQLite databases are ordinary operating system files, they are easy to work with, transport, and back up. Al ...
... Together the two can help with a wide variety of tasks, such as aggregating log file data, monitoring disk quotas, or performing bandwidth accounting in stateful firewalls. Furthermore, since SQLite databases are ordinary operating system files, they are easy to work with, transport, and back up. Al ...
Coupling Logic Programming with Relational Databases
... are returned as a solution. Relational databases can also be considered as a simpler First Order Logic model [23]. The axiomatic knowledge is now only represented extensionally in the form of database relations and the theorems to be proved correspond to (SQL) queries. There are two main differences ...
... are returned as a solution. Relational databases can also be considered as a simpler First Order Logic model [23]. The axiomatic knowledge is now only represented extensionally in the form of database relations and the theorems to be proved correspond to (SQL) queries. There are two main differences ...
Vulnerability Manager for Databases 5.1.0 Product Guide
... You define the checks that are included in a scan, and which databases or database groups to run the scans on. Scans can be scheduled to run at set intervals or they can be run on demand anytime. The credentials required to connect to the database for scanning are configured in the McAfee ePO consol ...
... You define the checks that are included in a scan, and which databases or database groups to run the scans on. Scans can be scheduled to run at set intervals or they can be run on demand anytime. The credentials required to connect to the database for scanning are configured in the McAfee ePO consol ...
CIM Database Model White Paper CIM Version 2.10 Abstract
... DMTF is a not-for-profit association of industry members dedicated to promoting enterprise and systems management and interoperability. Members and non-members may reproduce DMTF specifications and documents for uses consistent with this purpose, provided that correct attribution is given. As DMTF s ...
... DMTF is a not-for-profit association of industry members dedicated to promoting enterprise and systems management and interoperability. Members and non-members may reproduce DMTF specifications and documents for uses consistent with this purpose, provided that correct attribution is given. As DMTF s ...
Oracle Database 11g New Features
... Upgrades supported Can be a bit tedious and requires a number of manual steps. Recommend you use a checklist! More overall control over the upgrade process. Most steps can be re-executed if they fail once you have corrected the cause of the failure. ...
... Upgrades supported Can be a bit tedious and requires a number of manual steps. Recommend you use a checklist! More overall control over the upgrade process. Most steps can be re-executed if they fail once you have corrected the cause of the failure. ...
3. Temporal Specialization and Generalization
... i.e., how to use time-stamp values and stored attribute values to derive the value of a time-varying attribute. For example, we will not address the issues of how to derive the temperature of a chemical reaction at an arbitrary point in time from time-stamped and stored temperature measurements. We ...
... i.e., how to use time-stamp values and stored attribute values to derive the value of a time-varying attribute. For example, we will not address the issues of how to derive the temperature of a chemical reaction at an arbitrary point in time from time-stamped and stored temperature measurements. We ...
Not For Sale
... A filter is a set of criteria you place on the records in an open form or datasheet to isolate a subset of the records temporarily. A filter is similar to a query, but it applies only to the open form or datasheet. If you want to use a filter at another time, you can save the filter as a query. Four ...
... A filter is a set of criteria you place on the records in an open form or datasheet to isolate a subset of the records temporarily. A filter is similar to a query, but it applies only to the open form or datasheet. If you want to use a filter at another time, you can save the filter as a query. Four ...
Upgrade from Oracle9i to Oracle Database 11g
... attempt was made to upgrade directly to Oracle Database 11g, then the database has to be opened in STARTUP UPGRADE mode in the new environment with an increased COMPATIBLE setting (COMPATIBLE has to be set to at least 10.0.0 or higher). At this point an upgrade will fail because of the missing time ...
... attempt was made to upgrade directly to Oracle Database 11g, then the database has to be opened in STARTUP UPGRADE mode in the new environment with an increased COMPATIBLE setting (COMPATIBLE has to be set to at least 10.0.0 or higher). At this point an upgrade will fail because of the missing time ...
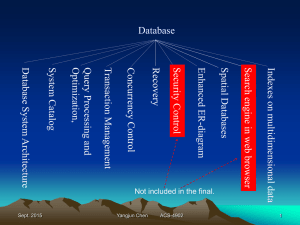
Database Processing
... The Oracle Express Edition was introduced with Oracle Database 10g, and it remains based on that version. The Oracle Express Edition, like the SQL Server Express Editions, seems to be designed to compete with MySQL (see Chapter 10B). MySQL, although not having as many features as Oracle Database 11g ...
... The Oracle Express Edition was introduced with Oracle Database 10g, and it remains based on that version. The Oracle Express Edition, like the SQL Server Express Editions, seems to be designed to compete with MySQL (see Chapter 10B). MySQL, although not having as many features as Oracle Database 11g ...
Document
... interaction with programming language compiler, global query optimization, structuring of complex objects from the data in the buffers, ... ...
... interaction with programming language compiler, global query optimization, structuring of complex objects from the data in the buffers, ... ...
Database Planning Workbook
... Disclaimer and Copyright This is the “Version 1” of the “Database Guide”. We are providing this guide in the hope that your organization will use it, test it and provide us feedback on how useful it is to them in their database planning process. Based on that feedback we will update this guide and ...
... Disclaimer and Copyright This is the “Version 1” of the “Database Guide”. We are providing this guide in the hope that your organization will use it, test it and provide us feedback on how useful it is to them in their database planning process. Based on that feedback we will update this guide and ...
Document
... Example: {customer-name} is a candidate key for Customer, since it is a superkey (assuming no two customers can possibly have the same name), and no subset of it is a superkey. ...
... Example: {customer-name} is a candidate key for Customer, since it is a superkey (assuming no two customers can possibly have the same name), and no subset of it is a superkey. ...
What is data? Databases - Introduction
... A DBMS can implement a number of storage strategies and optimizations to make the most common operations as fast as possible. In particular, the DBMS can maintain various indexes to the data to make querying the database quick; the user can control which indexes are present, but need not know how th ...
... A DBMS can implement a number of storage strategies and optimizations to make the most common operations as fast as possible. In particular, the DBMS can maintain various indexes to the data to make querying the database quick; the user can control which indexes are present, but need not know how th ...
Upgrade your Complex DB2 Environment
... Many companies today have a critical need for the updated versions of DB2 UDB 8.1 ESE and AIX 5.2L that will allow better performance and scalability for mission critical business applications. In addition with the new release of DB2 UDB for AIX, database self- managing SMART initiatives and self- ...
... Many companies today have a critical need for the updated versions of DB2 UDB 8.1 ESE and AIX 5.2L that will allow better performance and scalability for mission critical business applications. In addition with the new release of DB2 UDB for AIX, database self- managing SMART initiatives and self- ...
END
... Two or more DML statements as a set of activities can act as autonomously but can be controlled as groups using DCL commands; and these are known as transactions, not autonomous transactions: ...
... Two or more DML statements as a set of activities can act as autonomously but can be controlled as groups using DCL commands; and these are known as transactions, not autonomous transactions: ...
ppt
... How would we know to split up (decompose) it into borrower and loan? Write a rule “if there were a schema (loan_number, amount), then loan_number would be a candidate key” Denote as a functional dependency: loan_number amount In bor_loan, because loan_number is not a candidate key, the amoun ...
... How would we know to split up (decompose) it into borrower and loan? Write a rule “if there were a schema (loan_number, amount), then loan_number would be a candidate key” Denote as a functional dependency: loan_number amount In bor_loan, because loan_number is not a candidate key, the amoun ...
Database Management System
... Not only did the relational model ease the burden of application developers, but it also caused a paradigm shift in the data management industry. The separation between what and how data is retrieved provided an architecture by which the new database vendors could improve and innovate their products ...
... Not only did the relational model ease the burden of application developers, but it also caused a paradigm shift in the data management industry. The separation between what and how data is retrieved provided an architecture by which the new database vendors could improve and innovate their products ...
Chapter 7: Relational Database Design
... sometimes called a partial dependency. In this case, we store (X,A) pairs redundantly. X is not a proper subset of any key. Such a dependency is sometimes called a transitive dependency, because it means we have a chain of dependencies K XA. ...
... sometimes called a partial dependency. In this case, we store (X,A) pairs redundantly. X is not a proper subset of any key. Such a dependency is sometimes called a transitive dependency, because it means we have a chain of dependencies K XA. ...
Understanding the BarTender System Database
... Template designs and preview images (for reprinting items) ...
... Template designs and preview images (for reprinting items) ...
P6 EPPM Database Administration Guide
... Description: The administrative user owns most database objects within the schema including tables, indexes and constraints, procedures, triggers, and functions, and is primarily used during database creation and upgrades. Privileged User Default: PRIVUSER Description: The following is true for the ...
... Description: The administrative user owns most database objects within the schema including tables, indexes and constraints, procedures, triggers, and functions, and is primarily used during database creation and upgrades. Privileged User Default: PRIVUSER Description: The following is true for the ...
(A) R
... for each functional dependency f in F+ apply reflexivity and augmentation rules on f add the resulting functional dependencies to F+ for each pair of functional dependencies f1and f2 in F+ if f1 and f2 can be combined using transitivity then add the resulting functional dependency to F+ until F+ doe ...
... for each functional dependency f in F+ apply reflexivity and augmentation rules on f add the resulting functional dependencies to F+ for each pair of functional dependencies f1and f2 in F+ if f1 and f2 can be combined using transitivity then add the resulting functional dependency to F+ until F+ doe ...
Graph Databases
... Graph databases address one of the great macroscopic business trends of today: lever‐ aging complex and dynamic relationships in highly connected data to generate insight and competitive advantage. Whether we want to understand relationships between customers, elements in a telephone or data center ...
... Graph databases address one of the great macroscopic business trends of today: lever‐ aging complex and dynamic relationships in highly connected data to generate insight and competitive advantage. Whether we want to understand relationships between customers, elements in a telephone or data center ...
An Introduction to the Source Code of the Pyrrho DBMS
... computers, even mobile phones, but can also scale up to large enterprise uses. It assumes the .NET framework. For large databases it needs a lot of main memory (RAM). For best results the computer main memory should be about twice the size of the database. Pyrrho is designed for business uses. It is ...
... computers, even mobile phones, but can also scale up to large enterprise uses. It assumes the .NET framework. For large databases it needs a lot of main memory (RAM). For best results the computer main memory should be about twice the size of the database. Pyrrho is designed for business uses. It is ...