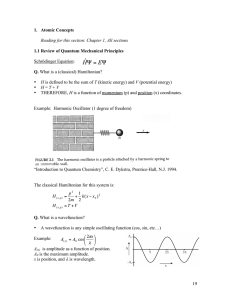
Wave
... will behave. The probability can be obtained from the intensity of the wave packet. – Accurate results can be obtained after repeating the same experiment with many particles and averaging. ...
... will behave. The probability can be obtained from the intensity of the wave packet. – Accurate results can be obtained after repeating the same experiment with many particles and averaging. ...
Coherence versus decoherence – a few illustrative examples
... yield an electric current, the latter generates a magnetic moment opposing the direction of the field, in accordance with the Faraday–Lenz law. A many-body system of such electrons is therefore expected to lead to a macroscopic moment and hence, a susceptibility which, for diamagnetism, has a negati ...
... yield an electric current, the latter generates a magnetic moment opposing the direction of the field, in accordance with the Faraday–Lenz law. A many-body system of such electrons is therefore expected to lead to a macroscopic moment and hence, a susceptibility which, for diamagnetism, has a negati ...
From Billiard Balls to Quantum Computing: Geoff Sharman
... the ultimate “virtual reality” machine, that could not be distinguished from the real world ...
... the ultimate “virtual reality” machine, that could not be distinguished from the real world ...
The unbreakable code: Is this the lock?
... free-space quantum key distribution between buildings on the NUS campus. These and many other exciting experiments are now carried out at the Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT), which is the first Research Centre of Excellence here, funded jointly by the National Research Foundation and Ministry ...
... free-space quantum key distribution between buildings on the NUS campus. These and many other exciting experiments are now carried out at the Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT), which is the first Research Centre of Excellence here, funded jointly by the National Research Foundation and Ministry ...
PHY140Y 32 The Pauli Exclusion Principle
... with a proton. However, the behaviour of multi-electron systems was quite enigmatic. What was observed was that multi-electron atoms seemed to have periodic properties. As you added electrons to the atom, one found that the electrons appeared to occupy increasingly higher-energy “shells,” with two e ...
... with a proton. However, the behaviour of multi-electron systems was quite enigmatic. What was observed was that multi-electron atoms seemed to have periodic properties. As you added electrons to the atom, one found that the electrons appeared to occupy increasingly higher-energy “shells,” with two e ...
The statistical interpretation of quantum mechanics
... force-free motion, to the case where the effect of force is taken into account, and gave an exact formulation of the subsidiary conditions, already suggested by De Broglie, to which the wave function ψ must be subjected, namely that it should be single-valued and finite in space and time. And he was ...
... force-free motion, to the case where the effect of force is taken into account, and gave an exact formulation of the subsidiary conditions, already suggested by De Broglie, to which the wave function ψ must be subjected, namely that it should be single-valued and finite in space and time. And he was ...
Quantum Postulates “Mastery of Fundamentals” Questions CH351
... A wavefunction€is well-behaved if it is normalizable, and if it and its first-derivative are single-valued, continuous and finite. 3. Why do we say the wavefunction completely specifies the state of a system? How do we use the wavefunction? We mean that any physically observable quantity is determin ...
... A wavefunction€is well-behaved if it is normalizable, and if it and its first-derivative are single-valued, continuous and finite. 3. Why do we say the wavefunction completely specifies the state of a system? How do we use the wavefunction? We mean that any physically observable quantity is determin ...
Introduction to Effective Field Theory
... Effective Field Theories? • In relativistic quantum theory, particles are created or annihilated. • Including the quantum fluctuations, it becomes effective field theory. • If some particles are heavy, eliminate them to make an effective theory. ...
... Effective Field Theories? • In relativistic quantum theory, particles are created or annihilated. • Including the quantum fluctuations, it becomes effective field theory. • If some particles are heavy, eliminate them to make an effective theory. ...
They survive monitoring by the environment to leave `descendants
... Now, Zurek and colleagues have proved a mathematical theorem that shows the pointer states do actually coincide with the states probed by indirect measurements of a system's environment. "The environment is modified so that it contains an imprint of the pointer state," he says. ...
... Now, Zurek and colleagues have proved a mathematical theorem that shows the pointer states do actually coincide with the states probed by indirect measurements of a system's environment. "The environment is modified so that it contains an imprint of the pointer state," he says. ...
Square Root of an Operator - Information Sciences and Computing
... means of the Pauli matrices how to linearize (second order operators) 1/2 associated to the Weyl and Dirac equations. ...
... means of the Pauli matrices how to linearize (second order operators) 1/2 associated to the Weyl and Dirac equations. ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... - It was known for some time that every atom when subjected to high temperatures or an electrical discharge emits electromagnetic radiation of characteristic frequencies which called emission spectrum. ...
... - It was known for some time that every atom when subjected to high temperatures or an electrical discharge emits electromagnetic radiation of characteristic frequencies which called emission spectrum. ...
Winter 2008 Physics 315 / 225
... The intensity is proportional to the number of photons (E=hf for each photon) A photon is transmitted with some Probability (depends on initial photon state and on transmission axis) After a Polaroid sheet we know the polarization state of the photon ...
... The intensity is proportional to the number of photons (E=hf for each photon) A photon is transmitted with some Probability (depends on initial photon state and on transmission axis) After a Polaroid sheet we know the polarization state of the photon ...
32 The Atom and the Quantum Answers and Solutions for Chapter
... 14. In the first orbit, one wavelength makes up the circumference. In the second, two wavelengths. In the nth orbit, n wavelengths. 15. Electrons don’t spiral because they are composed of waves that reinforce themselves. 16. The wave function represents the possibilities that can occur for a quantum ...
... 14. In the first orbit, one wavelength makes up the circumference. In the second, two wavelengths. In the nth orbit, n wavelengths. 15. Electrons don’t spiral because they are composed of waves that reinforce themselves. 16. The wave function represents the possibilities that can occur for a quantum ...
P430
... Three lectures, on average, will be devoted to each of the topics listed. As in any physics course, you will be asked to demonstrate your mastery of these topics by solving quantitative problems in each area from first principles, both on homework sets and on the exams. Course objectives: By the end ...
... Three lectures, on average, will be devoted to each of the topics listed. As in any physics course, you will be asked to demonstrate your mastery of these topics by solving quantitative problems in each area from first principles, both on homework sets and on the exams. Course objectives: By the end ...