Quantenmechanik mit Schaltkreisen: Photonen und Qubits auf einem supraleitenden Mikrochip (ETH Zurich) www.qudev.ethz.ch
... J. Faist (ETH Zurich) J. Gambetta (IBM) T. Ihn (ETH Zurich) F. Merkt (ETH Zurich) L. Novotny (ETH Zurich) ...
... J. Faist (ETH Zurich) J. Gambetta (IBM) T. Ihn (ETH Zurich) F. Merkt (ETH Zurich) L. Novotny (ETH Zurich) ...
Symmetry and Asymmetry in the Mendeleïev`s Periodic Table
... Niels Bohr established the relation between the position of each Element in the periodic table and its electronic structure. The chemical properties of each Element are thus COMPLETELY DETERMINED by the distribution of the electrons of this Element. The properties and positioning of these electrons, ...
... Niels Bohr established the relation between the position of each Element in the periodic table and its electronic structure. The chemical properties of each Element are thus COMPLETELY DETERMINED by the distribution of the electrons of this Element. The properties and positioning of these electrons, ...
Atomic Theory electron charge: -1.6 X 10-19C
... Electromagnetic waves, photons of light, are produced when a charge oscillates within an electric field, such as an electron in orbit within the positive proton's electric field. To account for the occurance of the line spectrum, Bohr assumed that the hydrogen atom can only exist in certain discreet ...
... Electromagnetic waves, photons of light, are produced when a charge oscillates within an electric field, such as an electron in orbit within the positive proton's electric field. To account for the occurance of the line spectrum, Bohr assumed that the hydrogen atom can only exist in certain discreet ...
ppt - Pavel Stránský
... • fast convergence towards zero for chaotic trajectories Ch. Skokos, J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 34, 10029 (2001); 37 (2004), 6269 ...
... • fast convergence towards zero for chaotic trajectories Ch. Skokos, J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 34, 10029 (2001); 37 (2004), 6269 ...
C. 1
... Uncertainty Principle for Photons •Waves are not generally localized in space p k –They have a spread in position x •You can make them somewhat localized by combining different wave numbers k –Now they have a spread in k, k •There is a precise inequality relating these two quantities xk 12 – ...
... Uncertainty Principle for Photons •Waves are not generally localized in space p k –They have a spread in position x •You can make them somewhat localized by combining different wave numbers k –Now they have a spread in k, k •There is a precise inequality relating these two quantities xk 12 – ...
Project A11
... [1] T. Kinoshita, T. Wenger, and D. S. Weiss, Nature 440, 900 (2006). [2] T. Enss and J. Sirker, New J. Phys. 14, 023008 (2012). [3] N. Sedlmayr, J. Ren, F. Gebhard, and J. Sirker, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 100406 (2013). [4] J. Sirker, N. P. Konstantinidis, F. Andraschko, and N. Sedlmayr, arXiv: 1303.3 ...
... [1] T. Kinoshita, T. Wenger, and D. S. Weiss, Nature 440, 900 (2006). [2] T. Enss and J. Sirker, New J. Phys. 14, 023008 (2012). [3] N. Sedlmayr, J. Ren, F. Gebhard, and J. Sirker, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 100406 (2013). [4] J. Sirker, N. P. Konstantinidis, F. Andraschko, and N. Sedlmayr, arXiv: 1303.3 ...
NonequilibriumDynamicsofQuarkGluonPlasma
... distances compared to particle energy and momentum. •Hydrodynamics: particles propagate classically between collisions, which are independent, uncorrelated events. ...
... distances compared to particle energy and momentum. •Hydrodynamics: particles propagate classically between collisions, which are independent, uncorrelated events. ...
Document
... This is the case for free particles. For the general case we can replace the equation E=KE+V for the total energy of the particle with operator ...
... This is the case for free particles. For the general case we can replace the equation E=KE+V for the total energy of the particle with operator ...
- City Research Online
... function of the number operator N . One may consider various types of Hamiltonian systems, either Hermitian or non-Hermitian, and replace the original standard canonical variables (x0 , p0 ), obeying [x0 , p0 ] = i~, by (X, P ). It is crucial to note that even when the undeformed Hamiltonian is Herm ...
... function of the number operator N . One may consider various types of Hamiltonian systems, either Hermitian or non-Hermitian, and replace the original standard canonical variables (x0 , p0 ), obeying [x0 , p0 ] = i~, by (X, P ). It is crucial to note that even when the undeformed Hamiltonian is Herm ...
ABSTRACTS Workshop on “Higher topological quantum field theory
... with an atlas of orbifold charts. Local charts were given in terms of an open subset of Euclidean space with an effective action of a finite group. Because of the effectiveness of the actions, embeddings between these charts could be taken to be all embeddings between the charts that commute with th ...
... with an atlas of orbifold charts. Local charts were given in terms of an open subset of Euclidean space with an effective action of a finite group. Because of the effectiveness of the actions, embeddings between these charts could be taken to be all embeddings between the charts that commute with th ...
Chiral kinetic theory
... Kinetic equation describes the motion of particles in the regime where collisions are rare enough that motion between collisions is classical. In terms of the distribution function f (t, x, p) the equation is ∂f ∂f ∂f df ...
... Kinetic equation describes the motion of particles in the regime where collisions are rare enough that motion between collisions is classical. In terms of the distribution function f (t, x, p) the equation is ∂f ∂f ∂f df ...
k - Marc Madou
... Solving this equation, say for an electron acted upon by a fixed nucleus, we will see that this results in standing waves. The more general Schrödinger equation does feature a time dependent potential V=V(x,t) and must be used for example when trying to find the wave function of say an atom in a ...
... Solving this equation, say for an electron acted upon by a fixed nucleus, we will see that this results in standing waves. The more general Schrödinger equation does feature a time dependent potential V=V(x,t) and must be used for example when trying to find the wave function of say an atom in a ...
Teaching the Atomic Theory: A Visual
... The Spin Quantum Number, ms • In the 1920s, it was discovered that two electrons in the same orbital do not have exactly the same energy. • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. ...
... The Spin Quantum Number, ms • In the 1920s, it was discovered that two electrons in the same orbital do not have exactly the same energy. • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. ...
Notes - Particle Theory
... – At high enough energies, the Higgs field is experiencing so much perturbation that it is no longer really in either natural resting place; here the symmetry is restored. – At these energies, the different masses of the four weak and electromagnetic mediators can be ignored, and they all look the s ...
... – At high enough energies, the Higgs field is experiencing so much perturbation that it is no longer really in either natural resting place; here the symmetry is restored. – At these energies, the different masses of the four weak and electromagnetic mediators can be ignored, and they all look the s ...
Notes
... 1. Maximum of two students in any one room 2. There are no elevators->students must be as close to the 1st floor as possible 3. When filling a type of room, all rooms must be full before going onto a different type of room. 4. When filling rooms on a floor, you must place one student in each type of ...
... 1. Maximum of two students in any one room 2. There are no elevators->students must be as close to the 1st floor as possible 3. When filling a type of room, all rooms must be full before going onto a different type of room. 4. When filling rooms on a floor, you must place one student in each type of ...
The D-Wave Quantum Computer Every so often - D
... computer returns many very good answers in a short amount of time - 10,000 answers in one second. This gives the user not only the optimal solution or a single answer, but also other alternatives to choose from. ...
... computer returns many very good answers in a short amount of time - 10,000 answers in one second. This gives the user not only the optimal solution or a single answer, but also other alternatives to choose from. ...
Lecture 24: The fundamental building blocks of matter 1
... • Fermions: Particles (like electrons) that can be created or destroyed only in combination with its antiparticle • Bosons: Particles (like photons) that can be created or destroyed in arbitrary numbers • The Fundamental Forces in Nature act between the particles (Fermions) and are carried by Bosons ...
... • Fermions: Particles (like electrons) that can be created or destroyed only in combination with its antiparticle • Bosons: Particles (like photons) that can be created or destroyed in arbitrary numbers • The Fundamental Forces in Nature act between the particles (Fermions) and are carried by Bosons ...
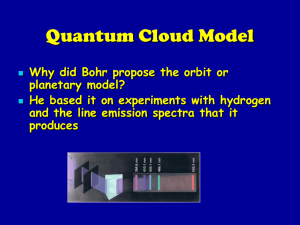
Quantum Cloud Model
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
Edge modes, zero modes and conserved charges in parafermion
... Simple way for 1d: can show it depends on (-1) of ground state. Even fancier way: compute sign of Pfaffian. Heuristic way: find evidence that that the fermionic zero mode is still present. Can we find raising or lowering operator Y so that [H, Y ]= (D E) Y ? ...
... Simple way for 1d: can show it depends on (-1) of ground state. Even fancier way: compute sign of Pfaffian. Heuristic way: find evidence that that the fermionic zero mode is still present. Can we find raising or lowering operator Y so that [H, Y ]= (D E) Y ? ...