Wednesday, Feb. 28, 2007
... • How is a motion described? – Motion of a particle or a group of particles can be expressed in terms of the position of the particle at any given time in classical mechanics. ...
... • How is a motion described? – Motion of a particle or a group of particles can be expressed in terms of the position of the particle at any given time in classical mechanics. ...
File
... interactions. Like all elementary particles, photons are currently best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, exhibiting properties of both waves and particles. For example, a single photon may be refracted by a lens or exhibit wave interference with itself, but also act ...
... interactions. Like all elementary particles, photons are currently best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, exhibiting properties of both waves and particles. For example, a single photon may be refracted by a lens or exhibit wave interference with itself, but also act ...
Collaborative learning of quantum measurement with on
... to students who were not studying physics [1, 2, 3]. To teach students some level of understanding of this complex topic we have frequently used inactive computer visualizations which enable students to visualize wave functions in a variety of situations and to make changes that affect these wave fu ...
... to students who were not studying physics [1, 2, 3]. To teach students some level of understanding of this complex topic we have frequently used inactive computer visualizations which enable students to visualize wave functions in a variety of situations and to make changes that affect these wave fu ...
Here
... I strongly believe that the principle of local gauge invariance is not a fundamental principle like the relativity principle or the uncertainty principle. It is just a consequence of local conservation of probability and the subsequent second quantization of the formalism. Then it is already contain ...
... I strongly believe that the principle of local gauge invariance is not a fundamental principle like the relativity principle or the uncertainty principle. It is just a consequence of local conservation of probability and the subsequent second quantization of the formalism. Then it is already contain ...
2010 midterm exam solutions
... 1. What is an observable in quantum mechanics and by which mathematical object is represented? An observable in QM is any physical quantity that can be measured. Observables are represented by hermitian operators. 2. How are the possible values of measurement outcomes of an observable determined? ...
... 1. What is an observable in quantum mechanics and by which mathematical object is represented? An observable in QM is any physical quantity that can be measured. Observables are represented by hermitian operators. 2. How are the possible values of measurement outcomes of an observable determined? ...
Chapter 6
... •Heisenberg showed that the more precisely the momentum of a particle is known, the less precisely is its position known: •In many cases, our uncertainty of the whereabouts of an electron is greater than the size of the atom itself! ...
... •Heisenberg showed that the more precisely the momentum of a particle is known, the less precisely is its position known: •In many cases, our uncertainty of the whereabouts of an electron is greater than the size of the atom itself! ...
Einstein-Rosen Bridge (ER), Einstein-Podolsky
... 3. What Is a Wormhole from the View Point of Measure Theory? It is almost a trivial conclusion that a wormhole [7]-[31] is the quintessential empty set with varying degrees of emptiness corresponding to varying degrees of entanglement [1] [37] [45]. Our spacetime consists exclusively of zero sets qu ...
... 3. What Is a Wormhole from the View Point of Measure Theory? It is almost a trivial conclusion that a wormhole [7]-[31] is the quintessential empty set with varying degrees of emptiness corresponding to varying degrees of entanglement [1] [37] [45]. Our spacetime consists exclusively of zero sets qu ...
A functional quantum programming language
... task to find new quantum algorithms. One of the reasons for this situation might be that quantum programs are very low level: they are usually represented as quantum circuits, or in some combinator language which gives rise to circuits. Here we attempt to remedy this situation by introducing the qua ...
... task to find new quantum algorithms. One of the reasons for this situation might be that quantum programs are very low level: they are usually represented as quantum circuits, or in some combinator language which gives rise to circuits. Here we attempt to remedy this situation by introducing the qua ...
Periodic orbit analysis of molecular vibrational spectra: Spectral
... Semiclassical periodic orbit ~po! theory has been extensively applied over the last few years to explore the connection between classical and quantum mechanics for classically nonintegrable systems.1,2 A central result of po theory is an approximate expression for the density of states in the semicl ...
... Semiclassical periodic orbit ~po! theory has been extensively applied over the last few years to explore the connection between classical and quantum mechanics for classically nonintegrable systems.1,2 A central result of po theory is an approximate expression for the density of states in the semicl ...
- RZ User
... Heisenberg then constructed an elegant algebraic framework that could be used to “quantize” all mechanical systems. This mathematical abstraction perfectly matched Heisenberg’s idealistic philosophy. Later, matrix mechanics was indeed shown to lead to the same observable predictions for measurement ...
... Heisenberg then constructed an elegant algebraic framework that could be used to “quantize” all mechanical systems. This mathematical abstraction perfectly matched Heisenberg’s idealistic philosophy. Later, matrix mechanics was indeed shown to lead to the same observable predictions for measurement ...
A1979HZ37600001
... calculate the mean square line width in magnetic resonance on the assumption that the line width is caused by dipolar interaction. The article also includes a discussion of the phenomenon of so-called ‘exchange narrowing.’ [The SCI ® indicates that this paper has been ...
... calculate the mean square line width in magnetic resonance on the assumption that the line width is caused by dipolar interaction. The article also includes a discussion of the phenomenon of so-called ‘exchange narrowing.’ [The SCI ® indicates that this paper has been ...
pdf
... a new dynamical law that is approximated by the Schrödinger equation, but they must also show that this new dynamical law is consistent with the relativity of simultaneity. On the other hand, modifying the orthodox interpretation’s way of assigning values to quantities is a nontrivial task, since t ...
... a new dynamical law that is approximated by the Schrödinger equation, but they must also show that this new dynamical law is consistent with the relativity of simultaneity. On the other hand, modifying the orthodox interpretation’s way of assigning values to quantities is a nontrivial task, since t ...
Natural Nonlinear Quantum Units and Human Artificial Linear
... the natural mass unit µ, the traditional approach with three constants can now be reduced to two constants, i.e. to one length and one time unit connected to the natural mass unit µ. Clearly, the human artificial SI references λu = 1m and u = 1m/s can not have any fundamental physical meaning at all ...
... the natural mass unit µ, the traditional approach with three constants can now be reduced to two constants, i.e. to one length and one time unit connected to the natural mass unit µ. Clearly, the human artificial SI references λu = 1m and u = 1m/s can not have any fundamental physical meaning at all ...
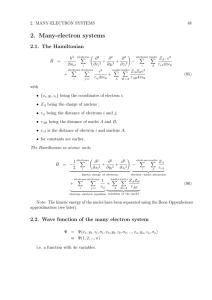
2. Many-electron systems
... Summarized: carbon atom in the 2p2 configuration has three energy levels. What is the order of these states? Hund’s rule (from experiment; „Nun, einfach durch Anstieren der Spektren”): • the state with the maximum multiplicity is the most stable: there is an interaction called „exchange” which exist ...
... Summarized: carbon atom in the 2p2 configuration has three energy levels. What is the order of these states? Hund’s rule (from experiment; „Nun, einfach durch Anstieren der Spektren”): • the state with the maximum multiplicity is the most stable: there is an interaction called „exchange” which exist ...
CHAPTER 2: Special Theory of Relativity
... first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for ...
... first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for ...
Lecture 4 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics, Operators
... Simply stated, the wave function and it’s derivative are smoothly varying (no discontinuities) . However, in a non-isotropic medium (examples at a heterojunction where the mass of an electron changes on either side of the junction or at an abrupt potential boundary) the full continuity equation MUST ...
... Simply stated, the wave function and it’s derivative are smoothly varying (no discontinuities) . However, in a non-isotropic medium (examples at a heterojunction where the mass of an electron changes on either side of the junction or at an abrupt potential boundary) the full continuity equation MUST ...
An Electromagnetic Basis for Inertia and Gravitation
... non-zero minimum energy for any oscillator. Calculating the minimum energy of such a quantum oscillator is one of the obligatory fundamental problems solved in most any textbook on Quantum Mechanics. Couching this in quantum language, one states that the lowest eigenvalue, E, of the oscillator Hamil ...
... non-zero minimum energy for any oscillator. Calculating the minimum energy of such a quantum oscillator is one of the obligatory fundamental problems solved in most any textbook on Quantum Mechanics. Couching this in quantum language, one states that the lowest eigenvalue, E, of the oscillator Hamil ...
Lecture 7 - United International College
... must rather bounce off one another when they collide. • All macroscopic objects are in fact combinations of atoms. Everything in the macroscopic world is subject to change, as their constituent atoms shift or move away. Thus, while the atoms themselves persist through all time, everything in the wor ...
... must rather bounce off one another when they collide. • All macroscopic objects are in fact combinations of atoms. Everything in the macroscopic world is subject to change, as their constituent atoms shift or move away. Thus, while the atoms themselves persist through all time, everything in the wor ...