Deadlock Conditions
... multiple processes may access the same memory location, and if a process is currently performing a testand-set, no other process may begin another test-and-set until the first process is done. ...
... multiple processes may access the same memory location, and if a process is currently performing a testand-set, no other process may begin another test-and-set until the first process is done. ...
Chap 7 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... The purpose of this assignment is for you to become familiar with threaded programming. You may choose to write any program you wish. Think of an interesting program to do. It does not have to be elaborate. For example, you can write a server that accepts multiple clients. ...
... The purpose of this assignment is for you to become familiar with threaded programming. You may choose to write any program you wish. Think of an interesting program to do. It does not have to be elaborate. For example, you can write a server that accepts multiple clients. ...
Multithreading
... When threads share access to a common object, they can conflict with each other. Consider several threads trying to access the same bank account, some trying to deposit and other to withdraw: these activities need to be synchronized. Java objects were designed with multithreading in mind: for every ...
... When threads share access to a common object, they can conflict with each other. Consider several threads trying to access the same bank account, some trying to deposit and other to withdraw: these activities need to be synchronized. Java objects were designed with multithreading in mind: for every ...
PPT
... • Programming is easier because threads are linear and we (usually) think linearly • Threads can take advantage of multiprocessors easily • Threads are synchronous i.e. it is okay for a thread to block because there are many of them running at once • Debugging a threaded program is considerably easi ...
... • Programming is easier because threads are linear and we (usually) think linearly • Threads can take advantage of multiprocessors easily • Threads are synchronous i.e. it is okay for a thread to block because there are many of them running at once • Debugging a threaded program is considerably easi ...
document
... • synchronization policy – At most one process may execute a monitor procedure at a time; this process is said to be in the monitor – If one process is in the monitor, any other process that calls a monitor procedure will be delayed ...
... • synchronization policy – At most one process may execute a monitor procedure at a time; this process is said to be in the monitor – If one process is in the monitor, any other process that calls a monitor procedure will be delayed ...
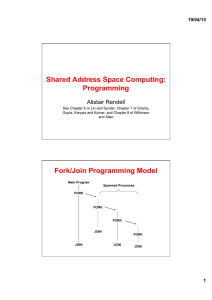
Shared Address Space Computing: Programming Fork/Join
... • At its lowest level a lock is a protocol for coordinating processes, – the CPU is not physically prevented from executing those instruction while (lock == 1) do_nothing; lock = 1; critical section lock = 0; ...
... • At its lowest level a lock is a protocol for coordinating processes, – the CPU is not physically prevented from executing those instruction while (lock == 1) do_nothing; lock = 1; critical section lock = 0; ...
1up
... • At its lowest level a lock is a protocol for coordinating processes, – the CPU is not physically prevented from executing those instruction while (lock == 1) do_nothing; lock = 1; critical section lock = 0; ...
... • At its lowest level a lock is a protocol for coordinating processes, – the CPU is not physically prevented from executing those instruction while (lock == 1) do_nothing; lock = 1; critical section lock = 0; ...
The IC Wall Collaboration between Computer science + Physics
... Thread-1 does: X = X + 1; Thread-2 does: X = X + 2; Result should be +3, not +1 or +2. Need to prevent concurrent access to same data: mutual exclusion synchronization ...
... Thread-1 does: X = X + 1; Thread-2 does: X = X + 2; Result should be +3, not +1 or +2. Need to prevent concurrent access to same data: mutual exclusion synchronization ...