5 Mass Spectroscopy I
... which shows the relative amounts of the different ions as a function of their mass, expressed as the ratio of mass to charge, m/z. Most of the ions formed in the electric field have a +1 charge. ...
... which shows the relative amounts of the different ions as a function of their mass, expressed as the ratio of mass to charge, m/z. Most of the ions formed in the electric field have a +1 charge. ...
P10
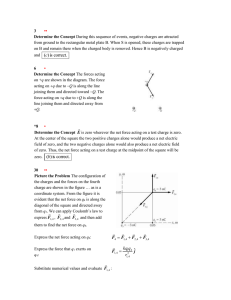
... the force on particle A, the force on particle B is 1) four times as much 2) twice as much 3) the same 4) half as much 5) one-fourth as much Q22-5) Two charged particles repel each other with a force F. If the charge of one of the particles is doubled and the distance between them is also doubled, t ...
... the force on particle A, the force on particle B is 1) four times as much 2) twice as much 3) the same 4) half as much 5) one-fourth as much Q22-5) Two charged particles repel each other with a force F. If the charge of one of the particles is doubled and the distance between them is also doubled, t ...
Fine Structure of the Spectral Lines of Hydrogen - Labs
... Where, + is the total or principal quantum number, which is an integer and positive. We can look at the principal quantum number for an atom free from externally applied fields as being a generalized angular momentum composed of multiple components, including one due to the linear momentum parallel ...
... Where, + is the total or principal quantum number, which is an integer and positive. We can look at the principal quantum number for an atom free from externally applied fields as being a generalized angular momentum composed of multiple components, including one due to the linear momentum parallel ...
Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields
... An important difference between electric charges and magnetic poles is that poles are ALWAYS found in pairs (N,S) while single electric charges (positive or negative) can be isolated. For example, if you cut a bar magnet in half each piece will have a N and S pole! 2) The forces between magnets are ...
... An important difference between electric charges and magnetic poles is that poles are ALWAYS found in pairs (N,S) while single electric charges (positive or negative) can be isolated. For example, if you cut a bar magnet in half each piece will have a N and S pole! 2) The forces between magnets are ...
Introduction to Electric Fields
... line, toward the center of the object causing the gravitational. Magnetic and gravitational fields can be represented by field diagrams, obtained by plotting field-strength arrows at different locations around the object producing the field. How to draw force diagrams for mutually attracting and ...
... line, toward the center of the object causing the gravitational. Magnetic and gravitational fields can be represented by field diagrams, obtained by plotting field-strength arrows at different locations around the object producing the field. How to draw force diagrams for mutually attracting and ...
Following are some practice problems
... is at < 0, 0, 0 >; it has a radius of 12 cm and a uniform positive charge of 4 x10-9 C. The center of the smaller sphere is at < 25, 0, 0 > cm; it has a radius of 3 cm and a uniform negative charge of -2 x10-9 C. What is the electric field at location A (6cm to the right of the center of the large s ...
... is at < 0, 0, 0 >; it has a radius of 12 cm and a uniform positive charge of 4 x10-9 C. The center of the smaller sphere is at < 25, 0, 0 > cm; it has a radius of 3 cm and a uniform negative charge of -2 x10-9 C. What is the electric field at location A (6cm to the right of the center of the large s ...
Mass Spectrometry - Flinn Scientific
... The origin of the basic principle of mass spectrometry dates back to J.J. Thomson’s discovery of the electron in 1897 and to his work with “positive rays,” positively charged streams of atoms generated in gas discharge tubes. When these positive ions were bent or deflected in the presence of electri ...
... The origin of the basic principle of mass spectrometry dates back to J.J. Thomson’s discovery of the electron in 1897 and to his work with “positive rays,” positively charged streams of atoms generated in gas discharge tubes. When these positive ions were bent or deflected in the presence of electri ...
Magnetic Force Exerted by a Magnetic Field on a Single
... If the magnetic field is perpendicular to the velocity of the electrons, the force exerted on the electrons is perpendicular to both the magnetic field and the velocity. c. Your friend says that the beam of electrons is deflected by the magnet because the electrons are charged particles and the magn ...
... If the magnetic field is perpendicular to the velocity of the electrons, the force exerted on the electrons is perpendicular to both the magnetic field and the velocity. c. Your friend says that the beam of electrons is deflected by the magnet because the electrons are charged particles and the magn ...
Energy - Nathan Dawson
... 2. Designate the initial and final points (points where you either know or want to know information about the object). 3. Apply the conservation of energy: Ki + Ui + W = Kf + Uf where W is the work done by all of the non-conservative forces acting on the object between the initial and final points, ...
... 2. Designate the initial and final points (points where you either know or want to know information about the object). 3. Apply the conservation of energy: Ki + Ui + W = Kf + Uf where W is the work done by all of the non-conservative forces acting on the object between the initial and final points, ...
Physics 272: Electricity and Magnetism
... Magnetic fields do no work (usually) • Since the force due to the magnetic field is always perpendicular to velocity, work=0 • Acceleration is always perpendicular to v. What shape does that sound like? Charged particles in a B field often move in a circle (they will if the field is 1) uniform and ...
... Magnetic fields do no work (usually) • Since the force due to the magnetic field is always perpendicular to velocity, work=0 • Acceleration is always perpendicular to v. What shape does that sound like? Charged particles in a B field often move in a circle (they will if the field is 1) uniform and ...
gravity theory based on mass–energy equivalence
... − log(ε)|ε=0 ) and a first-order singularity (i.e. proportional to 1/ε|ε=0 ) in the gravity force. As we develop later, if the FS is quantized into discrete units, the singularity equations show that both types of singularities act on the FS to effect any changes and interactions in the mass density ...
... − log(ε)|ε=0 ) and a first-order singularity (i.e. proportional to 1/ε|ε=0 ) in the gravity force. As we develop later, if the FS is quantized into discrete units, the singularity equations show that both types of singularities act on the FS to effect any changes and interactions in the mass density ...