Math 2250-4 Mon Jan 30
... attractive force between two objects of mass m, M has magnitude GMm F = r2 where r is the distance between their centers of mass and G is a universal constant. Write R for the radius of the earth; write r t for the distance of a projectile object of mass m from the center of the earth, and consider ...
... attractive force between two objects of mass m, M has magnitude GMm F = r2 where r is the distance between their centers of mass and G is a universal constant. Write R for the radius of the earth; write r t for the distance of a projectile object of mass m from the center of the earth, and consider ...
Bowling Ball Rolling ω
... 2) Normal reaction N, vertically upward through the point of contact 3) Forces of kinetic friction, fk = µN, horizontally through the point of contact and opposite to the direction of motion. The only horizontal force fk, produces horizontal acceleration, a = force/mass = µN/ M = µg [as N = Mg]. Thi ...
... 2) Normal reaction N, vertically upward through the point of contact 3) Forces of kinetic friction, fk = µN, horizontally through the point of contact and opposite to the direction of motion. The only horizontal force fk, produces horizontal acceleration, a = force/mass = µN/ M = µg [as N = Mg]. Thi ...
Conservative forces
... An electric potential V at a position r is related to the electric potential energy U of a test charge q at the position r through V = U/q. A good way to visualize a potential in two dimensions is to think of a landscape. For each point in the x-y plane, the height (z-coordinate) indicates the value ...
... An electric potential V at a position r is related to the electric potential energy U of a test charge q at the position r through V = U/q. A good way to visualize a potential in two dimensions is to think of a landscape. For each point in the x-y plane, the height (z-coordinate) indicates the value ...
Name:
... Summation: Provide an example of each of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion: An object at rest remains at rest or an object in motion remains in it’s state of motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
... Summation: Provide an example of each of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion: An object at rest remains at rest or an object in motion remains in it’s state of motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
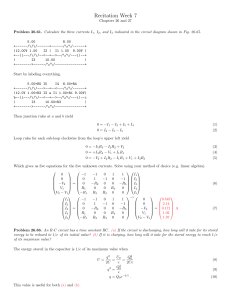
Recitation Week 7
... (a) From the figure, the particle rotates counterclockwise with the B field pointing out of the page. From the righthand rule and F = qv × B, the particle must have a negative charge. Because this centerward force makes the particle move in a circle, v2 r 0.950 m · 3 · 1.6 · 10−19 C · 0.250 T rqB = ...
... (a) From the figure, the particle rotates counterclockwise with the B field pointing out of the page. From the righthand rule and F = qv × B, the particle must have a negative charge. Because this centerward force makes the particle move in a circle, v2 r 0.950 m · 3 · 1.6 · 10−19 C · 0.250 T rqB = ...
Name: Notes - 4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
racing - MathinScience.info
... tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
File
... between mass and weight? MASS is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and doesn’t change from place to place in the universe. WEIGHT is the measurement of the gravitational pull on an object, so it will change if the force of gravity changes. ...
... between mass and weight? MASS is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and doesn’t change from place to place in the universe. WEIGHT is the measurement of the gravitational pull on an object, so it will change if the force of gravity changes. ...
Unit 9 Study Guide - Hewlett
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
Lecture_1 - Department of Mathematics
... WORK TO COMPRESS A SPRING The figure below shows a spring being compressed. k = spring constant ...
... WORK TO COMPRESS A SPRING The figure below shows a spring being compressed. k = spring constant ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...