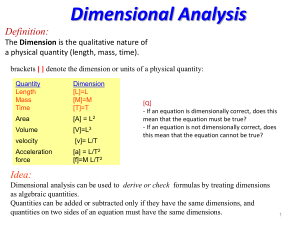
doc - Seth Baum
... 32) The relationship between voltage, current, and impedance b. What is V = I Z 33) The relationship between total capacitance and capacitors in series a. What is 1/R_s = sum of all 1/Ci 34) An explanation of what a solenoid is a. What is a metal coil 35) The relationship between total resistance an ...
... 32) The relationship between voltage, current, and impedance b. What is V = I Z 33) The relationship between total capacitance and capacitors in series a. What is 1/R_s = sum of all 1/Ci 34) An explanation of what a solenoid is a. What is a metal coil 35) The relationship between total resistance an ...
laws of motion
... Dropped big and small rock Fell at same rate If no interference – motion will go on forever ...
... Dropped big and small rock Fell at same rate If no interference – motion will go on forever ...
Newton`s Laws
... We use the term “friction” to describe any force caused by motion and that acts to slow motion down ...
... We use the term “friction” to describe any force caused by motion and that acts to slow motion down ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
... object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 6
... Note: please turn these problems into the mailbox of the grader, Wissam AlSaidi, by 5PM on Friday, May 23, 2003. Remember that you will be graded only on the best 5 out of the 7 problem sets. 1. Consider a single Abrikosov vortex parallel to the z axis. Assume that this vortex experiences three forc ...
... Note: please turn these problems into the mailbox of the grader, Wissam AlSaidi, by 5PM on Friday, May 23, 2003. Remember that you will be graded only on the best 5 out of the 7 problem sets. 1. Consider a single Abrikosov vortex parallel to the z axis. Assume that this vortex experiences three forc ...
PHY 101 Final Exam Preparation Notes
... c. Determine the magnitude field mouse’s net displacement. d. In what direction does the field mouse end at relative to his staring point? 6. An airplane is flying due east at 600 mph. However the pilot is unaware that he flying in a strong jet stream that has a speed of 150 mph and is directed 60 ...
... c. Determine the magnitude field mouse’s net displacement. d. In what direction does the field mouse end at relative to his staring point? 6. An airplane is flying due east at 600 mph. However the pilot is unaware that he flying in a strong jet stream that has a speed of 150 mph and is directed 60 ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... where rS ,i is the vector form the point S to where the ith force Fiext acts on the object. As the ball moves down the alley, the contact point will move, but the friction force will always be parallel to the line of contact between the bowling bowl and the surface. So, if we pick any fixed point S ...
... where rS ,i is the vector form the point S to where the ith force Fiext acts on the object. As the ball moves down the alley, the contact point will move, but the friction force will always be parallel to the line of contact between the bowling bowl and the surface. So, if we pick any fixed point S ...
F=ma Worksheet
... If we know the mass of an object in kilograms, and we know the acceleration that an object experiences then we can calculate the force exerted on that object by multiplying the _______________ x _____________. 1. An unbalanced force of 25 N in an Easterly direction is applied to a 12 kg mass. What w ...
... If we know the mass of an object in kilograms, and we know the acceleration that an object experiences then we can calculate the force exerted on that object by multiplying the _______________ x _____________. 1. An unbalanced force of 25 N in an Easterly direction is applied to a 12 kg mass. What w ...
x F F=kx
... about 45 kg. And since Work is equal to the change in kinetic energy, I found my work or KE to be 2.52*10^6, then plugging that into .5*m*v^2, I found v to be 335 m/s which seems utterly ...
... about 45 kg. And since Work is equal to the change in kinetic energy, I found my work or KE to be 2.52*10^6, then plugging that into .5*m*v^2, I found v to be 335 m/s which seems utterly ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
waves - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. (think inertia). 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied to that object. ...
... line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. (think inertia). 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied to that object. ...
DES601-Module13
... equation, such as Manning’s equation, Chezy equation, Darcy-Weisbach equation or HazenWilliams (water only!) ...
... equation, such as Manning’s equation, Chezy equation, Darcy-Weisbach equation or HazenWilliams (water only!) ...