Circular Motion RS
... 2. What is the direction of the centripetal acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion? Why? 3. A ball is whirled around in a circle. What happens to the centripetal acceleration if the velocity is doubled? 4. If a string breaks that holds a whirling can in it circular path, what causes it ...
... 2. What is the direction of the centripetal acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion? Why? 3. A ball is whirled around in a circle. What happens to the centripetal acceleration if the velocity is doubled? 4. If a string breaks that holds a whirling can in it circular path, what causes it ...
Forces 6 - Cobb Learning
... 9. A retired policewoman pushes on a 77.2 kg crate with a pole. The pole makes an angle of 32.0 to the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the crate and the deck is 0.350. The policewoman exerts a force of 535 N. What is the acceleration of the crate? ...
... 9. A retired policewoman pushes on a 77.2 kg crate with a pole. The pole makes an angle of 32.0 to the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the crate and the deck is 0.350. The policewoman exerts a force of 535 N. What is the acceleration of the crate? ...
pdf file
... acceleration is due to changing direction the tangential component of the acceleration is due to changing speed ► Total ...
... acceleration is due to changing direction the tangential component of the acceleration is due to changing speed ► Total ...
Momentum - Littlemiamischools.org
... A 100-kg fullback runs up the middle of the football field. He collides with a 75-kg defensive back running toward him. The more massive fullback is thrown back two meters. Although he has less mass, the defensive back has more momentum because he is moving faster than the fullback. ...
... A 100-kg fullback runs up the middle of the football field. He collides with a 75-kg defensive back running toward him. The more massive fullback is thrown back two meters. Although he has less mass, the defensive back has more momentum because he is moving faster than the fullback. ...
5th set - Nathan Dawson
... A satellite is in geosynchronous orbit. Geosynchronous orbit is when the satellite orbits at a radius that allows the period of orbit to be 1 day (24 hrs). - Remember that centripetal acceleration is - The magnitude of the force is ...
... A satellite is in geosynchronous orbit. Geosynchronous orbit is when the satellite orbits at a radius that allows the period of orbit to be 1 day (24 hrs). - Remember that centripetal acceleration is - The magnitude of the force is ...
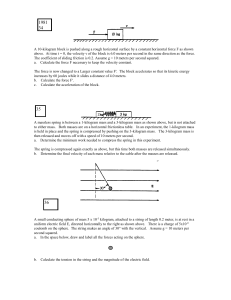
A 10 kilogram block Is pushed along a rough horizontal surface by a
... A 10-kilogram block is pushed along a rough horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force F as shown above. At time t = 0, the velocity v of the block is 6.0 meters per second in the same direction as the force. The coefficient of sliding friction is 0.2. Assume g = 10 meters per second squared. ...
... A 10-kilogram block is pushed along a rough horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force F as shown above. At time t = 0, the velocity v of the block is 6.0 meters per second in the same direction as the force. The coefficient of sliding friction is 0.2. Assume g = 10 meters per second squared. ...
laws of motion
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
Competency Goal 6: Students will conduct investigations
... For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
... For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
Work and Energy Homework
... c. How would your answers be different if it were going twice as fast? (Explain your answer.) ...
... c. How would your answers be different if it were going twice as fast? (Explain your answer.) ...
Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion:
... Newton’s second law of motion explains that the force of an object equals its mass times its acceleration. This law shows how force, mass, and acceleration are related. In other words, the net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration and its mass. The relation among force, mass ...
... Newton’s second law of motion explains that the force of an object equals its mass times its acceleration. This law shows how force, mass, and acceleration are related. In other words, the net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration and its mass. The relation among force, mass ...