ME 230 - Dynamics
... vector form.) Hint: dot products and unit vectors may be useful here, because you need to resolve the forces and acceleration in a direction parallel to the bar. ...
... vector form.) Hint: dot products and unit vectors may be useful here, because you need to resolve the forces and acceleration in a direction parallel to the bar. ...
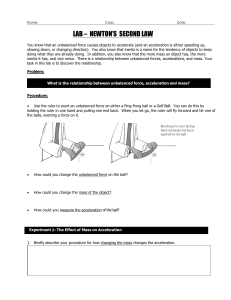
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... direction of the net force. To calculate the acceleration of an object, you need to know the object’s mass (in kilograms), the net force acting on it (in newtons), and use the equation below. ...
... direction of the net force. To calculate the acceleration of an object, you need to know the object’s mass (in kilograms), the net force acting on it (in newtons), and use the equation below. ...
U4 Kinetic-Potential Energy
... the energy stored in an object due to the Force of Gravity. We can determine how much gravitational potential energy an object has with this formula: ...
... the energy stored in an object due to the Force of Gravity. We can determine how much gravitational potential energy an object has with this formula: ...
Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... These accelerations tend to make the wheel slide at point P and a frictional force must act on the wheel at P to oppose the tendency to slide. If the wheel does NOT slide, the force is a static frictional force fs and the motion is smooth ...
... These accelerations tend to make the wheel slide at point P and a frictional force must act on the wheel at P to oppose the tendency to slide. If the wheel does NOT slide, the force is a static frictional force fs and the motion is smooth ...
No Slide Title - Laurel County Schools
... The cardinals are competing against the panthers in a game of volleyball on the moon. A cardinal player hits the ball with great force sending it over the net. Which of Newton’s Laws explains why the ball will continue moving until a panther player hits it? A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s Second ...
... The cardinals are competing against the panthers in a game of volleyball on the moon. A cardinal player hits the ball with great force sending it over the net. Which of Newton’s Laws explains why the ball will continue moving until a panther player hits it? A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s Second ...
Force and Momentum - the SASPhysics.com
... Force-time graphs • Force x time = change in momentum • So area under graph = impulse ...
... Force-time graphs • Force x time = change in momentum • So area under graph = impulse ...
The forces between electrical charges have an electrical potential
... (3.0m,0.0m). Find the total potential difference resulting from these charges between a point with coordinates (0.0m, 4.0m) and a point ...
... (3.0m,0.0m). Find the total potential difference resulting from these charges between a point with coordinates (0.0m, 4.0m) and a point ...
Practice Final Exam
... 18. Which one of the following statements is true concerning capacitors of unequal capacitance connected in series? (a) Each capacitor holds a different amount of charge. (b) The equivalent capacitance of the circuit is the sum of the individual capacitances. (c) The total voltage supplied by the ba ...
... 18. Which one of the following statements is true concerning capacitors of unequal capacitance connected in series? (a) Each capacitor holds a different amount of charge. (b) The equivalent capacitance of the circuit is the sum of the individual capacitances. (c) The total voltage supplied by the ba ...
final-96s
... Figure (a) is a diagram of the bones and muscle of a person’s arm supporting a mass. Tension in the biceps muscle holds the forearm in the horizontal position, as illustrated in the simple mechanical model in Fig. (b). The weight of the forearm is 9 N and the mass m = 2 kg. Determine the tension in ...
... Figure (a) is a diagram of the bones and muscle of a person’s arm supporting a mass. Tension in the biceps muscle holds the forearm in the horizontal position, as illustrated in the simple mechanical model in Fig. (b). The weight of the forearm is 9 N and the mass m = 2 kg. Determine the tension in ...
Potential Energy
... • Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. • Common units of kinetic energy: Joules – An object with mass of 1 kg, moving at 1 m/s, has a kinetic energy of 0.5 Joule. ...
... • Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. • Common units of kinetic energy: Joules – An object with mass of 1 kg, moving at 1 m/s, has a kinetic energy of 0.5 Joule. ...
Jeopardy
... (Multiple Choice) When one of two identical cars is traveling twice the speed of the other, it will take: (a, b, c, or d) twice the distance to come to a stop more than twice the distance to come to a stop less than twice the distance to come to a stop the same distance to come to a stop. Answer: (b ...
... (Multiple Choice) When one of two identical cars is traveling twice the speed of the other, it will take: (a, b, c, or d) twice the distance to come to a stop more than twice the distance to come to a stop less than twice the distance to come to a stop the same distance to come to a stop. Answer: (b ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...
... Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...