Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... that is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and connected to a spring having spring constant 183 N/m. The bullet becomes embedded in the block. The bullet-block system compresses the spring by a maximum amount 85 cm. What was the initial velocity of the bullet? ...
... that is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and connected to a spring having spring constant 183 N/m. The bullet becomes embedded in the block. The bullet-block system compresses the spring by a maximum amount 85 cm. What was the initial velocity of the bullet? ...
Gaining Momentum
... •An “elastic” collision is one in which the objects “bounce”, and energy is conserved. •An “inelastic” collision is one in which the objects stick together, and energy is lost to heat. ...
... •An “elastic” collision is one in which the objects “bounce”, and energy is conserved. •An “inelastic” collision is one in which the objects stick together, and energy is lost to heat. ...
Review for Final Exam Exams 1, 2, 3, and 4 How to Understand
... Which of the following forces exerts a torque on the bowling ball about its center? A. the weight of the ball B. the normal force exerted by the ramp C. the friction force exerted by the ramp ...
... Which of the following forces exerts a torque on the bowling ball about its center? A. the weight of the ball B. the normal force exerted by the ramp C. the friction force exerted by the ramp ...
Universal Gravitation
... For Newton’s idea to advance from hypothesis to scientific theory, it would have to be tested. • He reasoned that the mass of the moon should not affect how it falls, just as mass has no effect on the acceleration of freely falling objects on Earth. • How far the moon, or an apple at Earth’s surface ...
... For Newton’s idea to advance from hypothesis to scientific theory, it would have to be tested. • He reasoned that the mass of the moon should not affect how it falls, just as mass has no effect on the acceleration of freely falling objects on Earth. • How far the moon, or an apple at Earth’s surface ...
Torque
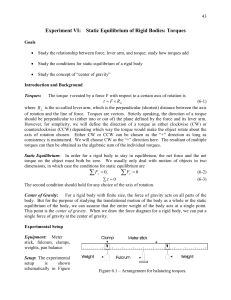
... torques. Experimental Procedure and Data Analysis A. Torques 1. Adjust the location of the fulcrum so that the meter stick, with no weights hanging on it, is in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Not ...
... torques. Experimental Procedure and Data Analysis A. Torques 1. Adjust the location of the fulcrum so that the meter stick, with no weights hanging on it, is in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Not ...
322. Two head lamps of a car are in parallel. They - DST
... Q 7. The length of a cylinder is measures with a metre rod having least count 0.1 cm. Its diameter is measured with vernier callipers having least count 0.01 cm. Given the length is 5·0 cm and radius is 2.00 cm. The percentage error in the calculated value of volume will be : (a) (c) ...
... Q 7. The length of a cylinder is measures with a metre rod having least count 0.1 cm. Its diameter is measured with vernier callipers having least count 0.01 cm. Given the length is 5·0 cm and radius is 2.00 cm. The percentage error in the calculated value of volume will be : (a) (c) ...
Motor Control Theory 1
... • In order for the full force to be delivered at the end point (foot on ground), any force contributed by the hip must be fully transferred to the knee, and then to the ankle and so on. ...
... • In order for the full force to be delivered at the end point (foot on ground), any force contributed by the hip must be fully transferred to the knee, and then to the ankle and so on. ...
Gravitational Induction and the Gyroscopic Force
... acceleration equation (1) below. There must be a deeper significance to Kepler’s law of areal velocity, which we will now investigate. The general acceleration equation is obtained by differentiating a position vector in polar coordinates twice with respect to time. It takes the form, ...
... acceleration equation (1) below. There must be a deeper significance to Kepler’s law of areal velocity, which we will now investigate. The general acceleration equation is obtained by differentiating a position vector in polar coordinates twice with respect to time. It takes the form, ...
Review 16 and 17
... • Directions determined by like repel and opposites attract (forces) or direction a small positive test charge would move (Electric Field) • Must add components separately i.e. all xcomponents first for resultant x-component. ...
... • Directions determined by like repel and opposites attract (forces) or direction a small positive test charge would move (Electric Field) • Must add components separately i.e. all xcomponents first for resultant x-component. ...