Unit 7
... Defining Torque as a Force at a distance from a pivot point Examples: Pushing on a door why is the hinge placed where it is? Meterstick determining the balancing point on a meterstick Torque is defined as the ability of a force to rotate an object around some axis. Second law of Equilibrium su ...
... Defining Torque as a Force at a distance from a pivot point Examples: Pushing on a door why is the hinge placed where it is? Meterstick determining the balancing point on a meterstick Torque is defined as the ability of a force to rotate an object around some axis. Second law of Equilibrium su ...
Energy and Work
... Work is not energy itself, but rather a transfer of energy. A force does work on an object if it causes the object to move. Work is always done on an object and results in a change in the object. The work done is equal to the change in energy. ...
... Work is not energy itself, but rather a transfer of energy. A force does work on an object if it causes the object to move. Work is always done on an object and results in a change in the object. The work done is equal to the change in energy. ...
Lecture 19: Motional emf
... Ex 18-3 A circular loop with a 10 cm-radius is placed in the presence of a uniform magnetic as shown in the figure. The field changes from 1.5 T to 0.5 T in 0.5 s. The loop has resistance 10W. What is the induced EMF? What current flows (specify the direction and magnitude)? ...
... Ex 18-3 A circular loop with a 10 cm-radius is placed in the presence of a uniform magnetic as shown in the figure. The field changes from 1.5 T to 0.5 T in 0.5 s. The loop has resistance 10W. What is the induced EMF? What current flows (specify the direction and magnitude)? ...
Ch 8.1 and 8.2 chap 8.1
... thrown at a wall with equal speeds. The rubber ball bounces, the clay bear sticks. Which one exerts a larger impulse on the wall? ...
... thrown at a wall with equal speeds. The rubber ball bounces, the clay bear sticks. Which one exerts a larger impulse on the wall? ...
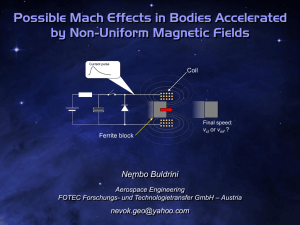
v mf - Yimg
... the derivation itself. How much is the magnitude of such acceleration affecting the expression of mass fluctuation, however, is not yet clear. At a first glance, the final equation: ...
... the derivation itself. How much is the magnitude of such acceleration affecting the expression of mass fluctuation, however, is not yet clear. At a first glance, the final equation: ...
Gravity - Tripod
... and acts along the line joining the centers of mass of the two masses. The forces on the two masses are equal in size but opposite in direction, obeying Newton's third law. Viewed as an exchange force, the massless exchange particle is called the graviton. The gravity force has the same form as Coul ...
... and acts along the line joining the centers of mass of the two masses. The forces on the two masses are equal in size but opposite in direction, obeying Newton's third law. Viewed as an exchange force, the massless exchange particle is called the graviton. The gravity force has the same form as Coul ...
Chp 12-2 Gravity Interactive Guide
... Think back to the astronauts on the moon. The moon’s mass is much smaller than Earth’s mass. Therefore, objects near the moon experience a smaller gravitational force than objects near Earth. The astronauts could jump very high on the moon because the gravitational force on them was small. Another w ...
... Think back to the astronauts on the moon. The moon’s mass is much smaller than Earth’s mass. Therefore, objects near the moon experience a smaller gravitational force than objects near Earth. The astronauts could jump very high on the moon because the gravitational force on them was small. Another w ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
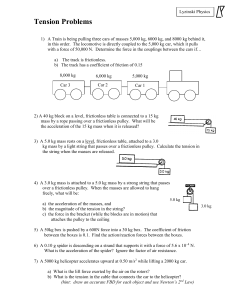
... 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignor ...
... 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignor ...