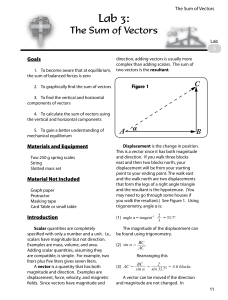
PHYSICAL SCI E06 11
... 1. The Student Will identify frames of reference and describe how they are used to measure motion. (p. 328 – 329) 2. TSW compare and contrast average speed and instantaneous speed and calculate the speed of an object using slopes. (p. 332 – 335) 3. TSW contrast speed and velocity and describe how ve ...
... 1. The Student Will identify frames of reference and describe how they are used to measure motion. (p. 328 – 329) 2. TSW compare and contrast average speed and instantaneous speed and calculate the speed of an object using slopes. (p. 332 – 335) 3. TSW contrast speed and velocity and describe how ve ...
E06 Physical Science TSW`s File
... 1. The Student Will identify frames of reference and describe how they are used to measure motion. (p. 328 – 329) 2. TSW compare and contrast average speed and instantaneous speed and calculate the speed of an object using slopes. (p. 332 – 335) 3. TSW contrast speed and velocity and describe how ve ...
... 1. The Student Will identify frames of reference and describe how they are used to measure motion. (p. 328 – 329) 2. TSW compare and contrast average speed and instantaneous speed and calculate the speed of an object using slopes. (p. 332 – 335) 3. TSW contrast speed and velocity and describe how ve ...
Air Resistance
... Recall that acceleration is the difference between the initial and final velocity, divided by the time. Also, from Newton’s second law, the net force on an object equals its mass times its acceleration. ...
... Recall that acceleration is the difference between the initial and final velocity, divided by the time. Also, from Newton’s second law, the net force on an object equals its mass times its acceleration. ...
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
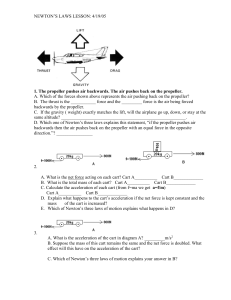
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
I Physics in Session 2
... Magnitude of B can change with time Area enclosed, A, can change with time Angle θ can change with time Any combination of the above can occur ...
... Magnitude of B can change with time Area enclosed, A, can change with time Angle θ can change with time Any combination of the above can occur ...
Amplitude (symbol: A)
... The focal length is a distance between the center of lens and its focus point. Focal length expresses a measure of how strongly lens converges or diverges light. A shorter focal length has greater optical power than one with a long focal length. ◆Converging lens Converging lens ,such as Biconvex, Pl ...
... The focal length is a distance between the center of lens and its focus point. Focal length expresses a measure of how strongly lens converges or diverges light. A shorter focal length has greater optical power than one with a long focal length. ◆Converging lens Converging lens ,such as Biconvex, Pl ...
doc - RPI
... ___ 1. To measure the mass of a planet, with the same radius as Earth, an astronaut drops an object from rest (relative to the surface of the planet) from a height h above the surface of the planet. The object arrives at the surface with a speed that is four (4) times what it would be if dropped fro ...
... ___ 1. To measure the mass of a planet, with the same radius as Earth, an astronaut drops an object from rest (relative to the surface of the planet) from a height h above the surface of the planet. The object arrives at the surface with a speed that is four (4) times what it would be if dropped fro ...
Electricity Unit Assignment
... rubber rod which had a charge of 2.3 x 10-8 C. The pithball then comes into contact with another pithball of equal size and shape. If the two pithballs are hung by two pieces of 3.00 cm thread from a single point (as shown) forming an angle of 15.0˚, what is the charge remaining on the original char ...
... rubber rod which had a charge of 2.3 x 10-8 C. The pithball then comes into contact with another pithball of equal size and shape. If the two pithballs are hung by two pieces of 3.00 cm thread from a single point (as shown) forming an angle of 15.0˚, what is the charge remaining on the original char ...