Magnetism 1. Which of the following does not create a magnetic field?
... 20. You are making a simple galvanometer to use as a voltmeter. You can select either a thin or thick wire to make the coil. A) Pick thick! The lower resistance means a more accurate reading of the current. B) Pick thin! The higher resistance will draw the least current when the voltmeter is wired i ...
... 20. You are making a simple galvanometer to use as a voltmeter. You can select either a thin or thick wire to make the coil. A) Pick thick! The lower resistance means a more accurate reading of the current. B) Pick thin! The higher resistance will draw the least current when the voltmeter is wired i ...
272 prac3
... (d) west (e) down 4. A charged particle is moving in a uniform, constant magnetic field. Which of the following statements concerning the magnetic force exerted on the particle is false? (a) it does no work on the particle (b) it increases the speed of the particle (c) it changes the velocity of the ...
... (d) west (e) down 4. A charged particle is moving in a uniform, constant magnetic field. Which of the following statements concerning the magnetic force exerted on the particle is false? (a) it does no work on the particle (b) it increases the speed of the particle (c) it changes the velocity of the ...
Magnetic Fields
... the directions of a needle near a spherical natural magnet formed lines that encircled the sphere and passed through two points diametrically opposite each other, which he called the poles of the magnet. Subsequent experiments showed that every magnet, regardless of its shape, has two poles, called ...
... the directions of a needle near a spherical natural magnet formed lines that encircled the sphere and passed through two points diametrically opposite each other, which he called the poles of the magnet. Subsequent experiments showed that every magnet, regardless of its shape, has two poles, called ...
Physics 272: Electricity and Magnetism
... N Current loops • If we have a bunch of loops sitting on top of each other, we can usually pretend they’re all in exactly the same place. • Field from N loops = N*Field from one loop ...
... N Current loops • If we have a bunch of loops sitting on top of each other, we can usually pretend they’re all in exactly the same place. • Field from N loops = N*Field from one loop ...
X-Ray Tube for Use in Magnetic Fields
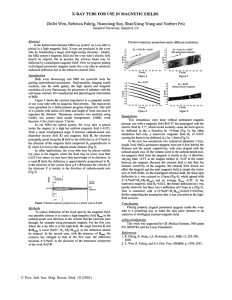
... present: one with a magnetic field B=0.3T but misaligned with the electric field by 5.7”, which would normally cause the focal spot to be deflected in the x direction by -0.9mm (Fig 2); the other simulation had only a transverse magnetic field B, of 0.02T causing the beam to be deflected in y by 1.8 ...
... present: one with a magnetic field B=0.3T but misaligned with the electric field by 5.7”, which would normally cause the focal spot to be deflected in the x direction by -0.9mm (Fig 2); the other simulation had only a transverse magnetic field B, of 0.02T causing the beam to be deflected in y by 1.8 ...
Electromagnetism: Home
... it is the south side. Opposite charges attract and so do opposite poles. Question 5: How could you determine the direction of the earth’s north and south poles? The easiest way is to use a compass. You can actually create a compass using an electromagnet that we created in this lab. ...
... it is the south side. Opposite charges attract and so do opposite poles. Question 5: How could you determine the direction of the earth’s north and south poles? The easiest way is to use a compass. You can actually create a compass using an electromagnet that we created in this lab. ...
Lecture 5: Pre-reading Magnetic Fields and Forces
... Our last topic for this lecture is electromagnetic induction, which was discovered by Faraday. Faraday found that if you change the flux of the magnetic field through a loop of wire, it will induce a current in the wire. Now what is flux? Imagine the magnetic field lines flowing through space. If yo ...
... Our last topic for this lecture is electromagnetic induction, which was discovered by Faraday. Faraday found that if you change the flux of the magnetic field through a loop of wire, it will induce a current in the wire. Now what is flux? Imagine the magnetic field lines flowing through space. If yo ...
magnetism
... This force has its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the magnetic field lines, decreases in value at other angles, and becomes zero when the particle moves along the field lines. We shall make use of these observations in describing the magnetic field. ...
... This force has its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the magnetic field lines, decreases in value at other angles, and becomes zero when the particle moves along the field lines. We shall make use of these observations in describing the magnetic field. ...
Magnetic Fabric in Granitic Rocks: its Intrusive Origin and
... the magma flowed vertically. On the other hand, it is oblique or horizontal in the bodies where magma could not ascend vertically and moved in a more complex way. Magnetic lineation can be vertical, horizontal or oblique according to the local direction of magma flow. Magnetic fabric elements usuall ...
... the magma flowed vertically. On the other hand, it is oblique or horizontal in the bodies where magma could not ascend vertically and moved in a more complex way. Magnetic lineation can be vertical, horizontal or oblique according to the local direction of magma flow. Magnetic fabric elements usuall ...
Jeopardy Review (PowerPoint)
... A motor that rotates clockwise has a magnetic field going from left to right What are the poles on the red and blue bobbins as they rotate? ...
... A motor that rotates clockwise has a magnetic field going from left to right What are the poles on the red and blue bobbins as they rotate? ...
P21 Homework Set #5
... Assess: Each point is affected by both wires, so the contributions must add according to the direction of the field points. The equation of the magnetic field does not give its direction, only its magnitude. To get the direction you must use the right-hand rule. If the fields are in the same directi ...
... Assess: Each point is affected by both wires, so the contributions must add according to the direction of the field points. The equation of the magnetic field does not give its direction, only its magnitude. To get the direction you must use the right-hand rule. If the fields are in the same directi ...
Magnetism, Electromagnetism, & Electromagnetic Induction
... Electromagnetic Induction Chapters 24-25 ...
... Electromagnetic Induction Chapters 24-25 ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.