Electromagnetics - University of Idaho
... • As devices get smaller and smaller, and frequencies get higher and higher, circuit theory is less able to adequately describe the performance or to predict the operation of circuits. • At very high frequencies, transmission line and guided wave theory must be used - high speed electronics, micro/n ...
... • As devices get smaller and smaller, and frequencies get higher and higher, circuit theory is less able to adequately describe the performance or to predict the operation of circuits. • At very high frequencies, transmission line and guided wave theory must be used - high speed electronics, micro/n ...
Electromagnetic Radiation Magnetism, and Electrostatics
... 22. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy? a. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency increase b. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency decrease c. as energy increases, wavelength increases and frequency de ...
... 22. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy? a. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency increase b. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency decrease c. as energy increases, wavelength increases and frequency de ...
Homework No. 05 (Fall 2014) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I Due date: Thursday, 2014 Oct 16, 4.00pm ...
... PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I Due date: Thursday, 2014 Oct 16, 4.00pm ...
Midterm Exam No. 03 (Spring 2015)
... 1. (20 points.) This question is not directly related to what we covered in class, but you will, hopefully, appreciate the content. Kindly watch the (54 minute) video at http://www.uctv.tv/shows/The-World-as-a-Hologram-11140, which contains a lecture titled “The World as a Hologram” by Raphael Bouss ...
... 1. (20 points.) This question is not directly related to what we covered in class, but you will, hopefully, appreciate the content. Kindly watch the (54 minute) video at http://www.uctv.tv/shows/The-World-as-a-Hologram-11140, which contains a lecture titled “The World as a Hologram” by Raphael Bouss ...
Chapter 15 Lesson 2 How are Electricity and Magnetism Related
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
Derivation of the Universal Force Law—Part 4
... The non-radial terms of the force law explain the experimentally observed curling of plasma currents, the tilting of the orbits of the planets with respect to the equatorial plane of the sun, and certain inertial gyroscope motions. The derived force law satisfies Newton’s third law, conservation of ...
... The non-radial terms of the force law explain the experimentally observed curling of plasma currents, the tilting of the orbits of the planets with respect to the equatorial plane of the sun, and certain inertial gyroscope motions. The derived force law satisfies Newton’s third law, conservation of ...
23.4 The Electric Field
... The electric field vector E at a point in space is defined as the electric force Fe acting on a positive test charge q0 placed at that point divided by the test charge: ...
... The electric field vector E at a point in space is defined as the electric force Fe acting on a positive test charge q0 placed at that point divided by the test charge: ...
Chapter 34
... around any closed path, equals the rate of change of the magnetic flux through any surface bounded by that path d B E ds dt ...
... around any closed path, equals the rate of change of the magnetic flux through any surface bounded by that path d B E ds dt ...
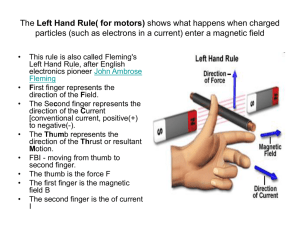
The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
... The Right Hand Rule simply shows how a current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field • point your thumb in the direction of the current and let your fingers assume a curved position, the magnetic field circling around the wires flows in the direction in which your ...
... The Right Hand Rule simply shows how a current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field • point your thumb in the direction of the current and let your fingers assume a curved position, the magnetic field circling around the wires flows in the direction in which your ...
Week 13 - Electromagnetic Waves
... they start to oscillate, i.e. they produce a current. For the charges to be able to move significantly they must have some space to move on. Therefore the vertical antennas indicate that the electromagnetic waves are vertically polarized so the electric field in the wave is able to do work on those ...
... they start to oscillate, i.e. they produce a current. For the charges to be able to move significantly they must have some space to move on. Therefore the vertical antennas indicate that the electromagnetic waves are vertically polarized so the electric field in the wave is able to do work on those ...
Gravitational Relativity Proposed by David Penny The only intrinsic
... medium of transport of the electromagnetic waves. The speed of light and other transverse electromagnetic waves is not constant but varies with the strength of the electric and magnetic constants of the medium of transport, even in deep space. Longitudinal gravo-electric wave-fields are the medium o ...
... medium of transport of the electromagnetic waves. The speed of light and other transverse electromagnetic waves is not constant but varies with the strength of the electric and magnetic constants of the medium of transport, even in deep space. Longitudinal gravo-electric wave-fields are the medium o ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.