The Top 5- Vectors
... 1. Charge only comes in whole multiples of the elementary charge (ex. +53e, -1000e ) OR charge only comes in multiples of 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs (ex. 4.8 x 10-18 C) 2. Positives DON’T move in solids. Negative charges move from the more negative to the ...
... 1. Charge only comes in whole multiples of the elementary charge (ex. +53e, -1000e ) OR charge only comes in multiples of 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs (ex. 4.8 x 10-18 C) 2. Positives DON’T move in solids. Negative charges move from the more negative to the ...
Diapositiva 1 - Instituto de Astronomía
... In the case of light, the wavelength is so short that a specific distance, called the ångstrom (Å), has been defined. One ångstrom = 10-10 m or 10-8 cm. Visible light 3900 Å to 7700 Å Electromagnetic energy outside this range is no longer visible to the human eye. ...
... In the case of light, the wavelength is so short that a specific distance, called the ångstrom (Å), has been defined. One ångstrom = 10-10 m or 10-8 cm. Visible light 3900 Å to 7700 Å Electromagnetic energy outside this range is no longer visible to the human eye. ...
Cathode Ray Research - ND
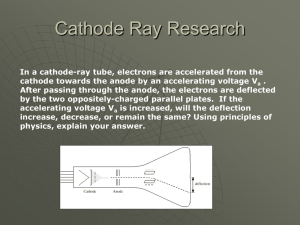
... cathode towards the anode by an accelerating voltage Va . After passing through the anode, the electrons are deflected by the two oppositely-charged parallel plates. If the accelerating voltage Va is increased, will the deflection increase, decrease, or remain the same? Using principles of physics, ...
... cathode towards the anode by an accelerating voltage Va . After passing through the anode, the electrons are deflected by the two oppositely-charged parallel plates. If the accelerating voltage Va is increased, will the deflection increase, decrease, or remain the same? Using principles of physics, ...
Slide 1
... You have seen how a changing magnetic field can induce a “swirling” current in a conductor (the beginning of this lecture). If a conductor and a magnetic field are in relative motion, the magnetic force on charged particles in the conductor causes circulating currents. These currents are called “edd ...
... You have seen how a changing magnetic field can induce a “swirling” current in a conductor (the beginning of this lecture). If a conductor and a magnetic field are in relative motion, the magnetic force on charged particles in the conductor causes circulating currents. These currents are called “edd ...
Ch 11 Self Assessment
... Physics 30 Self-Assessment Checklist Upon completion of Chapter 11: I will describe electrical phenomena using the electric field theory. To meet an acceptable standard I will be able to: ...
... Physics 30 Self-Assessment Checklist Upon completion of Chapter 11: I will describe electrical phenomena using the electric field theory. To meet an acceptable standard I will be able to: ...
Learning Goals - אתר מורי הפיזיקה
... Determine the variables that affect how charged bodies interact Predict how charged bodies will interact Describe the strength and direction of the electric field around a charged body. Use free-body diagrams and vector addition to help explain the interactions. Background: We will have brie ...
... Determine the variables that affect how charged bodies interact Predict how charged bodies will interact Describe the strength and direction of the electric field around a charged body. Use free-body diagrams and vector addition to help explain the interactions. Background: We will have brie ...
Charged particles moving in a magnetic field
... Some astrophysicists believe that the radio signals of 10 Hz reaching us from Jupiter are emitted by electrons orbiting in Jupiter’s magnetic field. Assuming the frequency of the radio emission is identical to the cyclotron frequency; find the strength of the magnetic field around Jupiter. ...
... Some astrophysicists believe that the radio signals of 10 Hz reaching us from Jupiter are emitted by electrons orbiting in Jupiter’s magnetic field. Assuming the frequency of the radio emission is identical to the cyclotron frequency; find the strength of the magnetic field around Jupiter. ...
About that problem that we did in class
... The other approach is via the Electric Field concept where we remove the charge B entirely from the picture and calculate the effect that the other charges have on the space where B was located. After this, we return the charge to the point to calculate the force on it. The beauty of this approach i ...
... The other approach is via the Electric Field concept where we remove the charge B entirely from the picture and calculate the effect that the other charges have on the space where B was located. After this, we return the charge to the point to calculate the force on it. The beauty of this approach i ...
Physics 2 - dhsphysics
... 10. What direction are the magnetic field lines drawn? 11. What happens to the voltage and current in a loop of wires if the number of coils is doubled or tripled? 12. What happens to the voltage and current in a loop of wires if the magnet is moved in and out of the coil more rapidly? 13. What are ...
... 10. What direction are the magnetic field lines drawn? 11. What happens to the voltage and current in a loop of wires if the number of coils is doubled or tripled? 12. What happens to the voltage and current in a loop of wires if the magnet is moved in and out of the coil more rapidly? 13. What are ...
Application of Newton`s Laws Circular Motion Answers
... b. The only horizontal force acting on the car is the frictional force, so the centripetal force is the frictional force. c. The frictional force must be static friction since the car is not sliding. d. Since the car is on the verge of sliding the force will be the maximum frictional force. ...
... b. The only horizontal force acting on the car is the frictional force, so the centripetal force is the frictional force. c. The frictional force must be static friction since the car is not sliding. d. Since the car is on the verge of sliding the force will be the maximum frictional force. ...
Chapter 7 Magnetism: Electromagnets
... o Loudspeaker (344) – a device that changes electrical energy into sound o Microphone (345) – a device that uses a magnet to convert sound into electrical signals What is an electromagnet? Main Idea An electric current flowing through a wire produces a magnetic field around the wire. Supporting Deta ...
... o Loudspeaker (344) – a device that changes electrical energy into sound o Microphone (345) – a device that uses a magnet to convert sound into electrical signals What is an electromagnet? Main Idea An electric current flowing through a wire produces a magnetic field around the wire. Supporting Deta ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.