PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... The problem of interaction of electromagnetic fields (EMF) with medium is being discussed for years, but a unique solution has not been found yet. In recent years attempts to create materials with unique electromagnetic values are being undertaken. Therefore, the issue of interaction of EMF with med ...
... The problem of interaction of electromagnetic fields (EMF) with medium is being discussed for years, but a unique solution has not been found yet. In recent years attempts to create materials with unique electromagnetic values are being undertaken. Therefore, the issue of interaction of EMF with med ...
What is a Force? (PowerPoint)
... but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of atoms. Molecular force: The attraction of molecules for each other results in two kinds of forc ...
... but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of atoms. Molecular force: The attraction of molecules for each other results in two kinds of forc ...
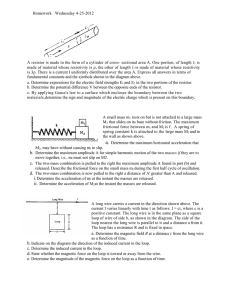
Homework Wednesday 4-25-2012 A resistor is made in the form of a
... released. Describe the frictional force on the small mass ml during the first half cycle of oscillation. d. The two-mass combination is now pulled to the right a distance of A' greater than A and released. i. Determine the acceleration of ml at the instant the masses are released. ii. Determine the ...
... released. Describe the frictional force on the small mass ml during the first half cycle of oscillation. d. The two-mass combination is now pulled to the right a distance of A' greater than A and released. i. Determine the acceleration of ml at the instant the masses are released. ii. Determine the ...
Force on a Current Carrying Wire
... A few words of caution to begin with. The magnets you are dealing with are fairly strong. Do not get them too close to the computers in the lab, your credit cards, or to your electronic devices. We will also be dealing with fairly high currents. Some caution and some common sense is essential. To st ...
... A few words of caution to begin with. The magnets you are dealing with are fairly strong. Do not get them too close to the computers in the lab, your credit cards, or to your electronic devices. We will also be dealing with fairly high currents. Some caution and some common sense is essential. To st ...
Vortex buoyancy in superfluid and superconducting neutron stars
... . The relation between these tensors will depend on a detailed microphysics model of a mixture. • This is in full analogy with the ordinary electrodynamics where, in order to close ...
... . The relation between these tensors will depend on a detailed microphysics model of a mixture. • This is in full analogy with the ordinary electrodynamics where, in order to close ...
5) – z (into page)
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
The Earth`s Magnetic Field
... The total field, then, will be the vector sum of the Earth's magnetic field and the magnet's field, and in the case when both fields are perpendicular to each other, it will be: Tan ө = B/Be Where ө is the angle between the total field and the Earth's field can be measured by using a compass, whose ...
... The total field, then, will be the vector sum of the Earth's magnetic field and the magnet's field, and in the case when both fields are perpendicular to each other, it will be: Tan ө = B/Be Where ө is the angle between the total field and the Earth's field can be measured by using a compass, whose ...
Newton`s Third Law of Motion
... A closer examination shows that a force is not a thing in itself, but a part of an interaction between one thing and another ...
... A closer examination shows that a force is not a thing in itself, but a part of an interaction between one thing and another ...
Solution to ST-1 - kaliasgoldmedal
... a certain time instant t, we record that the terminal voltage applied to the excitation winding is v, the excitation winding current i, the position of the movable plunger x, and the force acting on the plunger F with the reference direction chosen in the positive direction of the x axis, as shown i ...
... a certain time instant t, we record that the terminal voltage applied to the excitation winding is v, the excitation winding current i, the position of the movable plunger x, and the force acting on the plunger F with the reference direction chosen in the positive direction of the x axis, as shown i ...
Why is Maxwell`s Theory so hard to understand?
... How did it happen that Maxwell's theory was so widely ignored? After all, Maxwell was not like his contemporary Gregor Mendel, a monk working in an obscure monastery garden in Bohemia. Maxwell was a famous professor, director of the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge, a leading figure in the British ...
... How did it happen that Maxwell's theory was so widely ignored? After all, Maxwell was not like his contemporary Gregor Mendel, a monk working in an obscure monastery garden in Bohemia. Maxwell was a famous professor, director of the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge, a leading figure in the British ...
Document
... Ignore it: it’s just one of many experiments Perform an independent analysis of the data Perform a parallel, independent experiment Throw GR out: it’s clearly wrong Stop teaching GR in schools until it’s resolved B,C ...
... Ignore it: it’s just one of many experiments Perform an independent analysis of the data Perform a parallel, independent experiment Throw GR out: it’s clearly wrong Stop teaching GR in schools until it’s resolved B,C ...
Magnetic Force on an electric current
... the interaction of the surrounding field and the field caused by the current (electromagnetic induction). F= nBIl(sin) F: magnetic force on an electric current, n: number of current-carrying wires, B: magnetic field (strength) caused by magnets around the wires, I: current travelling through the wi ...
... the interaction of the surrounding field and the field caused by the current (electromagnetic induction). F= nBIl(sin) F: magnetic force on an electric current, n: number of current-carrying wires, B: magnetic field (strength) caused by magnets around the wires, I: current travelling through the wi ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.