Electrostatics Problems
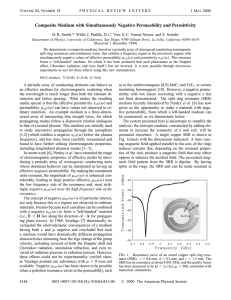
... object, and another with a negatively charged object. In each case, it is the electrons which move (they are more loosely bound than the protons): Neutral object ...
... object, and another with a negatively charged object. In each case, it is the electrons which move (they are more loosely bound than the protons): Neutral object ...
Lecture 2 - Department of Applied Physics
... be distinguished. Forces due to chemical bonds, van der Waals attraction, repulsion forces, and others have all such short ranges that ...
... be distinguished. Forces due to chemical bonds, van der Waals attraction, repulsion forces, and others have all such short ranges that ...
REFLECTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN GYROTROPIC
... a moving plasma and from an ionization wave produced in a stationary plasma. The calculations are made in the geometric optics approximation, and a more exact solution is found near the point at which this approximation becomes invalid. It is shown that in all cases considered the frequency increase ...
... a moving plasma and from an ionization wave produced in a stationary plasma. The calculations are made in the geometric optics approximation, and a more exact solution is found near the point at which this approximation becomes invalid. It is shown that in all cases considered the frequency increase ...
Electric Forces
... Chapter 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material throu ...
... Chapter 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material throu ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... • Upper Drawing: B Field from Magnet is INCREASING so Loop Current is Clockwise and Produces an Opposing B Field that Tries to CANCEL the INCREASING Magnet Field • Lower Drawing: B Field from Magnet is DECREASING so Loop Current is ...
... • Upper Drawing: B Field from Magnet is INCREASING so Loop Current is Clockwise and Produces an Opposing B Field that Tries to CANCEL the INCREASING Magnet Field • Lower Drawing: B Field from Magnet is DECREASING so Loop Current is ...
The Wonders Of Uranus
... of B. Soldano must be viewed. Is it not obviously the ca_"e that if Soldano is correct, what appears to us as matter is merely a singularity within a highly complex field structure: That is the proper implication of the divergence of the inertial and gravitational binding energy of matter. The only ...
... of B. Soldano must be viewed. Is it not obviously the ca_"e that if Soldano is correct, what appears to us as matter is merely a singularity within a highly complex field structure: That is the proper implication of the divergence of the inertial and gravitational binding energy of matter. The only ...
1 Equipotential and Electric Field Mapping Experiment
... If we push them together, we must act against the force of these charges. Let’s figure out how much energy we have to expend (how much work we must do) to get them closer to one another. According to the work-energy theorem, if one component in a closed system pushes or pulls on other components, th ...
... If we push them together, we must act against the force of these charges. Let’s figure out how much energy we have to expend (how much work we must do) to get them closer to one another. According to the work-energy theorem, if one component in a closed system pushes or pulls on other components, th ...
Localized Polaritons and Second-Harmonic
... [2], negative refractive index optics [3], nonlinear optics [4,5], and more. The linear and nonlinear responses of these materials are dominated by localized surface plasmons, exhibiting pronounced resonances in the extinction spectra. Basic nonlinear processes such as secondharmonic generation and ...
... [2], negative refractive index optics [3], nonlinear optics [4,5], and more. The linear and nonlinear responses of these materials are dominated by localized surface plasmons, exhibiting pronounced resonances in the extinction spectra. Basic nonlinear processes such as secondharmonic generation and ...
A New Constraint on Strongly Coupled Field Theories
... β function [2]. In fact, a combination of the ladder gap equation and the two-loop beta function give a critical value F crit/N = (100N 2 − 66)/(25N 2 − 15)(→ 4 as N → ∞). The reliability of this result is far from clear, however, since higher order effects are not obviously small. So whether the ch ...
... β function [2]. In fact, a combination of the ladder gap equation and the two-loop beta function give a critical value F crit/N = (100N 2 − 66)/(25N 2 − 15)(→ 4 as N → ∞). The reliability of this result is far from clear, however, since higher order effects are not obviously small. So whether the ch ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.