Static Electricity - HSphysics
... Then, the drum is rolled through the toner, which is positively charged so that it will cling to the areas of negative charge on the printer drum. The printer feeds a piece of paper, which is given an even stronger negative charge by the transfer corona wire before being rolled past the drum. The e ...
... Then, the drum is rolled through the toner, which is positively charged so that it will cling to the areas of negative charge on the printer drum. The printer feeds a piece of paper, which is given an even stronger negative charge by the transfer corona wire before being rolled past the drum. The e ...
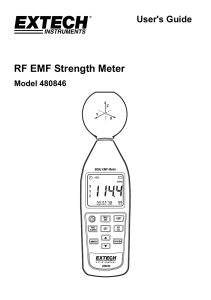
RF EMF Strength Meter
... This meter is a broadband device for monitoring high-frequency radiation in the range of 10MHz to 8GHz. The non-directional electric field and high sensitivity also allow measurements of electric field strength in TEM cells and absorber rooms. The unit of measurement and the measurement types are ex ...
... This meter is a broadband device for monitoring high-frequency radiation in the range of 10MHz to 8GHz. The non-directional electric field and high sensitivity also allow measurements of electric field strength in TEM cells and absorber rooms. The unit of measurement and the measurement types are ex ...
Electric Fields
... I had problems understanding the concept and calculation of charge on and infinite line ??Infinite lines of chargee??? it would help alot to go over those, everything else is simmplle Posi9ves and nega9ves, what do they really mean? ...
... I had problems understanding the concept and calculation of charge on and infinite line ??Infinite lines of chargee??? it would help alot to go over those, everything else is simmplle Posi9ves and nega9ves, what do they really mean? ...
Amber 8
... • Microcanonical ensemble (NVE) : The thermodynamic state characterized by a fixed number of atoms, N, a fixed volume, V, and a fixed energy, E. This corresponds to an isolated system. • Canonical Ensemble (NVT): This is a collection of all systems whose thermodynamic state is characterized by a fix ...
... • Microcanonical ensemble (NVE) : The thermodynamic state characterized by a fixed number of atoms, N, a fixed volume, V, and a fixed energy, E. This corresponds to an isolated system. • Canonical Ensemble (NVT): This is a collection of all systems whose thermodynamic state is characterized by a fix ...
Quasiparticles in the Quantum Hall Effect Janik Kailasvuori Stockholm University
... deals with properties of for example metals and other crystals. However, today this branch includes a very diverse range of subjects like for example, nanophysics, soft condensed matter (e.g. structures in polymer solutions) and macroscopic quantum mechanical effects such as superconductivity, super ...
... deals with properties of for example metals and other crystals. However, today this branch includes a very diverse range of subjects like for example, nanophysics, soft condensed matter (e.g. structures in polymer solutions) and macroscopic quantum mechanical effects such as superconductivity, super ...
Lecture 8 Plasma shaping and vertical stability
... (contamination of the machine) Tungsten has very high Z, but takes the heat loads very well ...
... (contamination of the machine) Tungsten has very high Z, but takes the heat loads very well ...
On the Theory of Quanta Louis-Victor de Broglie (1892-1987) P ARIS
... Following successful applications in acoustics, hydrodynamics, optics and capillary effects, it appears that Mechanics reigned over all physical phenomena. With somewhat more difficulty, in the 19th century the new discipline of Thermodynamics was also brought within reach of Mechanics. Although one ...
... Following successful applications in acoustics, hydrodynamics, optics and capillary effects, it appears that Mechanics reigned over all physical phenomena. With somewhat more difficulty, in the 19th century the new discipline of Thermodynamics was also brought within reach of Mechanics. Although one ...
Lecture Notes 09: AC EM Electromagnetic Fields Associated with a Circular Parallel-Plate Capacitor
... Eind r , t Eind r , t zˆ i.e. the induced E -field points in the ẑ direction (must be B Bˆ ) ...
... Eind r , t Eind r , t zˆ i.e. the induced E -field points in the ẑ direction (must be B Bˆ ) ...
lecture chapter 21
... 5. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a distance of 2.50 m from a 90.0-nC charge? 6. Two point charges of +40.0 μC and -10.00 μC are separated by a distance of 10.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges? 7. Three 3.0 μC charges are ...
... 5. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a distance of 2.50 m from a 90.0-nC charge? 6. Two point charges of +40.0 μC and -10.00 μC are separated by a distance of 10.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges? 7. Three 3.0 μC charges are ...
Essential Learning Outcomes (ELOs) Advanced Placement Physics (B & C)
... body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. b. [B/C] Students should be able to apply Newton's Third Law in analyzing the force of contact between two bodies that accelerate together along a horizontal or vertical line, or between two surfaces that s ...
... body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. b. [B/C] Students should be able to apply Newton's Third Law in analyzing the force of contact between two bodies that accelerate together along a horizontal or vertical line, or between two surfaces that s ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.