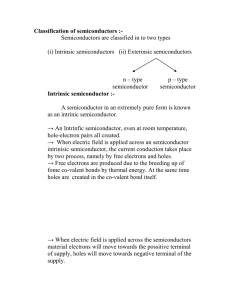
An Integrated Magnetic Isolated Two
... be in either nonisolated [9] or isolated format [10]. The isolated boost topology, which is shown in Fig. 1 [10], is attractive in applications such as power factor correction (PFC) with isolation and battery or fuel cell powered devices to generate high output voltage from low input voltage [9]–[12 ...
... be in either nonisolated [9] or isolated format [10]. The isolated boost topology, which is shown in Fig. 1 [10], is attractive in applications such as power factor correction (PFC) with isolation and battery or fuel cell powered devices to generate high output voltage from low input voltage [9]–[12 ...
LM35 Precision Centigrade Temperature Sensors (Rev. D)
... The LM35 is applied easily in the same way as other integrated-circuit temperature sensors. Glue or cement the device to a surface and the temperature should be within about 0.01°C of the surface temperature. This presumes that the ambient air temperature is almost the same as the surface temperatur ...
... The LM35 is applied easily in the same way as other integrated-circuit temperature sensors. Glue or cement the device to a surface and the temperature should be within about 0.01°C of the surface temperature. This presumes that the ambient air temperature is almost the same as the surface temperatur ...
1. Lecture #1
... earth’s magnetic field is small, so the motional emf will be small as well unless the speed and the length are quite large. The tethered satellite generated a much higher voltage due to its much greater speed and the great length of the tether, the moving conductor. ...
... earth’s magnetic field is small, so the motional emf will be small as well unless the speed and the length are quite large. The tethered satellite generated a much higher voltage due to its much greater speed and the great length of the tether, the moving conductor. ...
A Pulsed Field Gradient Spin-Echo Method for Diffusion
... the difference is in absolute magnitude between the gradient pulses in a bipolar pair, the less efficient is the cancellation of the magnetic field transients following the pair. As the calibrated gradient strength is dependent on the time integral of the magnetic field gradient over the test sample ...
... the difference is in absolute magnitude between the gradient pulses in a bipolar pair, the less efficient is the cancellation of the magnetic field transients following the pair. As the calibrated gradient strength is dependent on the time integral of the magnetic field gradient over the test sample ...
The amonalous transport in plasmas
... turbulent electrostatic field with long-range correlations was studied by the spectral methods from the abstract ergodic theory. By the extension of the methods from [1] to higher dimension three-dimensional linear model of the edge plasma turbulence was obtained. A stable numerical approximation sc ...
... turbulent electrostatic field with long-range correlations was studied by the spectral methods from the abstract ergodic theory. By the extension of the methods from [1] to higher dimension three-dimensional linear model of the edge plasma turbulence was obtained. A stable numerical approximation sc ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.