Full Syllabus Set-3
... Using Guass' law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spheri• cal conducting shell of radius R at a point (i) outside and (ii) inside the shell. Plot a graph showing variation of electric field as a function of r > R and r < R (r being the distance from the centre ...
... Using Guass' law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spheri• cal conducting shell of radius R at a point (i) outside and (ii) inside the shell. Plot a graph showing variation of electric field as a function of r > R and r < R (r being the distance from the centre ...
Slide 1 Magnetism - Spring Branch ISD
... voltage is the ____________ across all branch points (think of them as separate series circuits connected to a battery) ...
... voltage is the ____________ across all branch points (think of them as separate series circuits connected to a battery) ...
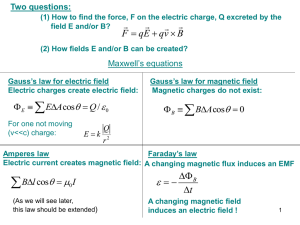
magnetic effect of electric current
... around that conductor this is known as magnetic effect of electric current. The strength of this magnetic field is measured in the form of magnetic induction which can be defined as: “The magnetic induction of a magnetic field at any point can be defined as the magnetic flux per unit area around tha ...
... around that conductor this is known as magnetic effect of electric current. The strength of this magnetic field is measured in the form of magnetic induction which can be defined as: “The magnetic induction of a magnetic field at any point can be defined as the magnetic flux per unit area around tha ...
Using Electricity - Summary Notes.CWK (DR)
... There is only one path for current in a series circuit and so the current is the same at all points. ...
... There is only one path for current in a series circuit and so the current is the same at all points. ...
Question 7
... bulk magnetization induces an electrical current the coil, which is recorded. The resulting signal is known as the Free Induction Decay (FID). (see below) The FID is a function of time. In order to obtain the spectrum this signal has to undergo a Fourier transform to represent it in the frequency ...
... bulk magnetization induces an electrical current the coil, which is recorded. The resulting signal is known as the Free Induction Decay (FID). (see below) The FID is a function of time. In order to obtain the spectrum this signal has to undergo a Fourier transform to represent it in the frequency ...
On a New Action of the Magnet on Electric Currents
... Some of the series seemed to show a sligoht increase of resistance due to the action of the inagnet, some a slight decrease, the greatest chang,e indicated by any complete series being a decrease of about one part in a hundred and fifty thousand. Nearly all the other series indicated a very much sma ...
... Some of the series seemed to show a sligoht increase of resistance due to the action of the inagnet, some a slight decrease, the greatest chang,e indicated by any complete series being a decrease of about one part in a hundred and fifty thousand. Nearly all the other series indicated a very much sma ...
Sample Question Paper Class XII Physics (Applicable for March
... The given graphs show the variation of intensity of magnetization I with strength of applied magnetic field H for two magnetic materials P and Q. ...
... The given graphs show the variation of intensity of magnetization I with strength of applied magnetic field H for two magnetic materials P and Q. ...
resistance - Erwin Sitompul
... Resistance and Resistivity One of the characteristics of a conductor is the electrical resistance. We determine the resistance between any two points of a conductor by applying a potential difference V between those points and measuring the current i that results. ...
... Resistance and Resistivity One of the characteristics of a conductor is the electrical resistance. We determine the resistance between any two points of a conductor by applying a potential difference V between those points and measuring the current i that results. ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.