Chapter 14 PowerPoint
... • Question 7 Read this question carefully – it’s an electron, not a photon p mv 9.11 10 31kg 0.110 3.00 108 m s 3.01 10 23 kg m s ...
... • Question 7 Read this question carefully – it’s an electron, not a photon p mv 9.11 10 31kg 0.110 3.00 108 m s 3.01 10 23 kg m s ...
Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy
... The quantum mechanical analysis of the simple harmonic oscillator is discussed at length in elementary textbooks. As expected, the system is quantized. The energies of the system are characterized by En= (n + %)hvowhere n is a positive integer and v, = [J(k/m)]~n.Note that the quantum mechanical and ...
... The quantum mechanical analysis of the simple harmonic oscillator is discussed at length in elementary textbooks. As expected, the system is quantized. The energies of the system are characterized by En= (n + %)hvowhere n is a positive integer and v, = [J(k/m)]~n.Note that the quantum mechanical and ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
The University of Georgia Department of Physics and Astronomy
... (b) The frequencies in the Lyman series get closer and closer together as the principal quantum number, n, of the excited state gets larger and larger. The observed spectral lines in a gas of atoms are not absolutely sharp, because the individual atoms are in motion, and therefore radiation emitted ...
... (b) The frequencies in the Lyman series get closer and closer together as the principal quantum number, n, of the excited state gets larger and larger. The observed spectral lines in a gas of atoms are not absolutely sharp, because the individual atoms are in motion, and therefore radiation emitted ...
CH 28 – Atomic Physics
... atoms were like a plum pudding, then the scattering would be more uniform and none would be expected to be completely deflected backwards. Rutherford’s interpretation was that the atom must have a massive, positively charged nucleus. Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom If a tube is filled with a gas su ...
... atoms were like a plum pudding, then the scattering would be more uniform and none would be expected to be completely deflected backwards. Rutherford’s interpretation was that the atom must have a massive, positively charged nucleus. Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom If a tube is filled with a gas su ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... The electrons in the outermost shell are the ___________ ____________ the electrons on an atom that can be gained or lost in a chemical reaction. ...
... The electrons in the outermost shell are the ___________ ____________ the electrons on an atom that can be gained or lost in a chemical reaction. ...
Atomic Physics
... atoms were like a plum pudding, then the scattering would be more uniform and none would be expected to be completely deflected backwards. Rutherford’s interpretation was that the atom must have a massive, positively charged nucleus. Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom If a tube is filled with a gas su ...
... atoms were like a plum pudding, then the scattering would be more uniform and none would be expected to be completely deflected backwards. Rutherford’s interpretation was that the atom must have a massive, positively charged nucleus. Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom If a tube is filled with a gas su ...
Types of Measurement
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
1 2016-17 Honors Chemistry Review for the Final Exam Each unit
... What would be the volume of this gas (in liters) if you allowed it to expand to the pressure of the surrounding air (0.974 atm)? Assume temperature remains constant. ...
... What would be the volume of this gas (in liters) if you allowed it to expand to the pressure of the surrounding air (0.974 atm)? Assume temperature remains constant. ...
Read PDF - Physics
... L1 L2 L3 . When all three photons take either the short or the long path the relative arrival time is the same, so the S1 S2 S3 , and L1 L2 L3 events overlap, forming the central peak. This overlap is a coherent superposition, leading to a three-photon coincidence rate that depends on the phases φn ...
... L1 L2 L3 . When all three photons take either the short or the long path the relative arrival time is the same, so the S1 S2 S3 , and L1 L2 L3 events overlap, forming the central peak. This overlap is a coherent superposition, leading to a three-photon coincidence rate that depends on the phases φn ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... energy level. Letter denoting the type of orbital. Superscript denoting the number of electrons in ...
... energy level. Letter denoting the type of orbital. Superscript denoting the number of electrons in ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
... Helium (2 valence electrons) is in the same column as neon (8 valence electrons) because both have full outer energy levels. This gives them similar properties. ...
... Helium (2 valence electrons) is in the same column as neon (8 valence electrons) because both have full outer energy levels. This gives them similar properties. ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... A) transition metals B) halogens C) alkali metals D) alkaline earth metals E) noble gases 34. Which one of the following elements is a transition element? A) antimony B) barium C) chromium D) potassium E) selenium 35. According to the zeroth law of thermodynamics: a) Energy is neither lost nor gaine ...
... A) transition metals B) halogens C) alkali metals D) alkaline earth metals E) noble gases 34. Which one of the following elements is a transition element? A) antimony B) barium C) chromium D) potassium E) selenium 35. According to the zeroth law of thermodynamics: a) Energy is neither lost nor gaine ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
2 - Castle High School
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
Multi-electron atoms
... a. because shape of outer most electron is similar. b. because energy of outer most electron is similar. c. both a and b d. some other reason ...
... a. because shape of outer most electron is similar. b. because energy of outer most electron is similar. c. both a and b d. some other reason ...
UV Spectroscopy
... UV and visible radiations absorbed by the molecules will bring transition of outer shell electrons(, and n electrons). According to molecular orbital theory when a organic molecule absorbs UV or visible radiations its electrons are promoted from a bonding to an antibonding orbital. ...
... UV and visible radiations absorbed by the molecules will bring transition of outer shell electrons(, and n electrons). According to molecular orbital theory when a organic molecule absorbs UV or visible radiations its electrons are promoted from a bonding to an antibonding orbital. ...
matter
... • One material disperses evenly into another material so the first one seems to disappear Example: stirring sugar in tea ...
... • One material disperses evenly into another material so the first one seems to disappear Example: stirring sugar in tea ...
MLSystems Lab 1 - Fourier v4 - RIT
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
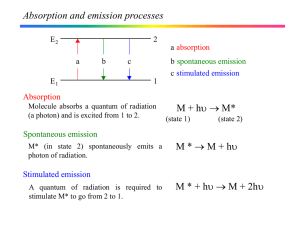
ppt1 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... • Natural linewidth of the lasing transition (uncertainty principle). • Number of modes active in the cavity. The linewidth of most lasers is still of the order of a wavenumber or less, sufficient for most spectroscopic applications. To achieve very narrow line widths (for rotational spectroscopy) o ...
... • Natural linewidth of the lasing transition (uncertainty principle). • Number of modes active in the cavity. The linewidth of most lasers is still of the order of a wavenumber or less, sufficient for most spectroscopic applications. To achieve very narrow line widths (for rotational spectroscopy) o ...
paper - Center for Ultracold Atoms
... phase space. As a result, for fermions the joint detection rate versus detector separation is expected to exhibit a dip around the null separation. Such a dip for a fermion ensemble must not be confused with the antibunching dip that one can observe with a single particle (boson or fermion) quantum ...
... phase space. As a result, for fermions the joint detection rate versus detector separation is expected to exhibit a dip around the null separation. Such a dip for a fermion ensemble must not be confused with the antibunching dip that one can observe with a single particle (boson or fermion) quantum ...
Conference title, upper and lower case, bolded, 18 point type
... Fig. S11. Experimentally measured J0 Bessel beam profile for different wavelengths. (a) to (k) Bessel beam profile at different wavelengths (labeled in the plots) generated by a silicon meta-axicon designed by using the same method described in the main text. This silicon meta-axicon was prepared by ...
... Fig. S11. Experimentally measured J0 Bessel beam profile for different wavelengths. (a) to (k) Bessel beam profile at different wavelengths (labeled in the plots) generated by a silicon meta-axicon designed by using the same method described in the main text. This silicon meta-axicon was prepared by ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.