PP_SSL_Modeling - LAS
... The round-trip condition delivers a simple quadratic equation for the q parameter. ...
... The round-trip condition delivers a simple quadratic equation for the q parameter. ...
Chapter 2
... 1. Calculate the number of free electrons for gold using its density and its atomic mass. 2. Does the conductivity of an alloy change when long-range ordering takes place? Explain. 3. Calculate the time between two collisions and the mean free path for pure copper at room temperature. Discuss whethe ...
... 1. Calculate the number of free electrons for gold using its density and its atomic mass. 2. Does the conductivity of an alloy change when long-range ordering takes place? Explain. 3. Calculate the time between two collisions and the mean free path for pure copper at room temperature. Discuss whethe ...
Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Scanning Electron Microscopy
... Since electrons would be too strongly scattered in air, a high vacuum is required in an electron microscope. In addition, the samples to be tested have to be electrically conductive, otherwise they would be overcharged with electrons during irradiation. For this reason, conductors and insulators of ...
... Since electrons would be too strongly scattered in air, a high vacuum is required in an electron microscope. In addition, the samples to be tested have to be electrically conductive, otherwise they would be overcharged with electrons during irradiation. For this reason, conductors and insulators of ...
Optical Coherence Tomography
... for the spectroscopic measurement, since it provides a better phase stability by removing the mechanical scanning in axial direction and with an improved signal to noise ratio [6]. The measurement of optical characteristics such as refractive index and extinction coefficient is important for many ap ...
... for the spectroscopic measurement, since it provides a better phase stability by removing the mechanical scanning in axial direction and with an improved signal to noise ratio [6]. The measurement of optical characteristics such as refractive index and extinction coefficient is important for many ap ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... between the valence electrons of two atoms. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost (highest) energy level. There are two main types of bonds within molecules, which are described below. -Ionic bonds involve the transfer of one or multiple electrons from one atom to another and the attr ...
... between the valence electrons of two atoms. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost (highest) energy level. There are two main types of bonds within molecules, which are described below. -Ionic bonds involve the transfer of one or multiple electrons from one atom to another and the attr ...
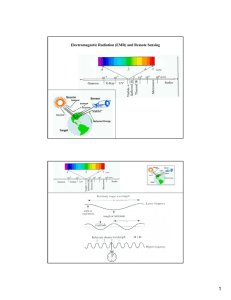
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing
... materials and which portion of the EMR is being measured. The nature of this reflected component over a range of wavelengths is called spectral response patterns. Spectral patterns are descriptions of the degree to which energy is reflected in different regions of the spectrum. ...
... materials and which portion of the EMR is being measured. The nature of this reflected component over a range of wavelengths is called spectral response patterns. Spectral patterns are descriptions of the degree to which energy is reflected in different regions of the spectrum. ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... make-believe element Katrayden (Ka). Based on the following, what is the average atomic mass? ...
... make-believe element Katrayden (Ka). Based on the following, what is the average atomic mass? ...
June review January 2012 part A
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
s 1
... Zeff is the effective nuclear charge and nl is the shielding constant. This gives rise to the shell model for multi-electron ...
... Zeff is the effective nuclear charge and nl is the shielding constant. This gives rise to the shell model for multi-electron ...
Calculation of Complete Absorption and Intensity of Optical
... limits of the absorption line [12,13]. Furthermore, transition probabilities and atomic lifetimes [4] and optical absorption and reflectance [14] have been reported. Predicted He I line intensities and line ratios in microwavegenerated plasmas and from a recently developed collisional-radiative mode ...
... limits of the absorption line [12,13]. Furthermore, transition probabilities and atomic lifetimes [4] and optical absorption and reflectance [14] have been reported. Predicted He I line intensities and line ratios in microwavegenerated plasmas and from a recently developed collisional-radiative mode ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... a) has the outer electron configuration 6s2 b) is in Group 18 but has no p electrons c) has three unpaired 4p electrons d) has four valence electrons in the Second Principal Energy level. e) is in Period 3 and has the same outer electron configuration as F. f) has only five 3d electrons. 12. Sketch ...
... a) has the outer electron configuration 6s2 b) is in Group 18 but has no p electrons c) has three unpaired 4p electrons d) has four valence electrons in the Second Principal Energy level. e) is in Period 3 and has the same outer electron configuration as F. f) has only five 3d electrons. 12. Sketch ...
Chapter 5 Mendeleev`s Periodic Table
... hydrogen had a discrete line spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. • Bohr's basic theory: electrons in atoms can only be at certain energy levels, and they can give off or absorb radiation only when they jump from one level to another. • In his model that an atom consists of an extremely dense ...
... hydrogen had a discrete line spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. • Bohr's basic theory: electrons in atoms can only be at certain energy levels, and they can give off or absorb radiation only when they jump from one level to another. • In his model that an atom consists of an extremely dense ...
Topic 12.1 Electron Configuration
... The principle quantum number (shell): electrons occupy the specific energy levels. The angular momentum quantum number (orbital shape): specifies the shape of the orbital. The magnetic quantum number (orbital orientation): specifies how this shape is arranged in three dimensions around the nucleus. ...
... The principle quantum number (shell): electrons occupy the specific energy levels. The angular momentum quantum number (orbital shape): specifies the shape of the orbital. The magnetic quantum number (orbital orientation): specifies how this shape is arranged in three dimensions around the nucleus. ...
Dielectric screening and band-structure effects in low
... apply a microscopic theory to the two available experiments on surface-state emission: to the well-studied case of Al共100兲 and to Be共0001兲, which has not been theoretically addressed. Our aim is to elucidate the relation between the spatial structure of the electric field and the photoemission inten ...
... apply a microscopic theory to the two available experiments on surface-state emission: to the well-studied case of Al共100兲 and to Be共0001兲, which has not been theoretically addressed. Our aim is to elucidate the relation between the spatial structure of the electric field and the photoemission inten ...
What is a photon, really - Philsci-Archive
... corresponds to a wave in the waveguide with a different wavelength. We can then apply the quantization method above, by treating the electronic charge on the plates as a wave instead of discrete particles, to obtain the same type of energy spectrum as (7), but with a different c, which in this case ...
... corresponds to a wave in the waveguide with a different wavelength. We can then apply the quantization method above, by treating the electronic charge on the plates as a wave instead of discrete particles, to obtain the same type of energy spectrum as (7), but with a different c, which in this case ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... a photon of light with century physics, part of the energy emitted by electrons should be a wavelength of 656 nm. Because line spectra result when atoms in an observable a continuous spectrum. Thistoisa not, however, the case. excited as state emit photons as they fall lower energy level, these Inst ...
... a photon of light with century physics, part of the energy emitted by electrons should be a wavelength of 656 nm. Because line spectra result when atoms in an observable a continuous spectrum. Thistoisa not, however, the case. excited as state emit photons as they fall lower energy level, these Inst ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW PROBLEMS
... 42. Calculate the joules of energy required to heat 298 g of water (c = 4.18 J/goC) from 7.6C to 81.5C? ...
... 42. Calculate the joules of energy required to heat 298 g of water (c = 4.18 J/goC) from 7.6C to 81.5C? ...
chapter_17_ppt - District 128 Moodle
... with certain atomic symbols. Many of these symbols come from Latin roots. Elements are named after people, places, or properties. EX: H for Hydrogen He for Helium O for Oxygen Fe for Iron ...
... with certain atomic symbols. Many of these symbols come from Latin roots. Elements are named after people, places, or properties. EX: H for Hydrogen He for Helium O for Oxygen Fe for Iron ...
CHAPTER 3 Optical Components of Spectrometers
... zero or constant for a long time are said to be coherent. • Waves emitted by separate sources are incoherent with respect to one another • Conditions for interference 1. The light reaching the point of interference comes from a single source by two different paths. 2. The interfering waves have very ...
... zero or constant for a long time are said to be coherent. • Waves emitted by separate sources are incoherent with respect to one another • Conditions for interference 1. The light reaching the point of interference comes from a single source by two different paths. 2. The interfering waves have very ...
Optics-Diffraction - The Wave Nature of Light
... magnitude of the wave’s electric field. The Principle of Linear Superposition arises because the differential wave equation governing all wave phenomena is linear. This means that if two waves satisfy the wave equation individually, then their sum also satisfies the wave equation. We therefore have ...
... magnitude of the wave’s electric field. The Principle of Linear Superposition arises because the differential wave equation governing all wave phenomena is linear. This means that if two waves satisfy the wave equation individually, then their sum also satisfies the wave equation. We therefore have ...
Iterative reconstruction algorithm for optoacoustic imaging
... can be imaged by scanning a focused acoustic transducer together with the optical source along a line on the surface of an object, creating an image of a two-dimensional section perpendicular to the surface.7,8 Scanning is, however, limited by the available pulse repetition rate of pulsed lasers, wh ...
... can be imaged by scanning a focused acoustic transducer together with the optical source along a line on the surface of an object, creating an image of a two-dimensional section perpendicular to the surface.7,8 Scanning is, however, limited by the available pulse repetition rate of pulsed lasers, wh ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.