Cardiovascular System Quiz 1. The left lower chamber of the heart
... 1. The left lower chamber of the heart that receives blood from the left atrium and pumps it out under high pressure through the aorta to the body. A) Arterioles B) Left Ventricle C) Arteries D) Right Ventricle ...
... 1. The left lower chamber of the heart that receives blood from the left atrium and pumps it out under high pressure through the aorta to the body. A) Arterioles B) Left Ventricle C) Arteries D) Right Ventricle ...
Unit J Notes #2 Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
... -Carries carbon dioxide filled blood to lungs for oxygenation. -Returns oxygen rich blood to heart so that it can be pumped out to systemic circuit. C) SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT: - Path from Left Ventricle out to all other tissues and organs of the body and then back to the right atrium of heart. - Carries ...
... -Carries carbon dioxide filled blood to lungs for oxygenation. -Returns oxygen rich blood to heart so that it can be pumped out to systemic circuit. C) SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT: - Path from Left Ventricle out to all other tissues and organs of the body and then back to the right atrium of heart. - Carries ...
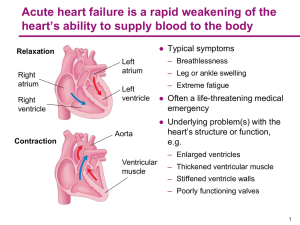
Heart failure
... Some types of HT caused by (combination of volume loading and vasoconstriction) as in coarctation of aorta which cause reduction in renal blood flow so stimulate rennin angiotensin system . ...
... Some types of HT caused by (combination of volume loading and vasoconstriction) as in coarctation of aorta which cause reduction in renal blood flow so stimulate rennin angiotensin system . ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... quickly followed by ventricular contraction atrial repolarization obscured by QRS complex ...
... quickly followed by ventricular contraction atrial repolarization obscured by QRS complex ...
Study guide
... 1. Trace the path of blood through the heart and through the body. Be complete!! I will be looking for terminology of the heart structures, veins and arteries, as well as general knowledge. You need to include the names of the primary arteries and veins associated with the heart, lungs, and branches ...
... 1. Trace the path of blood through the heart and through the body. Be complete!! I will be looking for terminology of the heart structures, veins and arteries, as well as general knowledge. You need to include the names of the primary arteries and veins associated with the heart, lungs, and branches ...
Chapter 9 – The Cardiovascular System Test
... 13. With a myocardial infarction, muscle tissue dies, but it can grow back. a. true b. false 14. With heart murmurs, there are unusual sounds, most often because of heart valve problems. a. true ...
... 13. With a myocardial infarction, muscle tissue dies, but it can grow back. a. true b. false 14. With heart murmurs, there are unusual sounds, most often because of heart valve problems. a. true ...
Cardiovascular
... a. surgical technique to bring new blood supply to heart muscles by detouring around blocked arteries b. condition of narrowing of the arteries that supply the heart c. death of a portion of the myocardium caused by lack of oxygen resulting from interrupted blood supply d. record of electrical activ ...
... a. surgical technique to bring new blood supply to heart muscles by detouring around blocked arteries b. condition of narrowing of the arteries that supply the heart c. death of a portion of the myocardium caused by lack of oxygen resulting from interrupted blood supply d. record of electrical activ ...
Slide ()
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
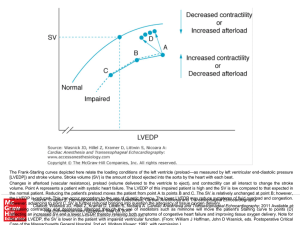
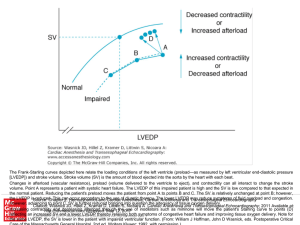
... However, advancing to point C, SV is further reduced bringing into question the adequacy of tissue oxygen delivery. Citation: Wasnick JD, Hillel Z, Kramer D, Littwin S, Nicoara A. Cardiac Anesthesia and Transesophageal Echocardiography; 2011 Available at: Increasing contractility and decreasing afte ...
... However, advancing to point C, SV is further reduced bringing into question the adequacy of tissue oxygen delivery. Citation: Wasnick JD, Hillel Z, Kramer D, Littwin S, Nicoara A. Cardiac Anesthesia and Transesophageal Echocardiography; 2011 Available at: Increasing contractility and decreasing afte ...
Read the Case Study from “Introduction to Medical Terminology
... Silicone catheters were placed in the pleural and substernal spaces. The sternum and soft tissue wound was closed. A.L. recovered from her surgery and was discharged 6 days later.CHAPTER 9 • CIRCULATION: THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS ...
... Silicone catheters were placed in the pleural and substernal spaces. The sternum and soft tissue wound was closed. A.L. recovered from her surgery and was discharged 6 days later.CHAPTER 9 • CIRCULATION: THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS ...
What is the cardiac cycle?
... the liver hepatic vein The first main blood vessel that an oxygen molecule reaches after being absorbed from an alveolus pulmonary vein Has the highest blood pressure aorta ...
... the liver hepatic vein The first main blood vessel that an oxygen molecule reaches after being absorbed from an alveolus pulmonary vein Has the highest blood pressure aorta ...
Simulating Initiation and Termination of Reentry in
... – Tachycardia - pace of the heart is faster than the regulatory signal from the sinus node (over 100 beats per min). • Rapid heart beating in the ventricles can be life-threatening. (ex. Ventricular fibrillation heart can’t pump any blood) Currently, over 2.2 million Americans are living with atrial ...
... – Tachycardia - pace of the heart is faster than the regulatory signal from the sinus node (over 100 beats per min). • Rapid heart beating in the ventricles can be life-threatening. (ex. Ventricular fibrillation heart can’t pump any blood) Currently, over 2.2 million Americans are living with atrial ...
SBI3UI - Review for Cardiovascular
... 2. Explain why planaria, a type of very simple flat worm, do not require a vascular system. 3. Describe the two types of vascular tissue in plants, including the role of each. 4. Distinguish between an open transport and a closed transport system. Give an example of one organism that has an open sys ...
... 2. Explain why planaria, a type of very simple flat worm, do not require a vascular system. 3. Describe the two types of vascular tissue in plants, including the role of each. 4. Distinguish between an open transport and a closed transport system. Give an example of one organism that has an open sys ...
Residual volume
... and circulates it to the lungs. This is called pulmonary circulation. The pump on the left side receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. This is called systemic circulation. ...
... and circulates it to the lungs. This is called pulmonary circulation. The pump on the left side receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. This is called systemic circulation. ...
Circulatory System Notes
... According to the American Heart Association, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Because of its vastness and critical nature, it is one of the systems of the body most prone to disease. One of the most common diseases of the circulatory system is arterioscleros ...
... According to the American Heart Association, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Because of its vastness and critical nature, it is one of the systems of the body most prone to disease. One of the most common diseases of the circulatory system is arterioscleros ...
Ch 20 – The Heart
... G. Valves –connect to bl.v leading out of heart -make “dub” sound when closing 1. pulmonary (semilunar) valve- between right ventricle and pulmonary artery 2. aortic (semilunar) valve -between left ventricle and aorta -Color Plate # 49, and 50 ...
... G. Valves –connect to bl.v leading out of heart -make “dub” sound when closing 1. pulmonary (semilunar) valve- between right ventricle and pulmonary artery 2. aortic (semilunar) valve -between left ventricle and aorta -Color Plate # 49, and 50 ...
warm ups! trimester 2
... How do the cells of the heart get oxygen and glucose for cellular respiration to ...
... How do the cells of the heart get oxygen and glucose for cellular respiration to ...
Ventricular Septal Defect
... from the left ventricle enters the right ventricle because there is greater pressure in the left ventricle and the resistance in the lungs is significantly lower that the body. This is known as a "left to right shunt." Ventricular septal defects are the most common forms of congenital heart disease, ...
... from the left ventricle enters the right ventricle because there is greater pressure in the left ventricle and the resistance in the lungs is significantly lower that the body. This is known as a "left to right shunt." Ventricular septal defects are the most common forms of congenital heart disease, ...
Biology 12 Name: Quiz #14 Match each term in the left
... 1. Match each term in the left-hand column with the best definition from the right-hand column. Please put the letter of the best definition beside the appropriate term. (1 mark each = 9 marks) ...
... 1. Match each term in the left-hand column with the best definition from the right-hand column. Please put the letter of the best definition beside the appropriate term. (1 mark each = 9 marks) ...
Heart
... Lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, it opens during ventricle systole when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery, then closes when the right ventricle pressure falls rapidly. ...
... Lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, it opens during ventricle systole when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery, then closes when the right ventricle pressure falls rapidly. ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.