Cardiovascular Physiology
... Section 1. Anatomy & Physiology of the Heart (Interactive Phys. -Anatomy Review) 1. Be able to diagram and/or label on a diagram the following: ventricles, atria, valves, vena cavas, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, coronary arteries, papillary muscle, chordae tendinea. Be able to describe t ...
... Section 1. Anatomy & Physiology of the Heart (Interactive Phys. -Anatomy Review) 1. Be able to diagram and/or label on a diagram the following: ventricles, atria, valves, vena cavas, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, coronary arteries, papillary muscle, chordae tendinea. Be able to describe t ...
Circulatory_system_311
... from the body back to the heart Pulmonary arteries – take blood from the heart to the lungs Pulmonary veins – take blood from the lungs to the heart Aorta – takes blood from the heart to the body ...
... from the body back to the heart Pulmonary arteries – take blood from the heart to the lungs Pulmonary veins – take blood from the lungs to the heart Aorta – takes blood from the heart to the body ...
File - Mr Murphy`s Science Blog
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
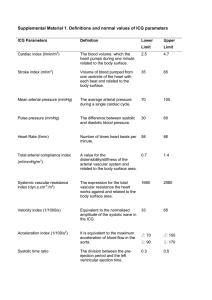
Supplemental Material 1. Definitions and normal
... Supplemental Material 1. Definitions and normal values of ICG parameters ICG Parameters ...
... Supplemental Material 1. Definitions and normal values of ICG parameters ICG Parameters ...
The Circulatory System
... • Two ventricles- larger stronger chambers below – they pump blood out of heart ...
... • Two ventricles- larger stronger chambers below – they pump blood out of heart ...
C11.2 Notes - Destiny High School
... 2. Describe different types of arrhythmia, or abnormal contractility conditions that can be detected via electrocardiogram. 3. Identify the components of the conduction system of the heart. Regulation of the Heart ...
... 2. Describe different types of arrhythmia, or abnormal contractility conditions that can be detected via electrocardiogram. 3. Identify the components of the conduction system of the heart. Regulation of the Heart ...
The Circulatory system
... 2.How many chambers does the heart have and what are they called? 3.Give a definition for the pulse. 4.Identify 3 places where you can take the pulse. 5.Name the 4 components of blood and give a brief description of each. 2 of 36 ...
... 2.How many chambers does the heart have and what are they called? 3.Give a definition for the pulse. 4.Identify 3 places where you can take the pulse. 5.Name the 4 components of blood and give a brief description of each. 2 of 36 ...
Sudden cardiac death in Children participating in organised sport
... Sudden cardiac death in Children participating in organised sport There has been concern in the media about sudden cardiac death in children during sport, particularly following the collapse of Fabrice Muamba. There are calls being made that all children should be screened prior to taking part in sp ...
... Sudden cardiac death in Children participating in organised sport There has been concern in the media about sudden cardiac death in children during sport, particularly following the collapse of Fabrice Muamba. There are calls being made that all children should be screened prior to taking part in sp ...
Human Reproductive System
... (from upper body) Pulmonary Artery (to right lung) Pulmonary Veins (from right lung) ...
... (from upper body) Pulmonary Artery (to right lung) Pulmonary Veins (from right lung) ...
Heart Anatomy
... composed of three flaps On the left side of the heart, the valve is called the bicuspid valve (or mitral valve) because it is composed of two flaps These valves are attached to muscular extensions of the ventricle walls (called papillary muscles) by strands of tissue called chordae tendinae ...
... composed of three flaps On the left side of the heart, the valve is called the bicuspid valve (or mitral valve) because it is composed of two flaps These valves are attached to muscular extensions of the ventricle walls (called papillary muscles) by strands of tissue called chordae tendinae ...
Cardiovascular System
... • Double Pump: Rt side is pulmonary circulation, left side is systemic circulation. • Pulmonary circulation – blood in the right side of heart, pulmonary vessels, and lungs. • Systemic circulation – blood in the left side of heart and the rest of the body. • Heart is the size of your fist. • Located ...
... • Double Pump: Rt side is pulmonary circulation, left side is systemic circulation. • Pulmonary circulation – blood in the right side of heart, pulmonary vessels, and lungs. • Systemic circulation – blood in the left side of heart and the rest of the body. • Heart is the size of your fist. • Located ...
Name
... would be more likely to raise or lower heart rate and why. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... would be more likely to raise or lower heart rate and why. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
Drugs used for Congestive Heart Failure
... pressure with pooling of blood in the veins. The preload and afterload will be decreased • ACE inhibitors: are agents that block the conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2. These drugs causes vasodilatation and decreased blood volume. The afterload will be decreased. • Diuretics: are employed ...
... pressure with pooling of blood in the veins. The preload and afterload will be decreased • ACE inhibitors: are agents that block the conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2. These drugs causes vasodilatation and decreased blood volume. The afterload will be decreased. • Diuretics: are employed ...
6.2 – The Blood System
... D. Systole of atria pushes open atrioventricular valves and moves blood into ventricles E. Systole of ventricles forces atrioventricular valves closed to prevent backflow (“lub”) F. As ventricle contracts, pressure increase until semilunar valves are forced open, pushing blood into aorta/pulmonary a ...
... D. Systole of atria pushes open atrioventricular valves and moves blood into ventricles E. Systole of ventricles forces atrioventricular valves closed to prevent backflow (“lub”) F. As ventricle contracts, pressure increase until semilunar valves are forced open, pushing blood into aorta/pulmonary a ...
for immediate release - Miami`s Community Newspapers
... mailto:MOUNT SINAI MEDICAL CENTER WELCOMES JASON JACOBSON, M.D. ...
... mailto:MOUNT SINAI MEDICAL CENTER WELCOMES JASON JACOBSON, M.D. ...
Chapter 19: The Heart
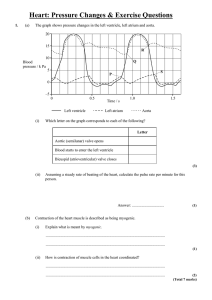
... (B) Heart Sounds Listening = auscultation. “lubb-dup”, corresponds to blood turbulence caused by valve closures. Triple rhythms common in children. (C) Phases of Cardiac Cycle all within one second -1- ventricular filling: AV valves open. Atrial systole towards end. AV valves close. Ventricles conta ...
... (B) Heart Sounds Listening = auscultation. “lubb-dup”, corresponds to blood turbulence caused by valve closures. Triple rhythms common in children. (C) Phases of Cardiac Cycle all within one second -1- ventricular filling: AV valves open. Atrial systole towards end. AV valves close. Ventricles conta ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Section 1. Anatomy & Physiology of the Heart (CD-Anatomy Review) 1. Be able to diagram and/or label on a diagram the following: ventricles, atria, valves, vena cavas, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, coronary arteries, papillary muscle, chordae tendinea. Be able to describe the function of e ...
... Section 1. Anatomy & Physiology of the Heart (CD-Anatomy Review) 1. Be able to diagram and/or label on a diagram the following: ventricles, atria, valves, vena cavas, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, coronary arteries, papillary muscle, chordae tendinea. Be able to describe the function of e ...
Congestive Heart Failure and CAD
... Hemostasis • Development of a thrombus is lifesaving when a large vessel is ruptured or is severed • However, when a thrombus develops in the unruptured cardiovascular system it can be life threatening ...
... Hemostasis • Development of a thrombus is lifesaving when a large vessel is ruptured or is severed • However, when a thrombus develops in the unruptured cardiovascular system it can be life threatening ...
Saturated fats - Garnet Valley
... Consistently lowers serum triglycerides and may also have an effect on lowering blood pressure. Found in oily fish such as salmon, tuna, and herring. Is available as a supplement. ...
... Consistently lowers serum triglycerides and may also have an effect on lowering blood pressure. Found in oily fish such as salmon, tuna, and herring. Is available as a supplement. ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.