Heart
... – Pain caused by ischemia of cardiac muscle – Obstruction partially blocks blood flow – Myocardium shifts to anaerobic fermentation, producing lactic acid and thus stimulating pain ...
... – Pain caused by ischemia of cardiac muscle – Obstruction partially blocks blood flow – Myocardium shifts to anaerobic fermentation, producing lactic acid and thus stimulating pain ...
CHOLESTEROL CRYSTAL EMBOLIZATION IN A SAUDI PATIENT AFTER CARDIAC SURGERY A m. e
... clinical history or intraoperative TEE38. In case of severe aortic atherosclerosis it might be necessary to modify the standard cannulation and clamping techniques39, to use filtration devices of the ascending aorta40 or even perform off-pump surgery and use of arterial grafts39, 41. Although some c ...
... clinical history or intraoperative TEE38. In case of severe aortic atherosclerosis it might be necessary to modify the standard cannulation and clamping techniques39, to use filtration devices of the ascending aorta40 or even perform off-pump surgery and use of arterial grafts39, 41. Although some c ...
Eisenmenger Syndrome and Pregnancy
... Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common cyanotic congenital heart defect and accounts for about 3.5% of all congenital cardiac lesions. It is characterized by four features: 1) a large, non-restrictive ventricular septal defect; 2) the aorta ‘overrides’ the interventricular septum; 3) right ventricul ...
... Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common cyanotic congenital heart defect and accounts for about 3.5% of all congenital cardiac lesions. It is characterized by four features: 1) a large, non-restrictive ventricular septal defect; 2) the aorta ‘overrides’ the interventricular septum; 3) right ventricul ...
first heart sound - Easymed.club
... Transmitted throughout the superior thoracic aorta and even into the large arteries of the neck ...
... Transmitted throughout the superior thoracic aorta and even into the large arteries of the neck ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Major goals of anaesthesia in PAPVC are to maintain systemic vascular resistance, minimize pulmonary vascular resistance and provide mild myocardial depression. Most of the patients have a dynamic right ventricular outflow obstruction which may be worsened by sympathetic stimulation during anaesthes ...
... Major goals of anaesthesia in PAPVC are to maintain systemic vascular resistance, minimize pulmonary vascular resistance and provide mild myocardial depression. Most of the patients have a dynamic right ventricular outflow obstruction which may be worsened by sympathetic stimulation during anaesthes ...
Fat and Cholesterol
... Healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels To reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke and other cardiovascular conditions, the Heart Foundation currently recommends a: • LDL cholesterol blood level less than 2.5 mmol/L (or less than 2.00 mmol/L for people with heart disease) • HDL cholesterol blo ...
... Healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels To reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke and other cardiovascular conditions, the Heart Foundation currently recommends a: • LDL cholesterol blood level less than 2.5 mmol/L (or less than 2.00 mmol/L for people with heart disease) • HDL cholesterol blo ...
Current outcomes and risk factors for the Norwood procedure
... Objective: Tremendous strides have been made in the outcomes for hypoplastic left heart syndrome and other functional single-ventricle malformations over the past 25 years. This progress relates primarily to improvements in survival for patients undergoing the Norwood procedure. Previous reports on ...
... Objective: Tremendous strides have been made in the outcomes for hypoplastic left heart syndrome and other functional single-ventricle malformations over the past 25 years. This progress relates primarily to improvements in survival for patients undergoing the Norwood procedure. Previous reports on ...
Surgical Ventricular Restoration
... great vessels. TACHYCARDIA is an abnormally rapid heart rate, greater than one hundred (100) beats per minute. ...
... great vessels. TACHYCARDIA is an abnormally rapid heart rate, greater than one hundred (100) beats per minute. ...
Ablation of ventricular tachycardia in patients with severe left
... • 17 men (ischemic cardiomyopathy 83%, 65±13 yrs, LVEF 27±7% with recurrent episodes of VT and/or arrhythmic storms despite antiarrhythmic drug therapy and optimal heart failure medication. EPS/mapping -‐ ventricular programmed stimulation (600 ms/S3) to ...
... • 17 men (ischemic cardiomyopathy 83%, 65±13 yrs, LVEF 27±7% with recurrent episodes of VT and/or arrhythmic storms despite antiarrhythmic drug therapy and optimal heart failure medication. EPS/mapping -‐ ventricular programmed stimulation (600 ms/S3) to ...
Ch42
... 3. Basophils contain histamine and are involved in allergic reactions. Some have heparin, and anticoagulant that prevents clotting in the blood vessels. Agranular leukocytes are manufactured in the red bone marrow. Their nuclei are round or kidney shaped and lacks granules. 1. Lymphocytes produce an ...
... 3. Basophils contain histamine and are involved in allergic reactions. Some have heparin, and anticoagulant that prevents clotting in the blood vessels. Agranular leukocytes are manufactured in the red bone marrow. Their nuclei are round or kidney shaped and lacks granules. 1. Lymphocytes produce an ...
Course Specifications: Clinical physiology
... a.3.Know the physiological anatomy of the skeletal muscle. a.4.Know the mechanism of contraction and changes occurring during it . a.5.Describe the oxygen debt mechanism and mechanical efficiency. ...
... a.3.Know the physiological anatomy of the skeletal muscle. a.4.Know the mechanism of contraction and changes occurring during it . a.5.Describe the oxygen debt mechanism and mechanical efficiency. ...
9 - KUET
... Measurement of Heart Rate (Contd…) Measurement: Manual MeasurementHeart rate is measured by finding the pulse of the heart. This pulse rate can be found at any point on the body where the artery's pulsation is transmitted to the surface by pressuring it with the index and middle fingers. (A good ...
... Measurement of Heart Rate (Contd…) Measurement: Manual MeasurementHeart rate is measured by finding the pulse of the heart. This pulse rate can be found at any point on the body where the artery's pulsation is transmitted to the surface by pressuring it with the index and middle fingers. (A good ...
Case AORTIC HEART DISEASE
... This is an incomplete closing of the leaflets during ventricular systole, accompanied by regurgitation of blood from the left ventricle in LP. Isolated aortic valve is about 5-10% of the total number of heart defects. Mitral regurgitation slightly more common in men. The clinical picture of Complain ...
... This is an incomplete closing of the leaflets during ventricular systole, accompanied by regurgitation of blood from the left ventricle in LP. Isolated aortic valve is about 5-10% of the total number of heart defects. Mitral regurgitation slightly more common in men. The clinical picture of Complain ...
Rationale for the Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure (AF
... with the highest incidence in those with the most severe symptoms [1-3] . Excessive ventricular rate, irregularity of ventricular response, and loss of atrial contraction associated with AF may result in adverse hemodynamic consequences and influence prognosis in patients with CHF [4-15] . Restorati ...
... with the highest incidence in those with the most severe symptoms [1-3] . Excessive ventricular rate, irregularity of ventricular response, and loss of atrial contraction associated with AF may result in adverse hemodynamic consequences and influence prognosis in patients with CHF [4-15] . Restorati ...
Full - Bahrain Medical Bulletin
... and syncope attacks in children without previously diagnosed heart disease are rarely of cardiac origin. Continued education and training of primary care physicians improve the skills in the clinical assessment and limit unnecessary referrals. Programs in performing basic echocardiogram could be ini ...
... and syncope attacks in children without previously diagnosed heart disease are rarely of cardiac origin. Continued education and training of primary care physicians improve the skills in the clinical assessment and limit unnecessary referrals. Programs in performing basic echocardiogram could be ini ...
diastolic pressure
... Pain is a warning from the body. Pain is personal. Types of pain – Acute pain – felt suddenly from an injury, disease, trauma, or surgery – Chronic pain – lasts longer than 6 months. Pain can be constant or occur on and off. – Radiating pain – felt at the site of tissue damage and in nearby areas. – ...
... Pain is a warning from the body. Pain is personal. Types of pain – Acute pain – felt suddenly from an injury, disease, trauma, or surgery – Chronic pain – lasts longer than 6 months. Pain can be constant or occur on and off. – Radiating pain – felt at the site of tissue damage and in nearby areas. – ...
NT-pro BNP B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is one of a family of
... B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is one of a family of bioactive peptides with effects on sodium and water balance. Because of the greater mass of ventricular tissue, the majority of BNP secretion is derived from the ventricles, especially from left ventricle. Any stretching of heart chambers increa ...
... B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is one of a family of bioactive peptides with effects on sodium and water balance. Because of the greater mass of ventricular tissue, the majority of BNP secretion is derived from the ventricles, especially from left ventricle. Any stretching of heart chambers increa ...
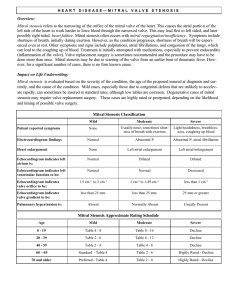
Mitral stenosis
... shortness of breath, initially during exertion. However, as the condition progresses, shortness of breath will be experienced even at rest. Other symptoms and signs include palpitations, atrial fibrillations, and congestion of the lungs, which can lead to the coughing up of blood. Treatment is initi ...
... shortness of breath, initially during exertion. However, as the condition progresses, shortness of breath will be experienced even at rest. Other symptoms and signs include palpitations, atrial fibrillations, and congestion of the lungs, which can lead to the coughing up of blood. Treatment is initi ...
THE CLINICAL OUTCOME AND THE INCIDENCE OF PACEMAKER
... One limitation of the study is the fail to study the relationship paced beats/ nonpaced beats in our patients. It might be a direct relationship between the percentage of VVI paced beats and the occurrence of the pacemaker syndrome. The echocardiographic measurement of the LVEF was a better predicto ...
... One limitation of the study is the fail to study the relationship paced beats/ nonpaced beats in our patients. It might be a direct relationship between the percentage of VVI paced beats and the occurrence of the pacemaker syndrome. The echocardiographic measurement of the LVEF was a better predicto ...
Claudication (leg pain) - Redlands Community Hospital
... performed to determine whether your arterial blood flow is normal. Arteries and Veins: During this test, the technologist will place blood pressure cuffs at several points along your legs and take the blood pressure using a Doppler, a microphone-like instrument. You may be asked to walk on a treadmi ...
... performed to determine whether your arterial blood flow is normal. Arteries and Veins: During this test, the technologist will place blood pressure cuffs at several points along your legs and take the blood pressure using a Doppler, a microphone-like instrument. You may be asked to walk on a treadmi ...
Full Text
... had a higher incidence of infectious complications (3, 4, 1214, 20, 25, 26) . The higher incidence of diabetes mellitus in the obese, and the decreased perfusion of subcutaneous fat tissue ,postoperative hemorrhage , prolonged operation time, age, renal failure, and low cardiac output syndrome may l ...
... had a higher incidence of infectious complications (3, 4, 1214, 20, 25, 26) . The higher incidence of diabetes mellitus in the obese, and the decreased perfusion of subcutaneous fat tissue ,postoperative hemorrhage , prolonged operation time, age, renal failure, and low cardiac output syndrome may l ...
Arterial blood pressure
... • Amount of blood flow received by each organ is determined by the number and diameter of its arterioles • Local (intrinsic) controls are changes within a tissue that alter the radii of arterioles • Local metabolic changes produce relaxation of arteriolar smooth muscle to increase blood flow to the ...
... • Amount of blood flow received by each organ is determined by the number and diameter of its arterioles • Local (intrinsic) controls are changes within a tissue that alter the radii of arterioles • Local metabolic changes produce relaxation of arteriolar smooth muscle to increase blood flow to the ...
Seeing Red: Harvey and the Circulation of the Blood
... The constantly beating heart would put out more blood than the veins could supply, or the arteries could hold (too much blood leaves the heart for it to be used up and replaced). - The sum of the parts (accumulation of blood over time, resulting from blood expelled by heart into aorta) cannot be g ...
... The constantly beating heart would put out more blood than the veins could supply, or the arteries could hold (too much blood leaves the heart for it to be used up and replaced). - The sum of the parts (accumulation of blood over time, resulting from blood expelled by heart into aorta) cannot be g ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.