Hemodynamic effects of cycle ergometer in critical cancer patients
... 10 minutes of activity, signaling a return to baseline. While performing the physical activity, mechanical stress causes an increase in blood flow to the muscles in action, since it is necessary to increase the supply of oxygen and nutrients and remove metabolic slag, such as carbon dioxide, lactate ...
... 10 minutes of activity, signaling a return to baseline. While performing the physical activity, mechanical stress causes an increase in blood flow to the muscles in action, since it is necessary to increase the supply of oxygen and nutrients and remove metabolic slag, such as carbon dioxide, lactate ...
Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information Booklet
... In this case areas within the left atrium are ablated, thus preventing AF from starting. In recent years it has been found that AF can originate from areas around the pulmonary veins (blood vessels linking the heart with the lungs), which are situated in the left atrium (upper chamber). The techniqu ...
... In this case areas within the left atrium are ablated, thus preventing AF from starting. In recent years it has been found that AF can originate from areas around the pulmonary veins (blood vessels linking the heart with the lungs), which are situated in the left atrium (upper chamber). The techniqu ...
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor prevents left
... ccumulating evidence supports the proposal that angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor blockers (ARBs) have nearly the same beneficial effects as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors on cardiac hypertrophy, remodelling, and heart failure.1–3 However, the pharmacological profiles of ARBs and ...
... ccumulating evidence supports the proposal that angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor blockers (ARBs) have nearly the same beneficial effects as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors on cardiac hypertrophy, remodelling, and heart failure.1–3 However, the pharmacological profiles of ARBs and ...
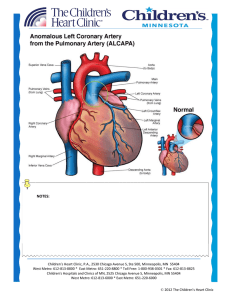
notes - Children`s Heart Clinic
... aortic valve. This arrangement allows the left coronary artery to provide the left ventricle with oxygenated blood. When the left coronary artery arises abnormally from the pulmonary artery, this is known as ALCAPA. In ALCAPA, blood flow goes from the right coronary artery, through the inter-coronar ...
... aortic valve. This arrangement allows the left coronary artery to provide the left ventricle with oxygenated blood. When the left coronary artery arises abnormally from the pulmonary artery, this is known as ALCAPA. In ALCAPA, blood flow goes from the right coronary artery, through the inter-coronar ...
Pharmaco-invasive vs. facilitated percutaneous coronary intervention strategies for ST-segment-
... The editor-in-chief of the European Heart Journal Thomas F. Lu¨scher, before accepting his new and demanding job, barely found time to think about things behind the noise of daily activities—yet managed to write a book about medicine, its origins, and what it means today as well as about the science ...
... The editor-in-chief of the European Heart Journal Thomas F. Lu¨scher, before accepting his new and demanding job, barely found time to think about things behind the noise of daily activities—yet managed to write a book about medicine, its origins, and what it means today as well as about the science ...
Human Physiology - Daniela Sartori
... of myocardial cells opens V-gated Ca2+ channels in sarcolemma This depolarization opens V-gated and Ca2+ release channels in SR (calcium-induced-calcium-release) Ca2+ binds to troponin and stimulates contraction (as in skeletal muscle) During repolarization Ca2+ pumped out of cell and into SR ...
... of myocardial cells opens V-gated Ca2+ channels in sarcolemma This depolarization opens V-gated and Ca2+ release channels in SR (calcium-induced-calcium-release) Ca2+ binds to troponin and stimulates contraction (as in skeletal muscle) During repolarization Ca2+ pumped out of cell and into SR ...
Medical Terminology Combining Form Combining Form With
... A piece of thrombus may break off and move through blood vessels to another part of the body. This moving thrombus is called an “Embolus”. Embolus can cause myocardial infarction or cerebral infarction also. ...
... A piece of thrombus may break off and move through blood vessels to another part of the body. This moving thrombus is called an “Embolus”. Embolus can cause myocardial infarction or cerebral infarction also. ...
CENTRAL LINES
... physician would not lean over The bed is high enough so physician would not have to stoop over Patient should be flat without a pillow, Trendelenburg position if patient is hypovolemic The head is turned away from the side of the procedure Wrist restraints if necessary ...
... physician would not lean over The bed is high enough so physician would not have to stoop over Patient should be flat without a pillow, Trendelenburg position if patient is hypovolemic The head is turned away from the side of the procedure Wrist restraints if necessary ...
PRACTICE Matters T C
... important prognostic information and to aid the clinician in determining appropriate therapy. According to the NYHA system, Class I patients are those with impaired LV function, but who have no limitation with ordinary physical activity. Class II patients have slight limitation of physical activity. ...
... important prognostic information and to aid the clinician in determining appropriate therapy. According to the NYHA system, Class I patients are those with impaired LV function, but who have no limitation with ordinary physical activity. Class II patients have slight limitation of physical activity. ...
A CARE STUDY OF A PATIENT WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
... • Thrombolytic medications: • Clot busting medications that can restore blood flow in a blocked artery • Examples include: streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator, andurokinase ...
... • Thrombolytic medications: • Clot busting medications that can restore blood flow in a blocked artery • Examples include: streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator, andurokinase ...
1. What is Heart Failure? The term "heart failure" makes it sound like
... listed below. Some of these can be present without you knowing it. Typically these conditions cause the "wear and tear" that leads to heart failure. Having more than one of these factors dramatically increases your risk. Coronary artery disease Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) Past heart ...
... listed below. Some of these can be present without you knowing it. Typically these conditions cause the "wear and tear" that leads to heart failure. Having more than one of these factors dramatically increases your risk. Coronary artery disease Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) Past heart ...
Christian T. Ruff Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation doi: 10.1161
... If the heart rate is allowed to be too fast for a long period of time, it can cause heart failure, which makes patients feel really tired and short of breath.  -blockers and calcium channel blockers are types of medications that can slow the heart rate. Sometimes your doctor may try to get you back ...
... If the heart rate is allowed to be too fast for a long period of time, it can cause heart failure, which makes patients feel really tired and short of breath.  -blockers and calcium channel blockers are types of medications that can slow the heart rate. Sometimes your doctor may try to get you back ...
Cor pulmonale - The Medical Post | Trusting Medicine
... 3. A variety of neurologic symptoms may be seen due to decreased cardiac output and hypoxemia ...
... 3. A variety of neurologic symptoms may be seen due to decreased cardiac output and hypoxemia ...
THE EFFECT OF SPIRONOLACTONE ON LEFT
... Chronic blood volume overload causes development of eccentric left ventricle hypertrophy, which manifests by its dilatation without significant thickening of the walls. This occurs because the increased blood volume (increased preload) enhances pressure on left ventricle walls, which leads to the ch ...
... Chronic blood volume overload causes development of eccentric left ventricle hypertrophy, which manifests by its dilatation without significant thickening of the walls. This occurs because the increased blood volume (increased preload) enhances pressure on left ventricle walls, which leads to the ch ...
The Circulatory System
... Aorta divides and branches into many smaller arteries 4. The only artery that does not carry oxygenated blood is Pulmonary artery. ...
... Aorta divides and branches into many smaller arteries 4. The only artery that does not carry oxygenated blood is Pulmonary artery. ...
Continuous Warm Blood Cardioplegia
... stop to infuse the heart with cardioplegia or add slush; the procedure continues rapidly. It is necessary to aid in the visualization as well as to prevent the chest from overflowing since fluid may build up from copious irrigation or the flow may drain into the chest. The surgical team must be aler ...
... stop to infuse the heart with cardioplegia or add slush; the procedure continues rapidly. It is necessary to aid in the visualization as well as to prevent the chest from overflowing since fluid may build up from copious irrigation or the flow may drain into the chest. The surgical team must be aler ...
Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
... Effects last up to 36 hours (longest of the three PDE5 inhibitors) Also now approved for daily dosing if activity ...
... Effects last up to 36 hours (longest of the three PDE5 inhibitors) Also now approved for daily dosing if activity ...
Mathematical Modeling of the Circulatory System
... monitoring of the state of the system. This is primarily accomplished by monitoring key blood pressures as well as blood gases. Systemic arterial blood pressure is monitored by baroreceptors located in the carotid arteries and aorta. These cells stretch in response to an increase in blood pressure, ...
... monitoring of the state of the system. This is primarily accomplished by monitoring key blood pressures as well as blood gases. Systemic arterial blood pressure is monitored by baroreceptors located in the carotid arteries and aorta. These cells stretch in response to an increase in blood pressure, ...
The Cardiovascular System
... illustration shows the narrowing of an artery as the result of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Lipid deposits (yellow) build up inside the blood vessel walls and block the flow of blood. Red blood cells and lipid particles (yellow balls) are shown escaping ...
... illustration shows the narrowing of an artery as the result of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Lipid deposits (yellow) build up inside the blood vessel walls and block the flow of blood. Red blood cells and lipid particles (yellow balls) are shown escaping ...
Taking Care of your HigH Blood Pressure
... the heart and arteries may not work as well as they should. This can also affect other parts of the body, including the kidneys, eyes and brain. your doctor may prescribe a daily medicine to help control high blood pressure. every person needs blood pressure to live. Without it, blood wouldn’t be ab ...
... the heart and arteries may not work as well as they should. This can also affect other parts of the body, including the kidneys, eyes and brain. your doctor may prescribe a daily medicine to help control high blood pressure. every person needs blood pressure to live. Without it, blood wouldn’t be ab ...
TEMA 1
... - Atherosclerosis: is the formation of fatty plaques (atherosclerotic plaque) lining blood vessels. It causes the arteries to narrow and restricts the blood flow. If a plaque ruptures a clot can be produced (thrombosis). - Hypertension: is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in t ...
... - Atherosclerosis: is the formation of fatty plaques (atherosclerotic plaque) lining blood vessels. It causes the arteries to narrow and restricts the blood flow. If a plaque ruptures a clot can be produced (thrombosis). - Hypertension: is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in t ...
Catheter Ablation of VT in Structural Heart Disease
... New ischemia or infarction during follow-up Modification of arrhythmic substrate by RF current application ...
... New ischemia or infarction during follow-up Modification of arrhythmic substrate by RF current application ...
Congestive Heart Failure in Dogs
... blood to its body. This condition can be caused by a failure of the left side, the right side, or both sides of the heart. When the heart starts to fail, the body can compensate to ensure that tissues receive the blood and oxygen they need. As the heart disease increases in severity, these compens ...
... blood to its body. This condition can be caused by a failure of the left side, the right side, or both sides of the heart. When the heart starts to fail, the body can compensate to ensure that tissues receive the blood and oxygen they need. As the heart disease increases in severity, these compens ...
1. Which of the following statements about arteries is FALSE? a. The
... 1. Which of the following statements about arteries is FALSE? a. The blood pressure in arteries is higher than that in the veins. b. Arteries have thick walls that contain layers of muscle and connective tissue c. Arteries have one-way valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards d. Arteries conta ...
... 1. Which of the following statements about arteries is FALSE? a. The blood pressure in arteries is higher than that in the veins. b. Arteries have thick walls that contain layers of muscle and connective tissue c. Arteries have one-way valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards d. Arteries conta ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.