QUANTUM KEY DISTRIBUTION 1. Cryptography In the course of
... theory the BB84 key distribution work perfectly. Heisenbergs uncertainty principle guarantees that Eve cannot measure the two chosen bases at the same time, and the no-cloning theorem states that Eve cannot make identical copies of the qubit to measure each basis on another identical qubit. The fact ...
... theory the BB84 key distribution work perfectly. Heisenbergs uncertainty principle guarantees that Eve cannot measure the two chosen bases at the same time, and the no-cloning theorem states that Eve cannot make identical copies of the qubit to measure each basis on another identical qubit. The fact ...
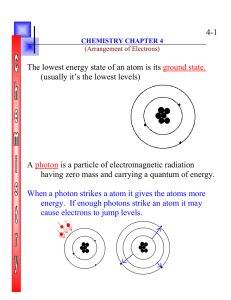
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... cause electrons to jump levels. ...
... cause electrons to jump levels. ...
Quantum Gravity: The View From Particle Physics
... correctly describe the physical degrees of freedom also at the very smallest distances. The first attempt of quantizing gravity relied on canonical quantization, with the spatial metric components and their conjugate momenta as the canonical variables, and the Wheeler-DeWitt equation governing the d ...
... correctly describe the physical degrees of freedom also at the very smallest distances. The first attempt of quantizing gravity relied on canonical quantization, with the spatial metric components and their conjugate momenta as the canonical variables, and the Wheeler-DeWitt equation governing the d ...
quiz 3 104 phy in class
... uniform electric field is directed upward. What is the direction of the force exerted on the electron once it has entered the field? A)to the left B)to the right C)upward D)downward E)out of the page, toward the reader ...
... uniform electric field is directed upward. What is the direction of the force exerted on the electron once it has entered the field? A)to the left B)to the right C)upward D)downward E)out of the page, toward the reader ...
Quantum Mechanics in the Early Universe
... Settings of detectors We can now form the C observable and check whether Bell’s inequalities are violated. Quantum mechanics allows a violation of up to a factor of In this model we indeed get such a violation. This proves that the variable determining the type of hotspot we have is quantum. ...
... Settings of detectors We can now form the C observable and check whether Bell’s inequalities are violated. Quantum mechanics allows a violation of up to a factor of In this model we indeed get such a violation. This proves that the variable determining the type of hotspot we have is quantum. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI M.Sc. SECOND
... functions. (b) If the box is a cubical one of side a, derive expression for energy eigen values and eigen functions. (9 + 3.5) 17. Prove that the matrix representation of an operator with respect to its own eigen functions is diagonal and the matrix elements are the eigen values of the operator. 18. ...
... functions. (b) If the box is a cubical one of side a, derive expression for energy eigen values and eigen functions. (9 + 3.5) 17. Prove that the matrix representation of an operator with respect to its own eigen functions is diagonal and the matrix elements are the eigen values of the operator. 18. ...
Physics 214b-2008 Walter F
... IMPORTANT: This exam will be truly cumulative, i.e. it will cover material from the entire semester. For example, it will cover material such as the quantum nature of light that we discussed back in chapter 1. However, there will be some extra emphasis on the material since exam 2, since you’ve not ...
... IMPORTANT: This exam will be truly cumulative, i.e. it will cover material from the entire semester. For example, it will cover material such as the quantum nature of light that we discussed back in chapter 1. However, there will be some extra emphasis on the material since exam 2, since you’ve not ...
Document
... R1 и R2 – auxilary resonator for excitation anf analysis of atoms. S – source of radiation at about 51 GHz. D – detector of atomic state: g or e . ...
... R1 и R2 – auxilary resonator for excitation anf analysis of atoms. S – source of radiation at about 51 GHz. D – detector of atomic state: g or e . ...
C. Heitzinger, C. Ringhofer. S. Ahmed, D. Vasileska
... As device sizes decrease, the standard mean-field theory for the treatment of electron-electron forces becomes less applicable. Motivated by this fact, effective quantum potentials have been established as a proven way to include quantum-mechanical effects into Monte-Carlo (MC) device simulations. T ...
... As device sizes decrease, the standard mean-field theory for the treatment of electron-electron forces becomes less applicable. Motivated by this fact, effective quantum potentials have been established as a proven way to include quantum-mechanical effects into Monte-Carlo (MC) device simulations. T ...
Contents
... -note masses for quarks are approximate. -note the antiparticles have the opposite charges and lepton numbers. -however they will all have the same masses as their matter counterparts. -gauge bosons or exchange particles (or force carriers) carry the fundamental forces. -they include the photon in t ...
... -note masses for quarks are approximate. -note the antiparticles have the opposite charges and lepton numbers. -however they will all have the same masses as their matter counterparts. -gauge bosons or exchange particles (or force carriers) carry the fundamental forces. -they include the photon in t ...
Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model
... magnitude of the wave function Ψ was equal to the probability of a quantum mechanical particle to be at the location r at time t. ...
... magnitude of the wave function Ψ was equal to the probability of a quantum mechanical particle to be at the location r at time t. ...
Department of Chemistry - The City College of New York
... Describe the internal states of atoms in terms of quantum numbers. Understand the concepts of orbitals and how they apply to both atoms and molecules. Become familiar with the concepts of rotational and vibrational spectra in terms of their origins from solution of the quantum mechanical wave equati ...
... Describe the internal states of atoms in terms of quantum numbers. Understand the concepts of orbitals and how they apply to both atoms and molecules. Become familiar with the concepts of rotational and vibrational spectra in terms of their origins from solution of the quantum mechanical wave equati ...
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom
... Building on de Broglie’s work, in 1926, Erwin Schrödinger devised a theory that could be used to explain the wave properties of electrons in atoms and molecules. The branch of physics that mathematically describes the wave properties of submicroscopic particles is called quantum mechanics or wave m ...
... Building on de Broglie’s work, in 1926, Erwin Schrödinger devised a theory that could be used to explain the wave properties of electrons in atoms and molecules. The branch of physics that mathematically describes the wave properties of submicroscopic particles is called quantum mechanics or wave m ...
Particle control in a quantum world
... Controlling single photons in a trap Serge Haroche and his research group employ a different method to reveal the mysteries of the quantum world. In the laboratory in Paris microwave photons bounce back and forth inside a small cavity between two mirrors, about three centimetres apart. The mirrors a ...
... Controlling single photons in a trap Serge Haroche and his research group employ a different method to reveal the mysteries of the quantum world. In the laboratory in Paris microwave photons bounce back and forth inside a small cavity between two mirrors, about three centimetres apart. The mirrors a ...