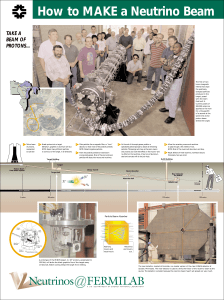
Nuclear Processes
... • Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides • They produce , and emissions. ...
... • Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides • They produce , and emissions. ...
Radioactive Decay
... • Radioactivity: Substances spontaneously emit radiation • Radiation: rays and particles emitted by radioactive material • Radioactive atoms go through changes that alter their identity – aka changes from one atom to another • How can this happen? ...
... • Radioactivity: Substances spontaneously emit radiation • Radiation: rays and particles emitted by radioactive material • Radioactive atoms go through changes that alter their identity – aka changes from one atom to another • How can this happen? ...
Proton decay studies in Liquid Argon TPC
... Purity - Efficiency for kaon and pion Kaon - Electronics noise is not taken into account - particles are very well recognized by the neural network with very high efficiency and purity ...
... Purity - Efficiency for kaon and pion Kaon - Electronics noise is not taken into account - particles are very well recognized by the neural network with very high efficiency and purity ...
nuclear physics in the vedas
... together. When neutrons were discovered, it was assumed to be charge neutral. The equation of Coulomb’s law does not apply to interaction between a charged body like proton or electron with that of a charge neutral body. This would make the atom unstable. Experiments have put a nonzero electric char ...
... together. When neutrons were discovered, it was assumed to be charge neutral. The equation of Coulomb’s law does not apply to interaction between a charged body like proton or electron with that of a charge neutral body. This would make the atom unstable. Experiments have put a nonzero electric char ...
Partial widths of the Z
... We can identify (tag) jets originating from b quarks by looking for the electrons and muons coming from b decay. Naively expect 1/8th of decays to each type of lepton. Reality is close ; BR(be) = 10.9 % , BR(bm) = 10.9 % . But there are other sources of leptons in jets, such as K+ m+n, p0 ge+e- ...
... We can identify (tag) jets originating from b quarks by looking for the electrons and muons coming from b decay. Naively expect 1/8th of decays to each type of lepton. Reality is close ; BR(be) = 10.9 % , BR(bm) = 10.9 % . But there are other sources of leptons in jets, such as K+ m+n, p0 ge+e- ...
unit 5: particle physics
... momentum (L=mvr). All known particles have spin, which must be either an integral or halfintegral multiple of the quantity h/(2π). ...
... momentum (L=mvr). All known particles have spin, which must be either an integral or halfintegral multiple of the quantity h/(2π). ...
The Strong Interaction
... In recent investigations with the photographic method, it has been shown that slow charged particles of small mass, present as a component of the cosmic radiation at high altitudes, can enter nuclei and produce disintegrations with the emission of heavy particles. It is convenient to apply the term ...
... In recent investigations with the photographic method, it has been shown that slow charged particles of small mass, present as a component of the cosmic radiation at high altitudes, can enter nuclei and produce disintegrations with the emission of heavy particles. It is convenient to apply the term ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Particle Physics Group
... Tracking Detectors Measure x-y-z location of all charged particles as the pass through predetermined parts of the detector Series of dots Get position of tracks Connect lines to find decay vertices ...
... Tracking Detectors Measure x-y-z location of all charged particles as the pass through predetermined parts of the detector Series of dots Get position of tracks Connect lines to find decay vertices ...
Tutorial material for weak interactions and more
... Additional reading on measurements of β decays to test whether neutrinos are Majorana particles: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.4791.pdf. The idea is that if the neutrino is its own anti-particle, one can join a neutrino and an antineutrino into a neutrino propagator and get a double β decay without neu ...
... Additional reading on measurements of β decays to test whether neutrinos are Majorana particles: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.4791.pdf. The idea is that if the neutrino is its own anti-particle, one can join a neutrino and an antineutrino into a neutrino propagator and get a double β decay without neu ...
student worksheet
... 12) There are two main types of radioactive decay: beta decay and alpha decay. Alpha is simpler to understand. The nucleus spits out an alpha particle, which is just a helium nucleus. For example, polonium-218 will emit an alpha particle and decay to lead-214. This just involves rearranging existing ...
... 12) There are two main types of radioactive decay: beta decay and alpha decay. Alpha is simpler to understand. The nucleus spits out an alpha particle, which is just a helium nucleus. For example, polonium-218 will emit an alpha particle and decay to lead-214. This just involves rearranging existing ...
Conception of Generations
... scattering took place in Chicago and the ∆ resonances were discovered. Artificial pions played a vital role in establishing charge independence or the conservation of isospin in pion-nucleon interactions. About the same time there was an important discovery in cosmic rays. In 1947 Rochester and Butle ...
... scattering took place in Chicago and the ∆ resonances were discovered. Artificial pions played a vital role in establishing charge independence or the conservation of isospin in pion-nucleon interactions. About the same time there was an important discovery in cosmic rays. In 1947 Rochester and Butle ...
ALICE Poster
... The ALICE Collaboration is building a dedicated heavy-ion detector to exploit the unique physics potential of nucleus-nucleus interactions at LHC energies. Our aim is to study the physics of strongly interacting matter at extreme energy densities, where the formation of a new phase of matter, the qu ...
... The ALICE Collaboration is building a dedicated heavy-ion detector to exploit the unique physics potential of nucleus-nucleus interactions at LHC energies. Our aim is to study the physics of strongly interacting matter at extreme energy densities, where the formation of a new phase of matter, the qu ...
All three experiments have identified specific B meson decays and
... What are the hints of new physics that you describe in your article? The hints originate from studies of an elementary particle, known as the B meson – an unstable particle produced in the collision of powerful particle beams. More precisely, these studies looked at decays of the B meson that invol ...
... What are the hints of new physics that you describe in your article? The hints originate from studies of an elementary particle, known as the B meson – an unstable particle produced in the collision of powerful particle beams. More precisely, these studies looked at decays of the B meson that invol ...
Particle Classification - Department of Physics, HKU
... realize that much of the classification of particles (i.e. Leptons, Mesons, Baryons, Hadrons, Bosons, and Fermions) have their roots in history. If we had to classify these particles today with what we now know about them we would probably choose different names. Looking at the history is however ...
... realize that much of the classification of particles (i.e. Leptons, Mesons, Baryons, Hadrons, Bosons, and Fermions) have their roots in history. If we had to classify these particles today with what we now know about them we would probably choose different names. Looking at the history is however ...
gg higgs - University of Southampton
... a bubble chamber due to cosmic rays of an electron but with 200 times more mass… To this day the muon interacts exactly like an electron only differing in its mass…. ...
... a bubble chamber due to cosmic rays of an electron but with 200 times more mass… To this day the muon interacts exactly like an electron only differing in its mass…. ...
The Standard Model - Stony Brook University
... S is strangeness (1 for s quark, -1 for anti-s) e is the elementary charge, 1.6 x 10-19 C I is isospin, where the number of particles in a family is 2I + 1 I3 is isospin component, which is related to sequence of a particle in a family, on the interval if (-I, I) ...
... S is strangeness (1 for s quark, -1 for anti-s) e is the elementary charge, 1.6 x 10-19 C I is isospin, where the number of particles in a family is 2I + 1 I3 is isospin component, which is related to sequence of a particle in a family, on the interval if (-I, I) ...
ppt - University of Warwick
... A. It's complicated...and can only be correctly described using the full mathematical machinery of quantum mechanics. ...
... A. It's complicated...and can only be correctly described using the full mathematical machinery of quantum mechanics. ...
PHY583 - Test 3 - 20.6.12 - with solution
... Elementary point-like particles with no structure Currently only six known leptons: electron, muon, tau, (e, ,) and their respective neutrinos: electron neutrino, muon neutrino and tau neutrino (e, , , ) Spin ½ Participate in electromagnetic and weak interactions ...
... Elementary point-like particles with no structure Currently only six known leptons: electron, muon, tau, (e, ,) and their respective neutrinos: electron neutrino, muon neutrino and tau neutrino (e, , , ) Spin ½ Participate in electromagnetic and weak interactions ...
Leggi in PDF - SIF Prima Pagina
... experiments were needed: the (g–2) and the muon lifetime. To measure with high precision the anomalous magnetic moment of the "muon", also known as the (g–2) value, it was necessary to invent a new technology able to capture in a "polynomial" magnetic field a muon in order to let it rotate thousands ...
... experiments were needed: the (g–2) and the muon lifetime. To measure with high precision the anomalous magnetic moment of the "muon", also known as the (g–2) value, it was necessary to invent a new technology able to capture in a "polynomial" magnetic field a muon in order to let it rotate thousands ...
People`s Physics Book 3e Ch 22-1 The Big Idea All matter is
... For any interaction between particles, the five conservation laws (energy, momentum, angular momentum, charge, and CPT) must be followed. For instance, the total electric charge must always be the same before and after an interaction. Electron lepton number is conserved. This means that the total nu ...
... For any interaction between particles, the five conservation laws (energy, momentum, angular momentum, charge, and CPT) must be followed. For instance, the total electric charge must always be the same before and after an interaction. Electron lepton number is conserved. This means that the total nu ...
quarks
... 1933-34 Yukawa combines relativity and quantum theory to describe nuclear interactions by an exchange of new particles (mesons called "pions") between protons and neutrons. From the size of the nucleus, Yukawa concludes that the mass of the conjectured particles (mesons) is about 200 electron masses ...
... 1933-34 Yukawa combines relativity and quantum theory to describe nuclear interactions by an exchange of new particles (mesons called "pions") between protons and neutrons. From the size of the nucleus, Yukawa concludes that the mass of the conjectured particles (mesons) is about 200 electron masses ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
... As mentioned above, all matter consists only of quarks and leptons. All detectable matter that is. In 1980 measurements of velocity curves in spiral galaxies first showed that there is much more matter in such galaxies than can be accounted for by direct observation2 [4]. At this moment the amount o ...
... As mentioned above, all matter consists only of quarks and leptons. All detectable matter that is. In 1980 measurements of velocity curves in spiral galaxies first showed that there is much more matter in such galaxies than can be accounted for by direct observation2 [4]. At this moment the amount o ...
quarks and leptons - answers to practice questions
... The neutrino has no charge. Don’t be put off by the unfamiliar sigma particle; the question is about general properties. A baryon always contains 3 quarks. Strange particles always decay by the weak interaction. All the other baryons decay into protons. The proton is the only stable baryon. The weak ...
... The neutrino has no charge. Don’t be put off by the unfamiliar sigma particle; the question is about general properties. A baryon always contains 3 quarks. Strange particles always decay by the weak interaction. All the other baryons decay into protons. The proton is the only stable baryon. The weak ...
Lecture 1
... 1973 First indications of weak interactions with no charge exchange (due to Z0 exchange.) A quantum field theory of strong interaction is formulated (QCD) Politzer, Gross, and Wilczek discover that the color theory of the strong interaction has a special property, now called “asymptotic freedom.” 19 ...
... 1973 First indications of weak interactions with no charge exchange (due to Z0 exchange.) A quantum field theory of strong interaction is formulated (QCD) Politzer, Gross, and Wilczek discover that the color theory of the strong interaction has a special property, now called “asymptotic freedom.” 19 ...