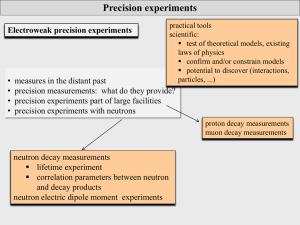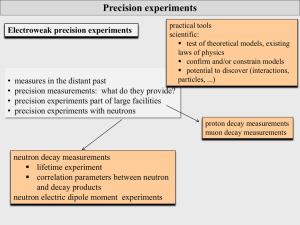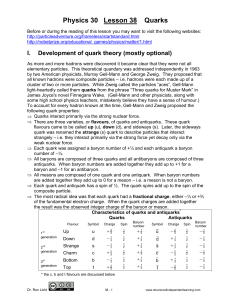
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... filled up, there were no more particles that could be accounted for with three quarks. The difficulty was soon settled by appealing to an idea, suggested by a DanishAmerican physicist named Sheldon L. Glashow, that had been around for some time but had found little support. Because there were then f ...
... filled up, there were no more particles that could be accounted for with three quarks. The difficulty was soon settled by appealing to an idea, suggested by a DanishAmerican physicist named Sheldon L. Glashow, that had been around for some time but had found little support. Because there were then f ...
Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE)
... Majorana Fermions, CP Violation, and the Matter/Antimatter Imbalance A Majorana fermion (named after the Italian physicist Ettore Majorana, who hypothesized its existence in 1937) is a fermion that is its own antiparticle. A particle and its antiparticle must have opposite charges, which means t ...
... Majorana Fermions, CP Violation, and the Matter/Antimatter Imbalance A Majorana fermion (named after the Italian physicist Ettore Majorana, who hypothesized its existence in 1937) is a fermion that is its own antiparticle. A particle and its antiparticle must have opposite charges, which means t ...
universo feature
... “meson” as being the quantum of the Nuclear Forces. Yukawa named his particle “meson” since its mass had to be “intermediate”, i.e. with a value between the lightest, the electron (0.5 MeV) and the heaviest, the nucleon (1000 MeV), particles known in 1947. And this, in order to account for the range ...
... “meson” as being the quantum of the Nuclear Forces. Yukawa named his particle “meson” since its mass had to be “intermediate”, i.e. with a value between the lightest, the electron (0.5 MeV) and the heaviest, the nucleon (1000 MeV), particles known in 1947. And this, in order to account for the range ...
neutrino
... neutral particles, that I wish to call neutrons, which have spin 1/2 and obey the exclusion principle and which further differ from light quanta in that they do not travel with the velocity of light. The mass of the neutrons should be of the same order of magnitude as the electron mass and in any ev ...
... neutral particles, that I wish to call neutrons, which have spin 1/2 and obey the exclusion principle and which further differ from light quanta in that they do not travel with the velocity of light. The mass of the neutrons should be of the same order of magnitude as the electron mass and in any ev ...
Muons, Inc. - This is the Muons, Inc. Internal Website.
... – Requires regions with large dispersion • Absorbers for ionization cooling have to be located in the region of small dispersion to reduce straggling impact • Suggested solution (Derbenev, LEMC08; Afanasev, Derbenev, Johnson, EPAC08): Design of an epicyclic HCC characterized by alternating dispersio ...
... – Requires regions with large dispersion • Absorbers for ionization cooling have to be located in the region of small dispersion to reduce straggling impact • Suggested solution (Derbenev, LEMC08; Afanasev, Derbenev, Johnson, EPAC08): Design of an epicyclic HCC characterized by alternating dispersio ...
10/29/2007 Julia Velkovska PHY 340a
... 5. Lepton number ( each individual L# is conserved, except in neutrino mixing) 1-5 are are conserved by any interaction In addition: 6. Hadronic flavor is conserved by EM & strong interactions ( but not in weak) 7. Parity is conserved in EM& strong, but not in weak Julia Velkovska ...
... 5. Lepton number ( each individual L# is conserved, except in neutrino mixing) 1-5 are are conserved by any interaction In addition: 6. Hadronic flavor is conserved by EM & strong interactions ( but not in weak) 7. Parity is conserved in EM& strong, but not in weak Julia Velkovska ...
Antonio Policicchio
... • Muon activity veto to remove cosmic/beam-halo backgrounds • Background • Mainly comes from cosmic, noise and beam halo interactions • Estimated using low-luminosity data (cosmic) and unpaired crossings (beam halo) •No excess observed ⇾ A limit of > 545-784 GeV (depending on the interaction model) ...
... • Muon activity veto to remove cosmic/beam-halo backgrounds • Background • Mainly comes from cosmic, noise and beam halo interactions • Estimated using low-luminosity data (cosmic) and unpaired crossings (beam halo) •No excess observed ⇾ A limit of > 545-784 GeV (depending on the interaction model) ...
SU(3) - Physics
... Leptonic Decays of Vector Mesons What is the experimental evidence that quarks have non-integer charge ? Both the mass splitting of baryons and mesons and baryon magnetic moments depend on (e/m) not e. Some quark models with integer charge quarks (e.g. Han-Nambu) were also successful in explaining ...
... Leptonic Decays of Vector Mesons What is the experimental evidence that quarks have non-integer charge ? Both the mass splitting of baryons and mesons and baryon magnetic moments depend on (e/m) not e. Some quark models with integer charge quarks (e.g. Han-Nambu) were also successful in explaining ...
Lecture 13 - PPD - STFC Particle Physics Department
... • 1927 Dirac intrinsic angular momentum and magnetic moment of electron quantified • measurements of g factors pushed further development of QED • May and November 1947 electron g factor measurement different from 2: g factor anomaly ae • Formulation of QED with first order radiative correction ...
... • 1927 Dirac intrinsic angular momentum and magnetic moment of electron quantified • measurements of g factors pushed further development of QED • May and November 1947 electron g factor measurement different from 2: g factor anomaly ae • Formulation of QED with first order radiative correction ...
Higgs Analysis for the CMS Lee Coates
... Evidence of the Higgs Mechanism • By reconstructing the decay products, we can see if the Higgs Boson really exists • Problem: hadron colliders produce messy collisions – Background elimination – Isolated signal will appear as some new physics that we haven’t seen yet • Mass peak, MET, etc.—no one k ...
... Evidence of the Higgs Mechanism • By reconstructing the decay products, we can see if the Higgs Boson really exists • Problem: hadron colliders produce messy collisions – Background elimination – Isolated signal will appear as some new physics that we haven’t seen yet • Mass peak, MET, etc.—no one k ...
Document
... • pions decay to polarised muons and are injected in storage ring • decay electrons emerge preferentially in direction of muon spin • detect those electrons with high enough energy to be in the direction of the muon motion detecting a signal of the muon spin in forward direction signal oscillates wi ...
... • pions decay to polarised muons and are injected in storage ring • decay electrons emerge preferentially in direction of muon spin • detect those electrons with high enough energy to be in the direction of the muon motion detecting a signal of the muon spin in forward direction signal oscillates wi ...
neutrinos: mysterious particles with fascinating features, which led to
... that some nuclei change their spin by 1 unit under β-decay, so he specified that this new particle should carry spin 1/2, just like the electron; thus also angular momentum conservation is saved. To further conserve the electric charge, it must be electrically neutral, therefore he wanted to call i ...
... that some nuclei change their spin by 1 unit under β-decay, so he specified that this new particle should carry spin 1/2, just like the electron; thus also angular momentum conservation is saved. To further conserve the electric charge, it must be electrically neutral, therefore he wanted to call i ...
PHY313 - CEI544 The Mystery of Matter From Quarks to the
... heavy elements into the interstellar medium. They are then incorporated into new stellar objects ...
... heavy elements into the interstellar medium. They are then incorporated into new stellar objects ...
here
... Other gauge bosons, mediating weak (W, Z), and strong interactions (the gluons g), only act at very short distances, less than the proton radius, albeit for very different reasons (confinement and symmetry breaking) It’s about time to take away that question mark! Peter Higgs ...
... Other gauge bosons, mediating weak (W, Z), and strong interactions (the gluons g), only act at very short distances, less than the proton radius, albeit for very different reasons (confinement and symmetry breaking) It’s about time to take away that question mark! Peter Higgs ...
constitution of matter, the standard model
... could be explained by a few types of yet smaller objects. Murray Gell-Mann in 1964 gave them the name: quarks. This is a nonsense word used by James Joyce in his novel: “Finnegan's Wake” in his exclamation: "Three quarks for Muster Mark!" The quarks could explain all the observed baryons and mesons ...
... could be explained by a few types of yet smaller objects. Murray Gell-Mann in 1964 gave them the name: quarks. This is a nonsense word used by James Joyce in his novel: “Finnegan's Wake” in his exclamation: "Three quarks for Muster Mark!" The quarks could explain all the observed baryons and mesons ...
Working Group Talks Gobinda Majumdar Issues In The Construction
... • In SUSY we need gaugino mass nonuniversality: M2/M1~4 at the weak scale • We found a good benchmark point with this property by “deforming” the SPS1a. • Substantial rate of dilepton cascade decays at this point will allow for a precise determination of the spectrum at the LHC • A more general scan ...
... • In SUSY we need gaugino mass nonuniversality: M2/M1~4 at the weak scale • We found a good benchmark point with this property by “deforming” the SPS1a. • Substantial rate of dilepton cascade decays at this point will allow for a precise determination of the spectrum at the LHC • A more general scan ...
OscSNS: Precision Neutrino Measurements at
... designed to produce 695 ns width pulses; the SNS has already produced pulses less than 500 ns wide. This pulse width is significantly shorter than previous accelerator based neutrino experiments LSND [3] and MiniBooNE [4]. In addition to the spallation neutrons, the interaction of protons with the t ...
... designed to produce 695 ns width pulses; the SNS has already produced pulses less than 500 ns wide. This pulse width is significantly shorter than previous accelerator based neutrino experiments LSND [3] and MiniBooNE [4]. In addition to the spallation neutrons, the interaction of protons with the t ...
Flipped SU(5) - cosmology - Arizona State University
... problematically fast. However, the lowering of the M32 scale will more than compensate for this lifetime increase. ...
... problematically fast. However, the lowering of the M32 scale will more than compensate for this lifetime increase. ...
Flavor Beyond Standard Model
... Processes, which are highly suppressed in the Standard Model (SM), such as decays mediated by flavour changing neutral currents (FCNC) allow stringent tests of our current understanding of particle physics. These transitions are forbidden at tree level in the SM, as all electrically neutral particle ...
... Processes, which are highly suppressed in the Standard Model (SM), such as decays mediated by flavour changing neutral currents (FCNC) allow stringent tests of our current understanding of particle physics. These transitions are forbidden at tree level in the SM, as all electrically neutral particle ...
χSR - MENU 2013
... 2. The novel mechanism for intermediate- and short-range nuclear interactions through the intermediate dibaryon production is presented. The dibaryon properties are governed by the χSR phenomenon and symmetries of QCD. 3. The new model for the famous ABC puzzle, based on dibaryon production with str ...
... 2. The novel mechanism for intermediate- and short-range nuclear interactions through the intermediate dibaryon production is presented. The dibaryon properties are governed by the χSR phenomenon and symmetries of QCD. 3. The new model for the famous ABC puzzle, based on dibaryon production with str ...
non-relativistic Breit
... production of W , eg. e− ν̄e → W − → fermions is not technically feasible since we cannot create a beam of neutrinos which is well enough focused. Instead at LEP2 (1996–2000) they used the processes e+ e− → W + W − (exchanging a neutrino) and e+ e− → Z ⋆ /γ ⋆ → W + W − (via an off-shell Z 0 or γ). T ...
... production of W , eg. e− ν̄e → W − → fermions is not technically feasible since we cannot create a beam of neutrinos which is well enough focused. Instead at LEP2 (1996–2000) they used the processes e+ e− → W + W − (exchanging a neutrino) and e+ e− → Z ⋆ /γ ⋆ → W + W − (via an off-shell Z 0 or γ). T ...
C1 and C2 are threshold Cerenkov counters filled with CO 2 , for
... Nicola Mazziotta, Dec. 6, 2005 ...
... Nicola Mazziotta, Dec. 6, 2005 ...
Our bodies are made of neutrons, protons and electrons
... electron, which have integer charges of +1 and -1 respectively. Quarks also carry another type of charge called color charge, which we will discuss later. The most elusive quark, the top quark, was discovered in 1995 after its existence had been theorized for 20 years. In addition, there are gluons, ...
... electron, which have integer charges of +1 and -1 respectively. Quarks also carry another type of charge called color charge, which we will discuss later. The most elusive quark, the top quark, was discovered in 1995 after its existence had been theorized for 20 years. In addition, there are gluons, ...
Experimental Apparatus
... Protons are extracted at 8 GeV from the booster into the main injector, which accelerates them to 150 GeV, ready for injection into the Tevatron. Antiprotons, p̄s, are produced by bombarding a Ni target with 120 GeV protons from the main injector, every 1.5 s. The angular spread of the produced part ...
... Protons are extracted at 8 GeV from the booster into the main injector, which accelerates them to 150 GeV, ready for injection into the Tevatron. Antiprotons, p̄s, are produced by bombarding a Ni target with 120 GeV protons from the main injector, every 1.5 s. The angular spread of the produced part ...