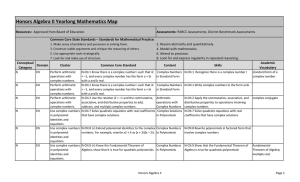
Review Problems
... forgotten. Use the problems below to refresh those skills which are rusty, rather than to try to learn new material. If you encounter an unfamiliar problem, you should not spend a lot of time trying to obtain the background necessary to successfully complete the problem; just skip that problem and t ...
... forgotten. Use the problems below to refresh those skills which are rusty, rather than to try to learn new material. If you encounter an unfamiliar problem, you should not spend a lot of time trying to obtain the background necessary to successfully complete the problem; just skip that problem and t ...
Test on Topic 15 Solving a System of Equations
... jobs cost the following. A 2000 page job cost him $150, while a 3000 page job cost him $200. (a) Set up a system of equations to reflect the above information. (b) Solve the system of equations and so find how much the fixed setup fee x is and how much is the charge per page y? (c) He needs to have ...
... jobs cost the following. A 2000 page job cost him $150, while a 3000 page job cost him $200. (a) Set up a system of equations to reflect the above information. (b) Solve the system of equations and so find how much the fixed setup fee x is and how much is the charge per page y? (c) He needs to have ...