7.1 Solving Linear systems by graphing
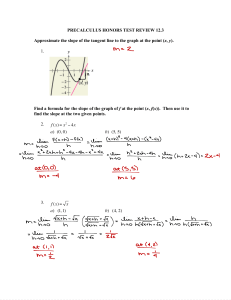
... SOLVING A SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS BY GRAPHING. Let's summarize! There are 3 steps to solving a system using a graph. Step 1: Graph both equations. ...
... SOLVING A SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS BY GRAPHING. Let's summarize! There are 3 steps to solving a system using a graph. Step 1: Graph both equations. ...
Linear graphs
... Activating prior knowledge for linear graphs Brainstorm what learners already know about linear graphs. Draw a mind map on the board and ask them to give you facts they remember. Use correct order of operation ...
... Activating prior knowledge for linear graphs Brainstorm what learners already know about linear graphs. Draw a mind map on the board and ask them to give you facts they remember. Use correct order of operation ...