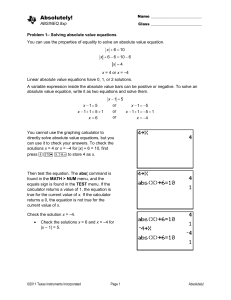
Causal Structure Learning in Process
... Markov Blanket: All variables that shield the node from the rest of the network Redundancy: Detection of edges through two Markov blankets Size of measurement data depends on Markov blanket and not on topology Detection of V-structures in the graph ...
... Markov Blanket: All variables that shield the node from the rest of the network Redundancy: Detection of edges through two Markov blankets Size of measurement data depends on Markov blanket and not on topology Detection of V-structures in the graph ...
Algebra 1 3rd Trimester Expectations Chapter CCSS covered Key
... reveal and explain different properties of the function. ★ a. Use the process of factoring and completing the square in a quadratic function to show zeros, extreme values, and symmetry of the graph, and interpret these in terms of a context. b. Use the properties of exponents to interpret expression ...
... reveal and explain different properties of the function. ★ a. Use the process of factoring and completing the square in a quadratic function to show zeros, extreme values, and symmetry of the graph, and interpret these in terms of a context. b. Use the properties of exponents to interpret expression ...
Algebra 2 - Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
... A-SSE.B4 Derive the formula for the sum of a finite geometric series (when the common ratio is not 1), and use the formula to solve problems. A-APR Arithmetic with polynomials and rational expressions Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials. A-APR.A.1 Understand that polynomials form a system a ...
... A-SSE.B4 Derive the formula for the sum of a finite geometric series (when the common ratio is not 1), and use the formula to solve problems. A-APR Arithmetic with polynomials and rational expressions Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials. A-APR.A.1 Understand that polynomials form a system a ...
A Quick Introduction to DC Analysis With MicroCap
... reference node. The 2 V drop across the 1 kΩ resistor implies a 2 mA current flowing from left to right. The 8 V across the 2 kΩ resistor would imply a 4 mA current flowing from top to bottom. Notice that Kirchhoff's Current Law is satisfied at the node where the 1 kΩ, 2 kΩ, and current source conne ...
... reference node. The 2 V drop across the 1 kΩ resistor implies a 2 mA current flowing from left to right. The 8 V across the 2 kΩ resistor would imply a 4 mA current flowing from top to bottom. Notice that Kirchhoff's Current Law is satisfied at the node where the 1 kΩ, 2 kΩ, and current source conne ...