Chapter 3 Clocked circuits
... 3.7. A staticizer is a pair of coupled inverters, with the inverter that may compete with the original state holding element so small that the set and reset transistors will allways win. Since the output of an inverter is allways driven, and because the pair of inverters is stable once the new value ...
... 3.7. A staticizer is a pair of coupled inverters, with the inverter that may compete with the original state holding element so small that the set and reset transistors will allways win. Since the output of an inverter is allways driven, and because the pair of inverters is stable once the new value ...
ADA4850-1
... The maximum safe power dissipation for the ADA4850-1/ ADA4850-2 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature (TJ) on the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass transition temperature, the plastic changes its properties. Even temporarily exceeding this temperature limit may chan ...
... The maximum safe power dissipation for the ADA4850-1/ ADA4850-2 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature (TJ) on the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass transition temperature, the plastic changes its properties. Even temporarily exceeding this temperature limit may chan ...
The UC1901 Simplifies the Problem of Isolated
... a simple toroid core can be used. The second requirement of the transformer primarily determines the amount of magnetizing inductance it must have. The magnetizing inductance of a transformer refers to the actual inductance formed by the windings around the core material. In many classical transform ...
... a simple toroid core can be used. The second requirement of the transformer primarily determines the amount of magnetizing inductance it must have. The magnetizing inductance of a transformer refers to the actual inductance formed by the windings around the core material. In many classical transform ...
ISSCC 2016 Digest of Technical Papers
... The target of this work is to develop a low-power 39.25MHz crystal oscillator (XO) with low phase noise for RF applications and to achieve the highest FOM in XO’s. To reduce the supply current at a constant negative resistance (RN) in the XO, a stacked-amplifier crystal oscillator (SAXO) operating a ...
... The target of this work is to develop a low-power 39.25MHz crystal oscillator (XO) with low phase noise for RF applications and to achieve the highest FOM in XO’s. To reduce the supply current at a constant negative resistance (RN) in the XO, a stacked-amplifier crystal oscillator (SAXO) operating a ...
DC to 50 MHz, Dual I/Q Demodulator and Phase Shifter AD8333
... Sixteen discrete phase rotations in 22.5° increments can be selected independently for each channel. For example, if Channel 1 is used as a reference and the RF signal applied to Channel 2 has an I/Q phase lead of 45°, Channel 2 can be phase aligned with Channel 1 by choosing the correct code. ...
... Sixteen discrete phase rotations in 22.5° increments can be selected independently for each channel. For example, if Channel 1 is used as a reference and the RF signal applied to Channel 2 has an I/Q phase lead of 45°, Channel 2 can be phase aligned with Channel 1 by choosing the correct code. ...
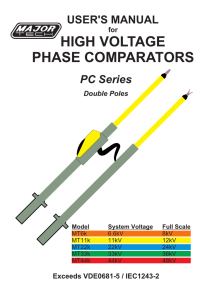
high voltage phase comparators
... • Before and after using a Phase Comparator and accessories, a functional test should be performed on the Phase Comparator as It is to be used on the source or circuit to test. • A High Voltage Insulation tester can be used for this purpose. • When using a High Voltage Insulation tester, the Phase C ...
... • Before and after using a Phase Comparator and accessories, a functional test should be performed on the Phase Comparator as It is to be used on the source or circuit to test. • A High Voltage Insulation tester can be used for this purpose. • When using a High Voltage Insulation tester, the Phase C ...
Solution
... can also be studied in the frequency domain. Neglecting the effect of the filter in the data path, determine the transfer function from xBB(t) to Φout. Beginning from the output, we write the feedback signal arriving at the PFD as Φout/N, subtract it from 0 (the input phase), and multiply the result ...
... can also be studied in the frequency domain. Neglecting the effect of the filter in the data path, determine the transfer function from xBB(t) to Φout. Beginning from the output, we write the feedback signal arriving at the PFD as Φout/N, subtract it from 0 (the input phase), and multiply the result ...
nemmani_paper
... width of the wider of the two pulses. The delay chain in a TDC generates delayed versions of the OR pulse. When these delayed versions are latched by the falling edge of the OR pulse, the number of latch outputs that are high is the width of the OR pulse in number of inverter delays. A matching dela ...
... width of the wider of the two pulses. The delay chain in a TDC generates delayed versions of the OR pulse. When these delayed versions are latched by the falling edge of the OR pulse, the number of latch outputs that are high is the width of the OR pulse in number of inverter delays. A matching dela ...
new dsmreport2
... upper C1 input capacitor on phase 2, and then the difference between the input and reference is integrated onto the upper C2 integrating capacitor on the next phase 1. The lower path feeds the inverted signal to the integrating capacitor also in phase 1, but samples the input on phase 1 and the refe ...
... upper C1 input capacitor on phase 2, and then the difference between the input and reference is integrated onto the upper C2 integrating capacitor on the next phase 1. The lower path feeds the inverted signal to the integrating capacitor also in phase 1, but samples the input on phase 1 and the refe ...
Lecture 4: RLC series circuit: V
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
Low-Noise, High-Speed,16-Bit Accurate, CMOS
... The OPA300 and OPA301 series op amps have 150MHz of unity-gain bandwidth, low 3nV/√Hz voltage noise, and 0.1% settling within 30ns. Single-supply operation from 2.7V (±1.35V) to 5.5V (±2.75V) and an available shutdown function that reduces supply current to 5µA are useful for portable low-power appl ...
... The OPA300 and OPA301 series op amps have 150MHz of unity-gain bandwidth, low 3nV/√Hz voltage noise, and 0.1% settling within 30ns. Single-supply operation from 2.7V (±1.35V) to 5.5V (±2.75V) and an available shutdown function that reduces supply current to 5µA are useful for portable low-power appl ...
CHAPTER 3: SiGe MONOLITHIC TECHNOLOGIES
... consists of equations for input impedance, input return loss (S11), forward gain (S21) and NF, as well as an approximation of the IIP3 of the LNA. From this model compact design equations were also derived. The above derivations are presented in this chapter. All mathematical modelling for the resea ...
... consists of equations for input impedance, input return loss (S11), forward gain (S21) and NF, as well as an approximation of the IIP3 of the LNA. From this model compact design equations were also derived. The above derivations are presented in this chapter. All mathematical modelling for the resea ...
Alexander
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
Bode plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. Both quantities are plotted against a horizontal axis proportional to the logarithm of frequency.