LCR and resonance
... This is known as the resonant condition for the circuit. You can see that since XL and XC are frequency-dependent, the resonant condition depends on the frequency of the applied a.c. Every series a.c. circuit has a frequency for which resonance occurs, known as its resonant frequency (fo). This is g ...
... This is known as the resonant condition for the circuit. You can see that since XL and XC are frequency-dependent, the resonant condition depends on the frequency of the applied a.c. Every series a.c. circuit has a frequency for which resonance occurs, known as its resonant frequency (fo). This is g ...
Experiment 6 - Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
... 1.2 Measurement of Current and Resistance Using a CRO : Using the general method, a correctly calibrated CRO can be used in conjunction with a known value of resistance R to determine the current I flowing through the resistor. 1.3 Measurement of Frequency Using a CRO : A simple method of determinin ...
... 1.2 Measurement of Current and Resistance Using a CRO : Using the general method, a correctly calibrated CRO can be used in conjunction with a known value of resistance R to determine the current I flowing through the resistor. 1.3 Measurement of Frequency Using a CRO : A simple method of determinin ...
(with corrections indicated in lecture) MSWord file, due session 22
... components of a space vector representation thereof. You may work in a per unit system of your choice if you prefer. b. Create a plot similar to what was presented in class. Plot all the vectors. Label each vector in the first hextant; that’s plenty. You can check your plot using Prof. Corzine’s ref ...
... components of a space vector representation thereof. You may work in a per unit system of your choice if you prefer. b. Create a plot similar to what was presented in class. Plot all the vectors. Label each vector in the first hextant; that’s plenty. You can check your plot using Prof. Corzine’s ref ...
frequency A - Physics | Oregon State University
... So now you can see how useful the admittance function is, and why it is important to know how its magnitude and phase shift vary with frequency: if there is a driving force that can be expressed as the sum of sinusoids, we simply use the admittance function to find the response at each of the drivin ...
... So now you can see how useful the admittance function is, and why it is important to know how its magnitude and phase shift vary with frequency: if there is a driving force that can be expressed as the sum of sinusoids, we simply use the admittance function to find the response at each of the drivin ...
PLL synthesizing oscillator (3)
... This IC is composed from the phase comparator which detects the difference between the reference frequency and the comparison frequency and the VCO which generates the digital pulse. There are two kinds of phase comparators. As for the 1st, it outputs the phase difference of the input signal (the re ...
... This IC is composed from the phase comparator which detects the difference between the reference frequency and the comparison frequency and the VCO which generates the digital pulse. There are two kinds of phase comparators. As for the 1st, it outputs the phase difference of the input signal (the re ...
Course code……EL-212…... Course title… Electrical Network
... This lab gives the foundation on which most other courses in electrical engineering curriculum rest. Subject areas included are, AC circuit quantities, AC voltage and currents, Phase measurements, Phase Shifters, AC bridges, Capacitance Multiplier, Oscillators, Kirchhoff’s Laws, Power factor Measure ...
... This lab gives the foundation on which most other courses in electrical engineering curriculum rest. Subject areas included are, AC circuit quantities, AC voltage and currents, Phase measurements, Phase Shifters, AC bridges, Capacitance Multiplier, Oscillators, Kirchhoff’s Laws, Power factor Measure ...
Exponential Carrier Wave Modulation
... In the Costas PLL (below) two phase discriminators are used to: – cancel out DSB modulation x(t) in the driving signal – synchronize the output frequency to the center frequency of the DSB spectra (the suppressed carrier) – to detect the DSB signal ...
... In the Costas PLL (below) two phase discriminators are used to: – cancel out DSB modulation x(t) in the driving signal – synchronize the output frequency to the center frequency of the DSB spectra (the suppressed carrier) – to detect the DSB signal ...
Homework 15
... 2. (a) Design a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 3400 Hz. Use a 0.2 µF capacitor and an appropriate resistor (calculate its value). (b) Sketch and label the circuit. (c) What is the gain of the filter at the cutoff frequency? Give your answer both as a ratio (Vout/Vin) and in dB. (d) What ...
... 2. (a) Design a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 3400 Hz. Use a 0.2 µF capacitor and an appropriate resistor (calculate its value). (b) Sketch and label the circuit. (c) What is the gain of the filter at the cutoff frequency? Give your answer both as a ratio (Vout/Vin) and in dB. (d) What ...
phy3722c: analog electronics
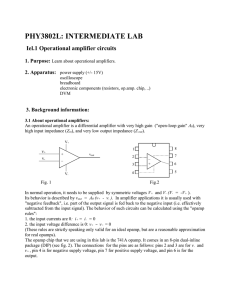
... In normal operation, it needs to be supplied by symmetric voltages V+ and V- (V- = -V+ ). Its behavior is described by vout = A0 (v+ - v- ). In amplifier applications it is usually used with "negative feedback", i.e. part of the output signal is fed back to the negative input (i.e. effectively subtr ...
... In normal operation, it needs to be supplied by symmetric voltages V+ and V- (V- = -V+ ). Its behavior is described by vout = A0 (v+ - v- ). In amplifier applications it is usually used with "negative feedback", i.e. part of the output signal is fed back to the negative input (i.e. effectively subtr ...
Bode plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. Both quantities are plotted against a horizontal axis proportional to the logarithm of frequency.