MAX1760/MAX1760H 0.8A, Low-Noise, 1MHz, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description
... The MAX1760 is a highly efficient, low-noise power supply for portable RF and hand-held instruments. It combines a boost switching regulator, N-channel power MOSFET, P-channel synchronous rectifier, precision reference, and shutdown control (Figure 1). The DC-DC converter boosts a 1-cell to 3-cell b ...
... The MAX1760 is a highly efficient, low-noise power supply for portable RF and hand-held instruments. It combines a boost switching regulator, N-channel power MOSFET, P-channel synchronous rectifier, precision reference, and shutdown control (Figure 1). The DC-DC converter boosts a 1-cell to 3-cell b ...
Leakage Current Reduction in CMOS VLSI Circuits by Input Vector
... voltage and/or length due to process variation, contribute more to the overall leakage. Although previously the leakage current was important only in systems with long inactive periods (e.g., pagers and networks of sensors), it has become a critical design concern in any system in today’s designs. U ...
... voltage and/or length due to process variation, contribute more to the overall leakage. Although previously the leakage current was important only in systems with long inactive periods (e.g., pagers and networks of sensors), it has become a critical design concern in any system in today’s designs. U ...
MAX9708 20W/40W, Filterless, Spread-Spectrum, Mono/Stereo, Class D Amplifier General Description
... The MAX9708 mono/stereo, Class D audio power amplifier delivers up to 2 x 21W into an 8Ω stereo mode and 1 x 42W into a 4Ω load in mono mode while offering up to 87% efficiency. The MAX9708 provides Class AB amplifier performance with the benefits of Class D efficiency, eliminating the need for a bu ...
... The MAX9708 mono/stereo, Class D audio power amplifier delivers up to 2 x 21W into an 8Ω stereo mode and 1 x 42W into a 4Ω load in mono mode while offering up to 87% efficiency. The MAX9708 provides Class AB amplifier performance with the benefits of Class D efficiency, eliminating the need for a bu ...
AD6644 数据手册DataSheet下载
... III. Sample tested only. IV. Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization testing. V. Parameter is a typical value only. ...
... III. Sample tested only. IV. Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization testing. V. Parameter is a typical value only. ...
BQ24314 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The device continuously monitors the input voltage, the input current, and the battery voltage as described in detail in the following sections. Input Overvoltage Protection If the input voltage rises above VOVP, the internal FET Q1 is turned off, removing power from the circuit. As shown in Figure ...
... The device continuously monitors the input voltage, the input current, and the battery voltage as described in detail in the following sections. Input Overvoltage Protection If the input voltage rises above VOVP, the internal FET Q1 is turned off, removing power from the circuit. As shown in Figure ...
MAX5550 Dual, 10-Bit, Programmable, 30mA High-Output-Current DAC General Description
... for PIN diode biasing applications. Outputs can also be paralleled for high-current applications (up to 60mA typ). Operating from a single +2.7V to +5.25V supply, the MAX5550 typically consumes 1.5mA per DAC in normal operation and less than 1µA (max) in shutdown mode. The MAX5550 also features low ...
... for PIN diode biasing applications. Outputs can also be paralleled for high-current applications (up to 60mA typ). Operating from a single +2.7V to +5.25V supply, the MAX5550 typically consumes 1.5mA per DAC in normal operation and less than 1µA (max) in shutdown mode. The MAX5550 also features low ...
AD5161 数据手册DataSheet下载
... read back the wiper register content. When the SPI mode is used, the device can be daisy-chained (SDO to SDI), allowing several parts to share the same control lines. In the I2C mode, address pin AD0 can be used to place up to two devices on the same bus. In this same mode, command bits are availabl ...
... read back the wiper register content. When the SPI mode is used, the device can be daisy-chained (SDO to SDI), allowing several parts to share the same control lines. In the I2C mode, address pin AD0 can be used to place up to two devices on the same bus. In this same mode, command bits are availabl ...
Discrete Input Modules
... (eg. 0 to 7 and 100 to 103) and are labeled 12 CIRCUITS. Above the first set of pins are the labels 12/24V and 5V. Above the second set of pins are the labels SINK and SRC (source). To select an operating mode for the first 12 circuits, place a jumper on the two pins nearest the appropriate labels. ...
... (eg. 0 to 7 and 100 to 103) and are labeled 12 CIRCUITS. Above the first set of pins are the labels 12/24V and 5V. Above the second set of pins are the labels SINK and SRC (source). To select an operating mode for the first 12 circuits, place a jumper on the two pins nearest the appropriate labels. ...
Maxim MAX13487 - RS232 converter
... receiver to keep the bus in the correct state. This AutoDirection circuitry consists of a state machine and an additional receive comparator that determines whether this device is trying to drive the bus, or another node on the network is driving the bus. The internal state machine has two inputs: • ...
... receiver to keep the bus in the correct state. This AutoDirection circuitry consists of a state machine and an additional receive comparator that determines whether this device is trying to drive the bus, or another node on the network is driving the bus. The internal state machine has two inputs: • ...
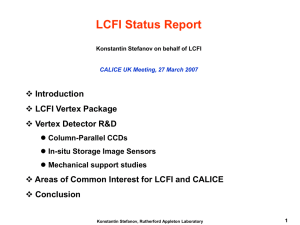
MAX11163 16-Bit, 250ksps, +5V Unipolar Input, SAR ADC, in Tiny 10-Pin µMAX
... Serial Data Input and Mode Select Input. Daisy-chain mode is selected if SDI is low during the CNVST rising edge. In this mode, SDI is used as a data input to daisy-chain the conversion results of two or more ADCs onto a single SDO line. CS mode is selected if SDI is high during the CNVST rising edg ...
... Serial Data Input and Mode Select Input. Daisy-chain mode is selected if SDI is low during the CNVST rising edge. In this mode, SDI is used as a data input to daisy-chain the conversion results of two or more ADCs onto a single SDO line. CS mode is selected if SDI is high during the CNVST rising edg ...
FAN7085_GF085 High Side Gate Driver with Recharge FET F
... and high speed driving of MOSFET or IGBT, which operates up to 300V. Fairchild's high-voltage process and common-mode noise cancellation technique provide stable operation in the high side driver under high-dV/dt noise circumstances. Logic input is compatible with standard CMOS outputs. The UVLO cir ...
... and high speed driving of MOSFET or IGBT, which operates up to 300V. Fairchild's high-voltage process and common-mode noise cancellation technique provide stable operation in the high side driver under high-dV/dt noise circumstances. Logic input is compatible with standard CMOS outputs. The UVLO cir ...
Low-Power Single Loop and Dual-Loop AGCs for Bionic Ears
... not required. This adds flexibility and modularity to the design choices in a potential hearing instrument. To make this possible, we implement low-power programmable peak detectors and current-mode decision circuits to support an all-analog gain control architecture. Second, discrete gain levels ca ...
... not required. This adds flexibility and modularity to the design choices in a potential hearing instrument. To make this possible, we implement low-power programmable peak detectors and current-mode decision circuits to support an all-analog gain control architecture. Second, discrete gain levels ca ...
MAX9376 LVDS/Anything-to-LVPECL/LVDS Dual Translator General Description Features
... The MAX9376 is a fully differential, high-speed, LVDS/ anything-to-LVPECL/LVDS dual translator designed for signal rates up to 2GHz. One channel is LVDS/ anything-to-LVPECL translator and the other channel is LVDS/anything-to-LVDS translator. The MAX9376’s extremely low propagation delay and high sp ...
... The MAX9376 is a fully differential, high-speed, LVDS/ anything-to-LVPECL/LVDS dual translator designed for signal rates up to 2GHz. One channel is LVDS/ anything-to-LVPECL translator and the other channel is LVDS/anything-to-LVDS translator. The MAX9376’s extremely low propagation delay and high sp ...
PCA9543A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... An active-low reset (RESET) input allows the PCA9543A to recover from a situation where one of the downstream I2C buses is stuck in a low state. Pulling RESET low resets the I2C state machine and causes all the channels to be deselected, as does the internal power-on reset function. The pass gates o ...
... An active-low reset (RESET) input allows the PCA9543A to recover from a situation where one of the downstream I2C buses is stuck in a low state. Pulling RESET low resets the I2C state machine and causes all the channels to be deselected, as does the internal power-on reset function. The pass gates o ...
SN74LVC162244A 16-Bit Buffer/Driver with 3
... This 16-bit buffer/driver is designed for 1.65-V to 3.6-V VCC operation. The SN74LVC162244A is designed specifically to improve the performance and density of 3-state memory address drivers, clock drivers, and busoriented receivers and transmitters. The device can be used as four 4-bit buffers, two ...
... This 16-bit buffer/driver is designed for 1.65-V to 3.6-V VCC operation. The SN74LVC162244A is designed specifically to improve the performance and density of 3-state memory address drivers, clock drivers, and busoriented receivers and transmitters. The device can be used as four 4-bit buffers, two ...
DAC8580 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... generation applications. It operates from dual ±5-V power supplies and requires only a single external reference. The DAC8580 is capable of generating output signal frequencies up to 1 MHz. The DAC8580 significantly relaxes, or removes, the need for ...
... generation applications. It operates from dual ±5-V power supplies and requires only a single external reference. The DAC8580 is capable of generating output signal frequencies up to 1 MHz. The DAC8580 significantly relaxes, or removes, the need for ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.