Multi-Amp Configuration Guide
... Throughout these instructions special emphasis is placed on good safety practices. The WARNING and CAUTION graphics are used to highlight certain topics that require extra precaution. ...
... Throughout these instructions special emphasis is placed on good safety practices. The WARNING and CAUTION graphics are used to highlight certain topics that require extra precaution. ...
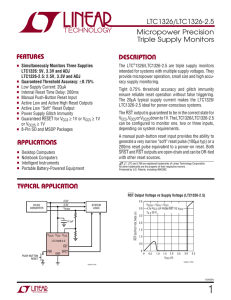
LTC1326/LTC1326-2.5 - Micropower
... narrow (100µs typ) soft reset pulse is generated on the SRST output pin after the button is released. The pushbutton circuitry contains an internal debounce counter which delays the output of the soft reset pulse by typically 20ms. This pin can be OR-tied to the RST pin and issue what is called a “s ...
... narrow (100µs typ) soft reset pulse is generated on the SRST output pin after the button is released. The pushbutton circuitry contains an internal debounce counter which delays the output of the soft reset pulse by typically 20ms. This pin can be OR-tied to the RST pin and issue what is called a “s ...
Foto 1 : Bagian Atas dari Alat A-1
... software. The content of the on-chip RAM and all the special functions registers remain unchanged during this mode. The idle mode can be terminated by any enabled interrupt or by a hardware reset. P1.0 and P1.1 should be set to “0” if no external pullups are used, or set to “1” if external pullups a ...
... software. The content of the on-chip RAM and all the special functions registers remain unchanged during this mode. The idle mode can be terminated by any enabled interrupt or by a hardware reset. P1.0 and P1.1 should be set to “0” if no external pullups are used, or set to “1” if external pullups a ...
MAX4810/MAX4811/MAX4812 Dual, Unipolar/Bipolar, High-Voltage Digital Pulsers General Description
... the positive and negative pulses and active clamp. Also included are two independent enable inputs. Disabling EN ensures the output MOSFETs are not accidentally turned on during fast power-supply ramping. This allows for faster ramp times and smaller delays between pulsing modes. A low-power shutdow ...
... the positive and negative pulses and active clamp. Also included are two independent enable inputs. Disabling EN ensures the output MOSFETs are not accidentally turned on during fast power-supply ramping. This allows for faster ramp times and smaller delays between pulsing modes. A low-power shutdow ...
M40SZ100W
... Operation The M40SZ100Y/W, as shown in Figure 5 on page 8, can control one (two, if placed in parallel) standard low-power SRAM. This SRAM must be configured to have the chip enable input disable all other input signals. Most slow, low-power SRAMs are configured like this, however many fast SRAMs ar ...
... Operation The M40SZ100Y/W, as shown in Figure 5 on page 8, can control one (two, if placed in parallel) standard low-power SRAM. This SRAM must be configured to have the chip enable input disable all other input signals. Most slow, low-power SRAMs are configured like this, however many fast SRAMs ar ...
MAX16927 Evaluation Kit Evaluates: MAX16927 General Description Features
... stated by the number inside their respective preceding parentheses, and likewise for Seq 2 and Seq 3. ...
... stated by the number inside their respective preceding parentheses, and likewise for Seq 2 and Seq 3. ...
K4J55323QF
... - Apply VDDQ before Vref. ( Inputs are not recognized as valid until after VREF is applied ) 2. Required minimum 100us for the stable power before RESET pin transition to HIGH - Upon power-up the address/command active termination value will automatically be set based off the state of RESET and CKE. ...
... - Apply VDDQ before Vref. ( Inputs are not recognized as valid until after VREF is applied ) 2. Required minimum 100us for the stable power before RESET pin transition to HIGH - Upon power-up the address/command active termination value will automatically be set based off the state of RESET and CKE. ...
model sr830 - Stanford Research Systems
... ±10.5 V full scale, 1 mV resolution. 10 mA max output current. 4 BNC Analog to Digital inputs. Differential inputs with1 MΩ input impedance on both shield and center conductor. ±10.5 V full scale, 1 mV resolution. TTL trigger input triggers stored data samples. Analog output of signal amplifiers (be ...
... ±10.5 V full scale, 1 mV resolution. 10 mA max output current. 4 BNC Analog to Digital inputs. Differential inputs with1 MΩ input impedance on both shield and center conductor. ±10.5 V full scale, 1 mV resolution. TTL trigger input triggers stored data samples. Analog output of signal amplifiers (be ...
MAX8973A 9A, Three-Phase Step-Down Switching Regulator General Description
... 4.5V input voltage range. An I2C 3.0-compatible serial interface, supporting clock rates up to 3.4MHz, controls key regulator parameters such as output voltage, output slew rate, and on/off control. Output voltage is programmable from 0.60625V to 1.4V in 6.25mV increments. The default output voltage ...
... 4.5V input voltage range. An I2C 3.0-compatible serial interface, supporting clock rates up to 3.4MHz, controls key regulator parameters such as output voltage, output slew rate, and on/off control. Output voltage is programmable from 0.60625V to 1.4V in 6.25mV increments. The default output voltage ...
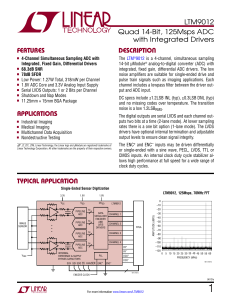
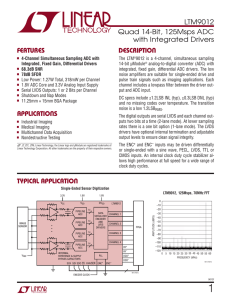
LTM9012 - Quad 14-Bit, 125Msps ADC with Integrated Drivers
... noise amplifiers are suitable for single-ended drive and pulse train signals such as imaging applications. Each channel includes a lowpass filter between the driver output and ADC input. ...
... noise amplifiers are suitable for single-ended drive and pulse train signals such as imaging applications. Each channel includes a lowpass filter between the driver output and ADC input. ...
MAX8660/MAX8660A/MAX8660B/MAX8661 High-Efficiency, Low-I , PMICs with Dynamic Voltage Management for Mobile Applications
... and an 8th always-on LDO are integrated with powermanagement functions. Two dynamically controlled DCDC outputs power the processor core and internal memory. Two other DC-DC converters power I/O, memory, and other peripherals. Additional functions include on/off control for outputs, low-battery dete ...
... and an 8th always-on LDO are integrated with powermanagement functions. Two dynamically controlled DCDC outputs power the processor core and internal memory. Two other DC-DC converters power I/O, memory, and other peripherals. Additional functions include on/off control for outputs, low-battery dete ...
LTC1664 - Micropower Quad 10-Bit DAC
... daisychain facility. A series of m chips is configured by connecting each DOUT (except the last) to DIN of the next chip, forming a single 16m -bit shift register. The SCK and CS/LD signals are common to all chips in the chain. In use, CS/LD is held low while m 16-bit words are clocked to DIN of the ...
... daisychain facility. A series of m chips is configured by connecting each DOUT (except the last) to DIN of the next chip, forming a single 16m -bit shift register. The SCK and CS/LD signals are common to all chips in the chain. In use, CS/LD is held low while m 16-bit words are clocked to DIN of the ...
LTM4603/LTM4603-1 - 6A DC/DC uModule with PLL, Output Tracking and Margining
... The LTM®4603 is a complete 6A step-down switch mode DC/DC µModule® regulator with onboard switching controller, MOSFETs, inductor and all support components. The device is housed in a small surface mount 15mm × 15mm × 2.82mm LGA package. Operating over an input voltage range of 4.5V to 20V, the LTM4 ...
... The LTM®4603 is a complete 6A step-down switch mode DC/DC µModule® regulator with onboard switching controller, MOSFETs, inductor and all support components. The device is housed in a small surface mount 15mm × 15mm × 2.82mm LGA package. Operating over an input voltage range of 4.5V to 20V, the LTM4 ...
On-chip phase noise measurement, design study in 65 nm CMOS technology
... Jitter is generally defined as a time deviation of the clock waveform from its desired position. The deviation which occurs can be on the leading or lagging side and it can be bounded (deterministic) or unbounded (random). Jitter is a critical specification in the digital system design. There are va ...
... Jitter is generally defined as a time deviation of the clock waveform from its desired position. The deviation which occurs can be on the leading or lagging side and it can be bounded (deterministic) or unbounded (random). Jitter is a critical specification in the digital system design. There are va ...
CHIP TALK - Talking Electronics
... 1. Electronics For You: In regular publication since 1969, EFY is the natural choice of the entire electronics fraternity, be it businessmen, industry professionals or hobbyists. From microcontrollers to DVD players, from PCB designing software to UPS systems, all are covered every month in EFY. 2. ...
... 1. Electronics For You: In regular publication since 1969, EFY is the natural choice of the entire electronics fraternity, be it businessmen, industry professionals or hobbyists. From microcontrollers to DVD players, from PCB designing software to UPS systems, all are covered every month in EFY. 2. ...
low-voltage logic (lvc) designer`s guide
... is increased due to lower temperature stress gradients on the device, and the integrity of the signal is improved due to the reduction of ground bounce and signal noise. An additional benefit of the reduced power consumption is the extended life of the battery when a system is not powered by a regul ...
... is increased due to lower temperature stress gradients on the device, and the integrity of the signal is improved due to the reduction of ground bounce and signal noise. An additional benefit of the reduced power consumption is the extended life of the battery when a system is not powered by a regul ...
Private Client Technical Editing 2
... One of the main objectives of this work is to derive simple and scalab.le~~els that can be used in design optimizati~ .&Hil.81 gIVemSlghts to how random WID variations affect delay, and how different design decisions can be used to reduce d.elay variation. In our efforts, we insure that the model is ...
... One of the main objectives of this work is to derive simple and scalab.le~~els that can be used in design optimizati~ .&Hil.81 gIVemSlghts to how random WID variations affect delay, and how different design decisions can be used to reduce d.elay variation. In our efforts, we insure that the model is ...
... PLC inputs are easily represented in ladder logic. In Figure 1.11 there are three types of inputs shown. The first two are normally open and normally closed inputs, discussed previously. The IIT (Immediate InpuT) function allows inputs to be read after the input scan, while the ladder logic is being ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.