Problem - UCLA.edu
... network system design is to have impedance (ZPDN) that is low with a flat response over a desired frequency range. ...
... network system design is to have impedance (ZPDN) that is low with a flat response over a desired frequency range. ...
Capacitor Self-Resonance
... sinusoid with a single cycle displayed has an amplitude of 8 divisions p-p (800 mVpp), which is also 4 divisions peak (400 mVp). ...
... sinusoid with a single cycle displayed has an amplitude of 8 divisions p-p (800 mVpp), which is also 4 divisions peak (400 mVp). ...
Microwave Integrated Circuits (MIC)
... Phase shifters like attenuators, can be mechanically or electronically adjustable Mechanically adjustable phase shifters It is a line stretchers. The phase shift can be adjusted by changing the signal path. ...
... Phase shifters like attenuators, can be mechanically or electronically adjustable Mechanically adjustable phase shifters It is a line stretchers. The phase shift can be adjusted by changing the signal path. ...
Ch 6
... • Suppose there is +10 mV (with respect to ground) on one input of a differential amplifier and –10 mV (with respect to ground) on the other input. Then the differential signal is 20 mV. If the diff amp has a gain of 10, the output will be 10 20 mV = 200 mV. • Now suppose that +100 mV (with respec ...
... • Suppose there is +10 mV (with respect to ground) on one input of a differential amplifier and –10 mV (with respect to ground) on the other input. Then the differential signal is 20 mV. If the diff amp has a gain of 10, the output will be 10 20 mV = 200 mV. • Now suppose that +100 mV (with respec ...
MTI TN113: The Series to Parallel Impedance Transformation
... parallel and series network numbers are both correct, and will result in the same impedance at that particular test frequency. Remember that the equivalent parallel and series network values are exact for only one frequency point. ...
... parallel and series network numbers are both correct, and will result in the same impedance at that particular test frequency. Remember that the equivalent parallel and series network values are exact for only one frequency point. ...
Untitled
... impedance and hence cannot deliver a voltage waveform to the circuit independent of frequency and test circuit configuration. The oscilloscope has input impedance that loads the circuit under test, by placing an undesired impedance across the measurement points. We also need to consider the effects ...
... impedance and hence cannot deliver a voltage waveform to the circuit independent of frequency and test circuit configuration. The oscilloscope has input impedance that loads the circuit under test, by placing an undesired impedance across the measurement points. We also need to consider the effects ...
EE 1202 Experiment #7 – Signal Amplification
... equipment flaw. It is due to detecting “environmental” noise, radio or other signals due to sources in or near the lab. This may increase measurement difficulty, but does not affect circuit performance. Note that 200 mV signal shows high-frequency "noise.” ...
... equipment flaw. It is due to detecting “environmental” noise, radio or other signals due to sources in or near the lab. This may increase measurement difficulty, but does not affect circuit performance. Note that 200 mV signal shows high-frequency "noise.” ...
ADC
... Interfacing ADC to 8051 The figure above shows the schematic for interfacing ADC0804 to 8051. The circuit initiates the ADC to convert a given analogue input , then accepts the corresponding digital data and displays it on the LED array connected at P0. For example, if the analogue input voltage Vi ...
... Interfacing ADC to 8051 The figure above shows the schematic for interfacing ADC0804 to 8051. The circuit initiates the ADC to convert a given analogue input , then accepts the corresponding digital data and displays it on the LED array connected at P0. For example, if the analogue input voltage Vi ...
AN1229
... Therefore, in order to achieve good input matching performances over the frequency range 88-108 MHz the unbalanced 50 Ω is to be transformed into an impedance with a value as close as possible to Rp of 5.38 Ω. From the circuit schematic given in Figure 6 , we can see that the input matching network ...
... Therefore, in order to achieve good input matching performances over the frequency range 88-108 MHz the unbalanced 50 Ω is to be transformed into an impedance with a value as close as possible to Rp of 5.38 Ω. From the circuit schematic given in Figure 6 , we can see that the input matching network ...
Op Amp Amplifier
... i. Apply a triangle wave to your amplifier. This is the measurement version of the DC Sweep. ii. The output should look like a clipped triangle wave. Be sure to be measuring both the input and output voltage signals. iii. Use the clipped triangle wave to determine the maximum input that will produce ...
... i. Apply a triangle wave to your amplifier. This is the measurement version of the DC Sweep. ii. The output should look like a clipped triangle wave. Be sure to be measuring both the input and output voltage signals. iii. Use the clipped triangle wave to determine the maximum input that will produce ...
3-phase short-circuit current (Isc) at any point within a LV installation
... Motors: At the instant of short-circuit, a running motor will act (for a brief period) as a generator, and feed current into the fault. ...
... Motors: At the instant of short-circuit, a running motor will act (for a brief period) as a generator, and feed current into the fault. ...
Homework Ch 4 - ECM
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
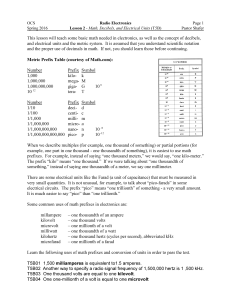
Lesson T5B - Math and Gain
... is less than input, we call this “loss.” We measure gain or loss in units called DECIBELS. The Decibel (abbreviated dB) is a “logarithmic” unit. That means it is based upon logarithmic calculations. If you do not know what a logarithm is, you should briefly study this concept. In simple terms, a log ...
... is less than input, we call this “loss.” We measure gain or loss in units called DECIBELS. The Decibel (abbreviated dB) is a “logarithmic” unit. That means it is based upon logarithmic calculations. If you do not know what a logarithm is, you should briefly study this concept. In simple terms, a log ...
07LAB4_rev - University of Guelph Physics
... Typically, Zf is on the order of 1 kΩ and A 105 and therefore the apparent impedance is 10-2 Ω and is usually negligible compared with Z1. In summary, we have seen that, if the open loop gain of the amplifier is large, we can have an amplifier circuit whose gain depends only on the ratio of passiv ...
... Typically, Zf is on the order of 1 kΩ and A 105 and therefore the apparent impedance is 10-2 Ω and is usually negligible compared with Z1. In summary, we have seen that, if the open loop gain of the amplifier is large, we can have an amplifier circuit whose gain depends only on the ratio of passiv ...
R - School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... proportional to the negative of its input voltage and that boosts the amplitude of an input signal, many times, i.e., has a very high gain.High-gain amplifiers. • They were developed to be used in synthesizing mathematical operations in early analog computers, hence their name. • Typified by the ser ...
... proportional to the negative of its input voltage and that boosts the amplitude of an input signal, many times, i.e., has a very high gain.High-gain amplifiers. • They were developed to be used in synthesizing mathematical operations in early analog computers, hence their name. • Typified by the ser ...