MAX9742 Single-/Dual-Supply, Stereo 16W, Class D Amplifier with Differential Inputs General Description
... Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C Maximum Junction Temperature .....................................+150°C Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
... Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C Maximum Junction Temperature .....................................+150°C Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
14-Bit, 150 MSPS, 1.8 V Analog-to-Digital Converter AD9254
... The wide bandwidth, truly differential SHA allows a variety of user-selectable input ranges and offsets, including single-ended applications. It is suitable for multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels and for sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies well ...
... The wide bandwidth, truly differential SHA allows a variety of user-selectable input ranges and offsets, including single-ended applications. It is suitable for multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels and for sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies well ...
LT6220/LT6221/LT6222 - Single/Dual/Quad 60MHz, 20V/µs Low Power, Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Precision Op Amp
... LT6220I/LT6221I/LT6222I are guaranteed to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C. Note 6: Minimum supply voltage is guaranteed by power supply rejection ratio test. Note 7: Output voltage swings are measured between the output and power supply rails. Note 8: This parameter is not 100% tested. ...
... LT6220I/LT6221I/LT6222I are guaranteed to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C. Note 6: Minimum supply voltage is guaranteed by power supply rejection ratio test. Note 7: Output voltage swings are measured between the output and power supply rails. Note 8: This parameter is not 100% tested. ...
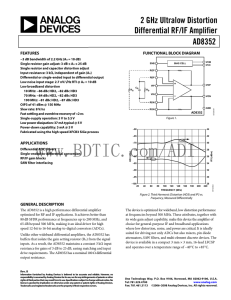
2 GHz Ultralow Distortion Differential RF/IF Amplifier AD8352
... The AD8352 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 80 dB SFDR performance at frequencies up to 200 MHz, and 65 dB beyond 500 MHz, making it an ideal driver for high speed 12-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Unlike o ...
... The AD8352 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 80 dB SFDR performance at frequencies up to 200 MHz, and 65 dB beyond 500 MHz, making it an ideal driver for high speed 12-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Unlike o ...
LT1805 - Single/Dual/Quad 100V/µs, 85MHz, Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Op Amps
... VS = 5V, VO = 0.5V to 4.5V, RL = 1k to VS/2 VS = 5V, VO = 1.5V to 3.5V, RL = 100Ω to VS/2 VS = 3V, VO = 0.5V to 2.5V, RL=1k to VS/2 ...
... VS = 5V, VO = 0.5V to 4.5V, RL = 1k to VS/2 VS = 5V, VO = 1.5V to 3.5V, RL = 100Ω to VS/2 VS = 3V, VO = 0.5V to 2.5V, RL=1k to VS/2 ...
AD9240 - Analog Devices
... For a sine wave, SINAD can be expressed in terms of the number of bits. Using the following formula, N = (SINAD – 1.76)/6.02 it is possible to get a measure of performance expressed as N, the effective number of bits. Thus, an effective number of bits for a device for sine wave inputs at a given inp ...
... For a sine wave, SINAD can be expressed in terms of the number of bits. Using the following formula, N = (SINAD – 1.76)/6.02 it is possible to get a measure of performance expressed as N, the effective number of bits. Thus, an effective number of bits for a device for sine wave inputs at a given inp ...
AD9254 14-Bit, 150 MSPS, 1.8 V Analog-to
... The wide bandwidth, truly differential SHA allows a variety of user-selectable input ranges and offsets, including single-ended applications. It is suitable for multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels and for sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies well ...
... The wide bandwidth, truly differential SHA allows a variety of user-selectable input ranges and offsets, including single-ended applications. It is suitable for multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels and for sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies well ...
THS6032
... Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolu ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolu ...
Crompton Instruments Integra and Paladin Transducers
... be configured via the optional menu driven Integra DIS-1540 display unit. A simple two button interface on the front panel of the unit allows display of 32 major electrical and power quality parameters. All set-up screens are password protected. Once configured, the status of each parameter can be v ...
... be configured via the optional menu driven Integra DIS-1540 display unit. A simple two button interface on the front panel of the unit allows display of 32 major electrical and power quality parameters. All set-up screens are password protected. Once configured, the status of each parameter can be v ...
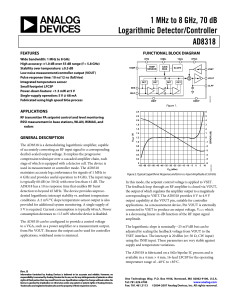
AD8318 1 MHz to 8 GHz, 70 dB Logarithmic Detector/Controller
... 6 GHz and provides useful operation to 8 GHz. The input range is typically 60 dB (re: 50 Ω) with error less than ±1 dB. The AD8318 has a 10 ns response time that enables RF burst detection to beyond 45 MHz. The device provides unprecedented logarithmic intercept stability vs. ambient temperature con ...
... 6 GHz and provides useful operation to 8 GHz. The input range is typically 60 dB (re: 50 Ω) with error less than ±1 dB. The AD8318 has a 10 ns response time that enables RF burst detection to beyond 45 MHz. The device provides unprecedented logarithmic intercept stability vs. ambient temperature con ...
250-mA DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER THS6022 FEATURES
... capable of providing 200-mA output current (minimum) into a 50-Ω load. These drivers can be configured differentially to drive a 50-V p-p output signal over low-impedance lines. The drivers are current feedback amplifiers, designed for the high slew rates necessary to support low total harmonic dist ...
... capable of providing 200-mA output current (minimum) into a 50-Ω load. These drivers can be configured differentially to drive a 50-V p-p output signal over low-impedance lines. The drivers are current feedback amplifiers, designed for the high slew rates necessary to support low total harmonic dist ...
NB6N239S - Any Differential Clock IN to LVDS OUT
... copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, representation o ...
... copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, representation o ...
Rebuilt and Modified Altec 1567A: A Technical
... low-impedance (low-Z) balanced input. (Only the transformers are shown in Figure 2.) With its center-tapped primary winding, the 4722 offers either 150- or 38-Ω nominal input impedance. Each input channel has a big knob labeled “MIX N,” where N = channel number, which is a channel fader in today’s j ...
... low-impedance (low-Z) balanced input. (Only the transformers are shown in Figure 2.) With its center-tapped primary winding, the 4722 offers either 150- or 38-Ω nominal input impedance. Each input channel has a big knob labeled “MIX N,” where N = channel number, which is a channel fader in today’s j ...
Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits
... using temperature sensor which provides a voltage in the range of 0-30mv .Design a suitable signal conditioning circuit using Op-Amp to obtain an output voltage in the range of 0-5V, which is proportional to input voltage. ...
... using temperature sensor which provides a voltage in the range of 0-30mv .Design a suitable signal conditioning circuit using Op-Amp to obtain an output voltage in the range of 0-5V, which is proportional to input voltage. ...
SKY12209-478LF 数据资料DataSheet下载
... important to use a printed circuit board design that provides adequate cooling capability to keep the junction temperature of the PIN diodes below their maximum rated operating temperature. As indicated in Figure 11, the x-axis temperature is referenced to the bottom of the QFN package. A printed ci ...
... important to use a printed circuit board design that provides adequate cooling capability to keep the junction temperature of the PIN diodes below their maximum rated operating temperature. As indicated in Figure 11, the x-axis temperature is referenced to the bottom of the QFN package. A printed ci ...
AD8352 - Analog Devices
... The AD8352 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 80 dB SFDR performance at frequencies up to 200 MHz, and 65 dB beyond 500 MHz, making it an ideal driver for high speed 12-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Unlike o ...
... The AD8352 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 80 dB SFDR performance at frequencies up to 200 MHz, and 65 dB beyond 500 MHz, making it an ideal driver for high speed 12-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Unlike o ...
A DC-4-ghz true logarithmic amplifier: theory and implementation
... amplifier in parallel with a unity-gain buffer. For small signals, this structure will simply amplify. However, as the signal becomes larger, a point will be reached at which the limiting amplifier in the last stage ceases to amplify and provides a constant voltage . As the input signal becomes larg ...
... amplifier in parallel with a unity-gain buffer. For small signals, this structure will simply amplify. However, as the signal becomes larger, a point will be reached at which the limiting amplifier in the last stage ceases to amplify and provides a constant voltage . As the input signal becomes larg ...
Impact of VSWR on the Uncertainty Analysis of Harmonics
... interest. The 2nd harmonic adds a dc component that is usually not important. Higher order harmonics are generally are lower levels and do not have the impact as the 3rd harmonic. Impact of VSWR VSWR is a ratio of the reflected and incident voltage: VSWR = (Vincident + Vreflected) ¸ (Vincident - Vre ...
... interest. The 2nd harmonic adds a dc component that is usually not important. Higher order harmonics are generally are lower levels and do not have the impact as the 3rd harmonic. Impact of VSWR VSWR is a ratio of the reflected and incident voltage: VSWR = (Vincident + Vreflected) ¸ (Vincident - Vre ...
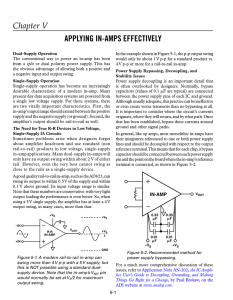
In the example shown in Figure 5-1, the p-p output... The conventional way to power ...
... capacitors (values of 0.1 F are typical) are connected between the power supply pins of each IC and ground. Although usually adequate, this practice can be ineffective or even create worse transients than no bypassing at all. It is important to consider where the circuit’s currents originate, where ...
... capacitors (values of 0.1 F are typical) are connected between the power supply pins of each IC and ground. Although usually adequate, this practice can be ineffective or even create worse transients than no bypassing at all. It is important to consider where the circuit’s currents originate, where ...
CHAPTER 3: ANALOGUE SUB-SYSTEMS DESIGN
... process allows for a minimum gate length of 0.35 μm, and has four metal layers and two layers of poly. A cross section of the wafer, shown in Figure 3.1 highlights the available layers and illustrates the layout of the transistor and capacitor modules. The process allows for n-channel MOSFETs (NMOS) ...
... process allows for a minimum gate length of 0.35 μm, and has four metal layers and two layers of poly. A cross section of the wafer, shown in Figure 3.1 highlights the available layers and illustrates the layout of the transistor and capacitor modules. The process allows for n-channel MOSFETs (NMOS) ...